|
Frank Bell (educator)
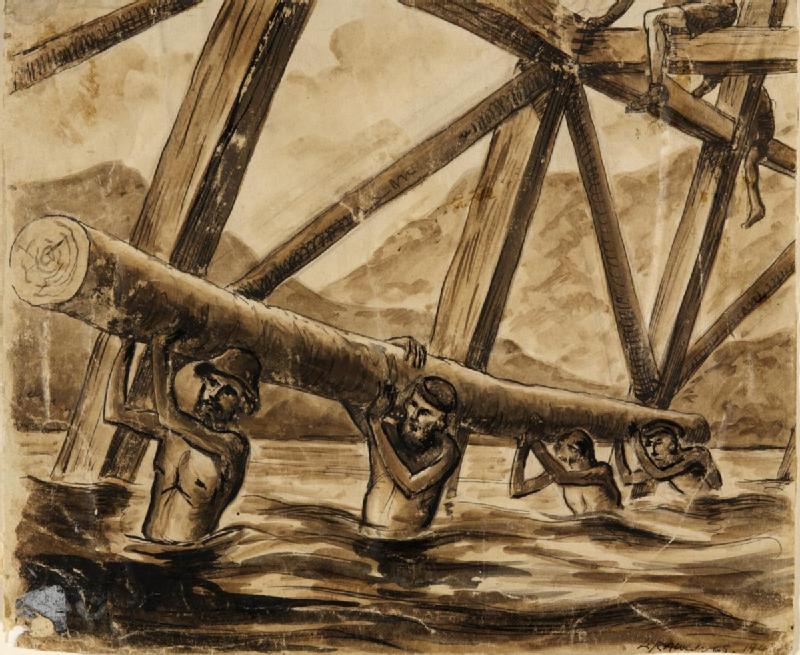
Frank Erskine Bell OBE (18 September 1916 – 14 July 1989) was a British educator. Whilst a prisoner of war (POW) in Borneo during World War II he organised a "secret university" to provide educational opportunities for his fellow prisoners. He founded the first Bell Language School in Cambridge, England in 1955 and later established the Bell Educational Trust, a charity involved in language education. Early life Bell was educated at Haileybury and Imperial Service College and then at Peterhouse, Cambridge, from where he graduated in 1938 with a first in French and Spanish. He joined the British Army in 1940, was commissioned into the Royal Artillery in 1941, and was posted to the 48th Light Anti-Aircraft Regiment which left England on 3 December 1941, destined for North Africa. It never arrived. On 7 December the Japanese attacked Pearl Harbor, and the British force, of which the Regiment was a part, was diverted to the Far East (see Pacific War). It arrived in Batavia, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The British Empire
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding valuable service in a wide range of useful activities. It comprises five classes of awards across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two of which make the recipient either a Orders, decorations, and medals of the United Kingdom#Modern honours, knight if male or a dame (title), dame if female. There is also the related British Empire Medal, whose recipients are affiliated with the order, but are not members of it. The order was established on 4 June 1917 by King George V, who created the order to recognise 'such persons, male or female, as may have rendered or shall hereafter render important services to Our Empire'. Equal recognition was to be given for services rendered in the UK and overseas. Today, the majority of recipients are UK citizens, though a number of Commonwealth realms outside the UK continue to make appointments to the order. Honorary awards may be made to cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far East Prisoners Of War
Far East prisoners of war is a term used in the United Kingdom to describe former United Kingdom, British and Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth prisoners of war held in the Far East during the Second World War. The term is also used as the initialism FEPOW, or as the abbreviation Far East POWs. Compensation scheme Since 2000, following a campaign led by the Royal British Legion, former Far East POWs are eligible for UK Government compensation for their suffering in POW and internment camps operated by the Japanese during the War. Compensation may be payable to any member of all British Groups imprisoned by the Japanese in the Second World War. It is therefore available to British civilians and British Merchant Navy, merchant seamen as well as members of British and Commonwealth forces. An amendment of the scheme in 2002 extended compensation to former Gurkha, Gurkha soldiers. An application may be made by either a former POW or their family or Estate (law), estate. A s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Willink
Sir Henry Urmston Willink, 1st Baronet, (7 March 1894 – 20 July 1973) was a British politician and public servant. A Conservative Member of Parliament from 1940, he became Minister of Health in 1943. During his time in power he was appointed Special Commissioner for those made homeless by the London Blitz and was involved with the production of the Beveridge Report. The details of the report proposed a comprehensive free healthcare system, this led to the white paper ''A National Health Service'', published in 1944, suggesting the creation of such a service, which did not include the nationalisation of hospitals. Such a policy was later implemented by the Labour Party through the creation of the National Health Service which differed from the proposals suggested by Willink. At the time he claimed the nationalisation of voluntary hospitals "will destroy so much in this country that we value". Early life and wartime service Willink was born in Liverpool. He was educated as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concord College, Acton Burnell
Concord College is an independent co-educational international day/boarding school in Shropshire, England, situated in the grounds of Acton Burnell Castle. The college admits students aged between 12 and 19, the majority coming from overseas. Concord College excels academically, achieving 85% A*-A at A-level and 82% A*-A at GCSE level. In 2009, to celebrate its 60th year, Concord was visited by the Princess Royal. History The main building of Concord College is Acton Burnell Hall, which is the manor house of Acton Burnell Castle. Ranking In 2016, The Times league table for independent co-educational schools in the UK placed Concord tenth. In 2022, The Telegraph ranked Concord College's A-level results at 16th among all UK independent schools, and 7th among those offering boarding. Notable alumni * Zeinal Bava, telecoms entrepreneur * Bowie Cheung ( 張寶兒), Hong Kong presenter and actress, Miss Hong Kong 2016 contestant * Anthony Chow ( 周永健), practising solicit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of The United States During World War II
The military history of the United States during World War II covers the nation's role as one of the major Allies of World War II, Allies in their victory over the Axis powers. The United States is generally considered to have entered the conflict with the 7 December 1941 surprise attack on Pearl Harbor by Empire of Japan, Japan and exited it with the surrender of Japan on 2 September 1945. During the first two years of World War II, the U.S. maintained formal Non-interventionism, neutrality, which was officially announced in the Quarantine Speech delivered by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1937. While officially neutral, the U.S. supplied United Kingdom, Britain, the Soviet Union, and Republic of China (1912–1949), China with war materiel through the Lend-Lease, Lend-Lease Act signed into law on 11 March 1941, and Occupation of Iceland#United States occupation, deployed the U.S. military to replace the Invasion of Iceland, British forces stationed in Iceland. Following th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allies of World War I, Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has played History of the Royal Air Force, a significant role in Military history of the United Kingdom, British military history. In particular, during the Second World War, the RAF established Air supremacy, air superiority over Nazi Germany's Luftwaffe during the Battle of Britain, and led the Allied strategic bombing effort. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities nee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Library
Cambridge University Library is the main research library of the University of Cambridge. It is the largest of over 100 libraries Libraries of the University of Cambridge, within the university. The library is a major scholarly resource for members of the University of Cambridge and external researchers. It is often referred to within the university as the UL. Thirty-three Libraries of the University of Cambridge#Affiliated Libraries, faculty and departmental libraries are associated with the University Library for the purpose of central governance and administration, forming "Cambridge University Libraries". Cambridge University Library is one of six legal deposit libraries under UK law. It holds about 9 million items (including maps and sheet music) and, through legal deposit, purchase and donation it receives around 100,000 items every year. The University Library is unique among the legal deposit libraries in keeping a large proportion of its material on open access and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarong
A sarong or a sarung (, ) is a large tube or length of textile, fabric, often wrapped around the waist, worn in Southeast Asia, South Asia, Western Asia, Northern Africa, East Africa, West Africa, and on many Pacific islands. The fabric often employs woven plaid (pattern), plaid or checkered patterns or may be brightly colored by means of batik or ikat dyeing. Many modern sarongs have printed designs, often depicting animals or plants. Different types of sarongs are worn in different places in the world, notably the lungi in the Indian subcontinent and the izaar in the Arabian Peninsula. The unisex sarong is typically longer than the men's lungi. Etymology The term ''sarong'' is a loanword from Malay language, Malay (, old spelling: ), meaning 'to cover' or 'to sheath'. It was first used in 1834 referring to the skirt-like garment of the Malays (ethnic group), Malays. ''Sarong'' is the older Malay spelling, still used colloquially and persists in English, while () is the sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, referred to as White and Black in chess, "White" and "Black", each control sixteen Chess piece, pieces: one king (chess), king, one queen (chess), queen, two rook (chess), rooks, two bishop (chess), bishops, two knight (chess), knights, and eight pawn (chess), pawns, with each type of piece having a different pattern of movement. An enemy piece may be captured (removed from the board) by moving one's own piece onto the square it occupies. The object of the game is to "checkmate" (threaten with inescapable capture) the enemy king. There are also several ways a game can end in a draw (chess), draw. The recorded history of chess goes back to at least the emergence of chaturanga—also thought to be an ancesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India, Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India. Quote: "The Eighth Schedule recognizes India's national languages as including the major regional languages as well as others, such as Sanskrit and Urdu, which contribute to India's cultural heritage. ... The original list of fourteen languages in the Eighth Schedule at the time of the adoption of the Constitution in 1949 has now grown to twenty-two." Quote: "As Mahapatra says: "It is generally believed that the significance for the Eighth Schedule lies in providing a list of languages from which Hindi is directed to draw the appropriate forms, style and expressions for its enrichment" ... Being recognized in the Constitution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |