|
Frauenberg (Bavaria)
Frauenberg is a mountain of 728m in the Bavarian Forest, close to Grafenau in Bavaria, Germany. Despite its inferior height, it is a recognizable part of the environment, as its conical form distinguishes it from the surrounding mountains of the Bavarian Forest. The Kleine Ohe (also Grafenauer Ohe) at this point crosses the Pfahl in the Elsenthaler Leite. Its more plain northern and eastern flank is foremost vegetated by spruces, whereas the more cliffy western and southern flanks going towards the Kleine Ohe are more grown over with deciduous forest, dominated by common beech, largeleaf linden and sycamore maple. There on 460m to 560m since 1978 a natural reserve of 19,5ha was established. Additionally there is one known viewing point on the southern side. To the pilgrimage chapel of Brudersbrunn, being located in the forest north of the peak, stations of the cross The Stations of the Cross or the Way of the Cross, also known as the Way of Sorrows or the Via Crucis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of . It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and Czechia to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in what is now Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavarian Forest
The village of Zell in the Bavarian Forest The Bavarian Forest ( German: ' or ''Bayerwald''; bar, Boarischa Woid) is a wooded, low-mountain region in Bavaria, Germany that is about 100 kilometres long. It runs along the Czech border and is continued on the Czech side by the Bohemian Forest (Czech: ''Šumava''). Most of the Bavarian Forest lies within the province of Lower Bavaria, but the northern part lies within Upper Palatinate. In the south it reaches the border with Upper Austria. Geologically and geomorphologically, the Bavarian Forest is part of the Bohemian Forest - the highest of the truncated highlands of the Bohemian Massif. The area along the Czech border has been designated as the Bavarian Forest National Park (240 km2), established in 1970 as the first national park in Germany. Another 3,008 km2 has been designated as the Bavarian Forest Nature Park, established 1967, and another 1,738 km2 as the Upper Bavarian Forest Nature Park, estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grafenau, Bavaria
Grafenau () is a town in the Freyung-Grafenau district, in Bavaria, Germany. 32 km north of Passau, the town is situated in the Bavarian Forest and is the base of the Bavarian Forest National Park Authority. Grafenau is a holiday destination with a variety of kinds of accommodation from self-catering apartments to a "holiday village". Location and facilities The town lies in the Bavarian Forest at a height between 600 and 700 meters over sea level, right beside the Bavarian Forest National Park. The Kleine Ohe river flows along the east and south of the town. It is close to the Frauenberg. In April 1945, Major General Stafford LeRoy Irwin opened his XII Corps Headquarters there. Since 1976 there has been an artificial lake (surrounded by a park) which is used for sport and recreation. There are museums about the town and surrounding area, including a museum with a collection of traditional furniture, and also a museum about snuff. The town has curling and ice ska ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleine Ohe (Ilz)
Kleine Ohe is a river of Bavaria, Germany. It is a headwater of the Ilz The Ilz () is a river running through the Bavarian Forest, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Danube and in length ( including its main source river Große Ohe), during which it travels down a height difference of ~140m. The Ilz is formed a ... in Eberhardsreuth. See also * List of rivers of Bavaria References Rivers of Bavaria Rivers of Germany {{Bavaria-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfahl (Bavarian Forest)
The Pfahl is a 150-kilometre-long quartz vein that runs through the northeastern Bavarian Forest in Germany. From a geomorphological point of view, it represents a residual ridge that has been formed by weathering and erosion over millions of years. Formation The Pfahl consists of quartz that was deposited as a hydrothermal vein about 275 million years ago within the existing fault structure. The Pfahl was probably active as a fault several times. Because the rock of the Pfahl was harder than the surrounding rock, it was left standing like a wall as softer rocks were eroded. Today the Pfahl forms a residual ridge 150 kilometres long and 10 to 40 metres high. The shining white quartz of the Pfahl consists of up to 98% silicic acid; any yellowish to reddish or grey coloration is caused by iron compounds and impurities (''Pfahlschiefer''). The interpretation of the actual Pfahl fault as a suture is disputed; but it has been confirmed that it separates various magmatic rocks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
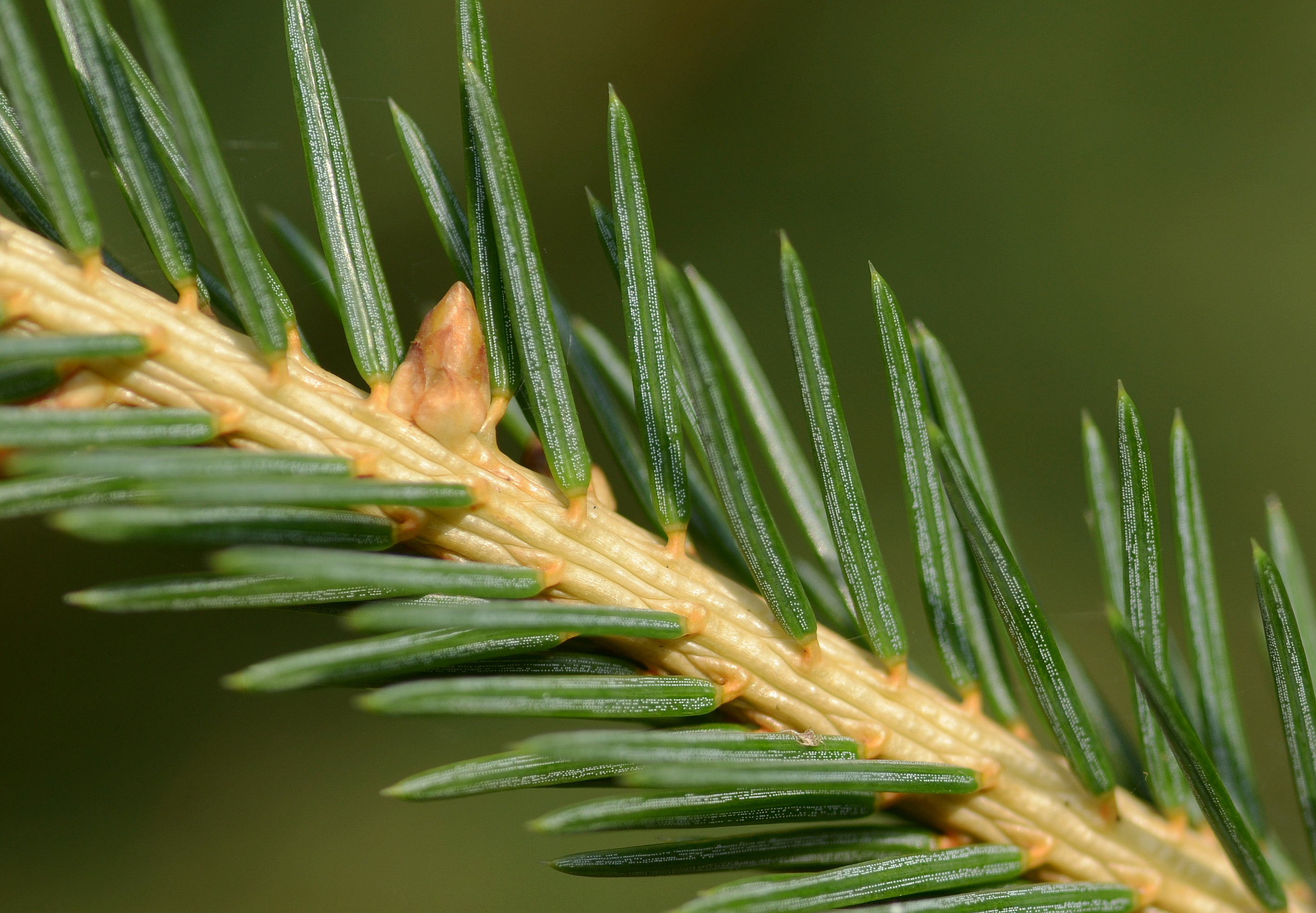
Spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal ( taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Piceoideae. Spruces are large trees, from about 20 to 60 m (about 60–200 ft) tall when mature, and have whorled branches and conical form. They can be distinguished from other members of the pine family by their needles (leaves), which are four-sided and attached singly to small persistent peg-like structures ( pulvini or sterigmata) on the branches, and by their cones (without any protruding bracts), which hang downwards after they are pollinated. The needles are shed when 4–10 years old, leaving the branches rough with the retained pegs. In other similar genera, the branches are fairly smooth. Spruce are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera (moth and butterfly) species, such as the eastern spru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fagus Sylvatica
''Fagus sylvatica'', the European beech or common beech is a deciduous tree belonging to the beech family Fagaceae. Description ''Fagus sylvatica'' is a large tree, capable of reaching heights of up to tall and trunk diameter, though more typically tall and up to trunk diameter. A 10-year-old sapling will stand about tall. It has a typical lifespan of 150–200 years, though sometimes up to 300 years. In cultivated forest stands trees are normally harvested at 80–120 years of age. 30 years are needed to attain full maturity (as compared to 40 for American beech). Like most trees, its form depends on the location: in forest areas, ''F. sylvatica'' grows to over , with branches being high up on the trunk. In open locations, it will become much shorter (typically ) and more massive. The leaves are alternate, simple, and entire or with a slightly crenate margin, long and 3–7 cm broad, with 6–7 veins on each side of the leaf (as opposed to 7–10 veins in ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilia Platyphyllos
''Tilia platyphyllos'', the large-leaved lime or large-leaved linden, is a species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae (Tiliaceae). It is a deciduous tree, native to much of Europe, including locally in southwestern Great Britain, growing on lime-rich soils. The common names largeleaf linden and large-leaved linden are in standard use throughout the English-speaking world except in the British Isles, where it is known as large-leaved lime. The name "lime", possibly a corruption of "line" originally from "lind", has been in use for centuries and also attaches to other species of ''Tilia''. It is not, however, closely related to the lime fruit tree, a species of citrus. The specific epithet ''platyphyllos'' (greek: πλατύφυλλος) means in greek "with broad leaves". Description ''Tilia platyphyllos'' is a narrowly domed tree with a moderate growth rate, and can eventually attain a height of 40 m. The reddish-brown young stems later develop dark grey bark w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
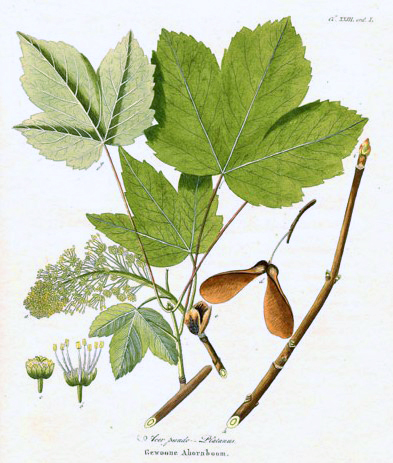
Acer Pseudoplatanus
''Acer pseudoplatanus'', known as the sycamore in the British Isles and as the sycamore maple in the United States, is a species of flowering plant in the soapberry and lychee family Sapindaceae. It is a large deciduous, broad-leaved tree, tolerant of wind and coastal exposure. It is native to Central Europe and Western Asia, from France eastward to Ukraine, northern Turkey and the Caucasus and southward in the mountains of Italy and northern Iberia. The sycamore establishes itself easily from seed and was introduced to the British Isles by 1500. It is now naturalised there and in other parts of Europe, North America, Australia and New Zealand, where it may become an invasive species. The sycamore can grow to a height of about and the branches form a broad, rounded crown. The bark is grey, smooth when young and later flaking in irregular patches. The leaves grow on long leafstalks and are large and palmate, with five large radiating lobes. The flowers are greenish-yellow an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or other special interest, which is reserved and managed for purposes of conservation and to provide special opportunities for study or research. They may be designated by government institutions in some countries, or by private landowners, such as charities and research institutions. Nature reserves fall into different IUCN categories depending on the level of protection afforded by local laws. Normally it is more strictly protected than a nature park. Various jurisdictions may use other terminology, such as ecological protection area or private protected area in legislation and in official titles of the reserves. History Cultural practices that roughly equate to the establishment and maintenance of reserved areas for animals date b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stations Of The Cross
The Stations of the Cross or the Way of the Cross, also known as the Way of Sorrows or the Via Crucis, refers to a series of images depicting Jesus Christ on the day of his crucifixion and accompanying prayers. The stations grew out of imitations of the Via Dolorosa in Jerusalem, which is a traditional processional route symbolising the actual path Jesus walked to Mount Calvary. The objective of the stations is to help the Christian faithful to make a spiritual pilgrimage through contemplation of the Passion of Christ. It has become one of the most popular devotions and the stations can be found in many Western Christian churches, including those in the Roman Catholic, Lutheran, Anglican, and Methodist traditions. Commonly, a series of 14 images will be arranged in numbered order along a path, along which worshippers—individually or in a procession—move in order, stopping at each station to say prayers and engage in reflections associated with that station. These devo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |