|
François-Joseph D'Offenstein
François-Joseph d'Offenstein (27 July 1760 – 27 September 1837), Baron of the Ist Empire, was a French general and military commander during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Biography Early life Offenstein was born in Erstein, France on 27 July 1760 to François-Joseph Offenstein and Catherine Reibel. He grew up in Alsace during the French Ancien Régime before joining the Regiment of Royal Dragoons in Deux-Pont in the French army in 1777 at age 16. He left the regiment in 1786 and reenlisted as a grenadier in the Infantry Regiment of Alsace at the beginning of 1787. Military career Offenstein became a major in the National Guard in 1790 and a lieutenant colonel of the 1st Battalion of Volunteers of Bas-Rhin in 1971. In 1972 and 1973, respectively, he became the lieutenant colonel of the 1st Battalion of Volunteers of Moselle and Rhine. By July 1973, he had been nominated as a brigadier-general; in September, he became a major general. Within weeks, Offenstein w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erstein
Erstein (, ; ) is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department, in the region of Grand Est, France. History An important necropolis from the Merovingian era (6th-7th century) has been excavated near Erstein in 1999–2000. Erstein was known in Alsace in the Middle Age for its canonesses monastery, founded in the 9th century and abandoned in 1422. The buildings were destroyed in the 16th and 19th centuries. Demographics Twin towns * Endingen am Kaiserstuhl * São João de Loure File:Erstein1.JPG, Erstein Street File:Erstein2.JPG, Near Ill River File:Erstein3.jpg, Calvaire (1746) File:Erstein4.JPG, Old Factory People * Laure Diebold, (1915–1965), Compagnon de la Libération, was born in Erstein * François-Joseph d'Offenstein (1760–1837) French general, was born in Erstein See also * Communes of the Bas-Rhin department The following is a list of the 514 communes of the Bas-Rhin department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renchen
Renchen () is a small city in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, part of the district of Ortenau. Geography Renchen is located in the foothills of the northern Black Forest at the entrance to the Rench valley at the edge of the Upper Rhine River Plains. Neighboring communities The city shares borders with the following cities and towns, listed clock-wise from the north: Achern, Kappelrodeck, Oberkirch, Appenweier, and Rheinau. Boroughs In addition to Renchen (proper) the city includes the boroughs of Erlach and Ulm zu Renchen. History Renchen was first in official documents in 1115. In 1326 it received a town charter but the town lost it again as well as all significance when it was destroyed during the Thirty Years' War. In 1838 the Grand Duke of Baden again granted a town charter to Renchen but it again lost the right to call itself a town as a result of the German district reform in 1935. Renchen then received a town charter for the third time in 1950 in recognition of its hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonel
Colonel ( ; abbreviated as Col., Col, or COL) is a senior military Officer (armed forces), officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations. In the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of a regiment in an army. Modern usage varies greatly, and in some cases, the term is used as an Colonel (title), honorific title that may have no direct relationship to military. In some smaller military forces, such as those of Monaco or the Holy See, Vatican, colonel is the highest Military rank, rank. Equivalent naval ranks may be called Captain (naval), captain or ship-of-the-line captain. In the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth's air force ranking system, the equivalent rank is group captain. History and origins By the end of the late medieval period, a group of "companies" was referred to as a "column" of an army. According to Raymond Oliver, , the Spanish began explicitly reorganizing part of thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Marie Claude Alexandre Goujon
Jean Marie Claude Alexandre Goujon (13 April 1766, Bourg-en-Bresse – 17 June 1795, Paris) was a politician of the French Revolution. He was a member of the National Convention from 1793 to 1795, was sentenced to death after the Revolt of 1 Prairial Year III and committed suicide before he could be executed. Early life His grandfather, Claude Goujon, was director of a tax farm (les droits réunis) in Dijon, and his father, Claude Alexandre Goujon, was a Ferme générale, tax farmer from Bourg-en-Bresse. On 9 February 1762, Claude Alexandre married Joan Margaret Nicole Ricard, daughter of Joseph Ricard, a barrister, and First Secretary of the Stewardship of Burgundy (born 1745). In 1774 the family moved to Provins. The young Jean-Marie Goujon abandoned his studies after his father encountered financial difficulties, going first to Dieppe, Seine-Maritime, Dieppe and then Saint-Malo to join the Navy. Having enlisted at the age of twelve as a seaman aboard the ''French ship Diadèm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Hentz
Nicholas Charles Arnould Hentz (5 June 1753, Metz, France – after 1 July 1830, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania) was a French revolutionary and politician. After fleeing France in 1815, he assumed the name Charles Arnould. Early life Coming from a family of nineteen children of a farrier, Nicolas Hentz was born in Metz, France on 5 June 1753. In 1780 he became a lawyer at the Parliament of Metz. He was elected Justice of the Peace of Sierck-les-Bains in December 1790, and embraced the revolutionary ideas. As Justice of the Peace, he made arrests of emigres on the road to Trier. He was a deputy for Moselle to the Revolutionary National Convention 1789 after which he was elected MP for the Moselle in September 1792. Hentz belonged to the party of the Montagne in the National Assembly of France during the French Revolution. He became a member of the Legislation Committee, where he proposed a limitation of inheritances. Regicide and revolution At the trial of King Louis XVI in De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trier
Trier ( , ; ), formerly and traditionally known in English as Trèves ( , ) and Triers (see also Names of Trier in different languages, names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle (river), Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the west of the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, near the border with Luxembourg and within the important Mosel (wine region), Moselle wine region. Founded by the Ancient Romans, Romans in the late 1st century BC as ''Augusta Treverorum'' ("The City of Augustus among the Treveri"), Trier is considered Germany's oldest city. It is also the oldest cathedral, seat of a bishop north of the Alps. Trier was one of the four capitals of the Roman Empire during the Tetrarchy period in the late 3rd and early 4th centuries. In the Middle Ages, the archbishop-elector of Trier was an important prince of the Church who controlled land from the French border to the Rhine. The archbishop-elector of Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saarlouis
Saarlouis (; , ; formerly Sarre-Libre and Saarlautern) is a town in Saarland, Germany, capital of the district of Saarlouis (district), Saarlouis. In 2020, the town had a population of 34,409. Saarlouis is located on the river Saar (river), Saar. It was built as a fortress in 1680 and was named after Louis XIV of France. History With the Treaties of Nijmegen, Treaties of Peace of Nijmegen in 1678/79, Lorraine (province), Lorraine fell to France. In 1680, Louis XIV of France gave orders to build a fortification (to defend the new French eastern frontier) on the banks of the river Saar which was called ''Sarre-Louis''. Notable French military engineer, Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, constructed the town, which would serve as the capital of the Province de la Sarre. The plans were made by Thomas de Choisy, the town's first Gouvenour. In 1683, Louis XIV visited the fortress and granted arms. The coat of arms shows the rising sun and three Fleur-de-lis. The heraldic motto is ''Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
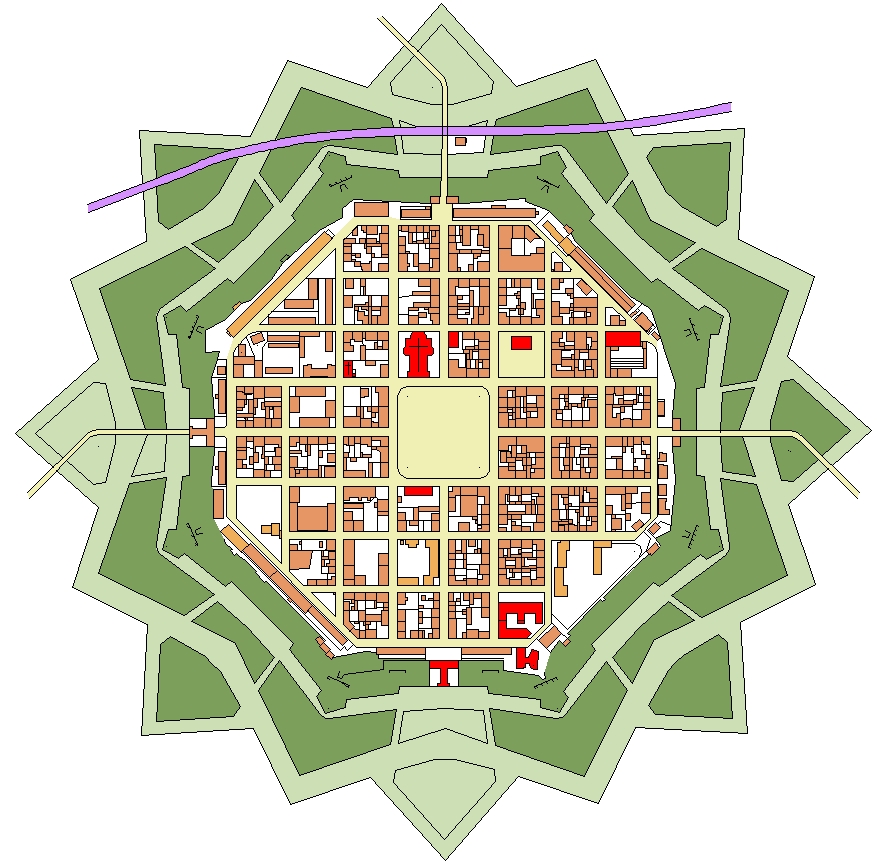
Neuf-Brisach
Neuf-Brisach ( or , ; , , in contrast to " Old Breisach"; ) is a fortified town and commune of the department of Haut-Rhin in the French region of Alsace. The fortified town was intended to guard the border between France and the Holy Roman Empire and, subsequently, the German states. It was built after the Treaty of Ryswick in 1697 that resulted in France losing the town of Breisach, on the opposite bank of the Rhine. The town's name means ''New Breisach''. The town is a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of quintessential military fortifications and its testimony to the influence of Vauban on military architecture during the 17–19th centuries. History Work began on the fortified town in 1698, to plans drawn by Vauban, a military engineer at the service of Louis XIV. Vauban died in 1707 and this, his last work, was completed by Louis de Cormontaigne. The city's layout was that of an 'ideal city', as was popular at the time, with a regular square grid street pattern in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |