|
Francis Knight (surgeon)
Francis Knight (1832) was a British surgeon, an army medical man as well as a society doctor with court connections, who became Inspector of Military Hospitals in 1802. Life to 1801 Knight was according to research of the antiquarian Henry Longden Isham a grandson of Walter Chapman (1676–1761), son of John Chapman of Puddletown, Dorset; and had an uncle George Chapman with a court connection. In 1780 Knight became medical officer of the Coldstream Guards. In time, his work there brought him to the notice of Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany. He became a surgeon extraordinary to George III. He was impressed by a vaccination carried out by Jonathan Wathen Phipps, an eye doctor also with a court position. He became a vaccinator himself, and in 1799 vaccinated two of the children of Mrs Jordan and the Duke of Clarence. Army Medical Board When John Rush, Inspector of Regimental Hospitals, died in 1801 at the end of the year, his replacement was Knight, who was given the broad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puddletown
Puddletown is a village and civil parish in Dorset, England. It is situated by the River Piddle, from which it derives its name, about northeast of the county town Dorchester. Its earlier name Piddletown fell out of favour, probably because of connotations of the word "piddle". The name Puddletown was officially sanctioned in the late 1950s. Puddletown's civil parish covers and extends to the River Frome to the south. In 2013 the estimated population of the civil parish was 1450. Puddletown's parish church has significant architectural interest, particularly its furnishings and monuments. It has a 12th-century font and well-preserved woodwork, including 17th-century box pews. Thomas Hardy took an interest in the church, and the village provided the inspiration for the fictional settlement of Weatherbury in his novel ''Far from the Madding Crowd''; Weatherbury Farm, the home of principal character Bathsheba Everdene, is based on a manor house within the parish. Toponymy The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelsea, London
Chelsea is an affluent area in west London, England, due south-west of Charing Cross by approximately 2.5 miles. It lies on the north bank of the River Thames and for postal purposes is part of the south-western postal area. Chelsea historically formed a manor and parish in the Ossulstone hundred of Middlesex, which became the Metropolitan Borough of Chelsea in 1900. It merged with the Metropolitan Borough of Kensington, forming the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea upon the creation of Greater London in 1965. The exclusivity of Chelsea as a result of its high property prices historically resulted in the coining of the term " Sloane Ranger" in the 1970s to describe some of its residents, and some of those of nearby areas. Chelsea is home to one of the largest communities of Americans living outside the United States, with 6.53% of Chelsea residents having been born in the U.S. History Early history The word ''Chelsea'' (also formerly ''Chelceth'', ''Chelchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Corunna
The Battle of Corunna (or ''A Coruña'', ''La Corunna'', ''La Coruña'' or ''La Corogne''), in Spain known as Battle of Elviña, took place on 16 January 1809, when a French corps under Marshal of the Empire Jean de Dieu Soult attacked a British army under Lieutenant-General Sir John Moore. The battle took place amidst the Peninsular War, which was a part of the wider Napoleonic Wars. It was a result of a French campaign, led by Napoleon, which had defeated the Spanish armies and caused the British army to withdraw to the coast following an unsuccessful attempt by Moore to attack Soult's corps and divert the French army. Doggedly pursued by the French under Soult, the British made a retreat across northern Spain while their rearguard fought off repeated French attacks. Both armies suffered extremely from the harsh winter conditions. Much of the British army, excluding the elite Light Brigade under Robert Craufurd, suffered from a loss of order and discipline during the ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain, it is considered to overlap with the Spanish War of Independence. The war started when the French and Spanish armies invaded and occupied Portugal in 1807 by transiting through Spain, and it escalated in 1808 after Napoleonic France occupied Spain, which had been its ally. Napoleon Bonaparte forced the abdications of Ferdinand VII and his father Charles IV and then installed his brother Joseph Bonaparte on the Spanish throne and promulgated the Bayonne Constitution. Most Spaniards rejected French rule and fought a bloody war to oust them. The war on the peninsula lasted until the Sixth Coalition defeated Napoleon in 1814, and is regarded as one of the first wars of national liberation. It is also significant for the emergence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Borland (surgeon)
James Borland (April 1774 – 22 February 1863) was a Scottish inspector-general of army hospitals. Biography Borland was born at Ayr, Scotland, in April 1774, and entered the army medical department as surgeon's mate in the 42nd Highlanders in 1792. Having been promoted to the staff next year, he made two campaigns under the Duke of York in Flanders, after which he proceeded to the West Indies as surgeon, 23rd royal Welsh Fusiliers. He was then again transferred to the staff, and did duty in St. Domingo from 1796 until the last remnant of the British army was withdrawn from that pestilential shore in 1798. In 1799 he accompanied the expedition to the Helder, and after its failure was sent by the Duke of York to the headquarters of the French general, Guillaume Brune, with a flag of truce, to arrange for the exchange of the wounded. For this service he was promoted to the then newly constituted rank of deputy inspector of army hospitals. He was also attached to the Russian troop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Campaign In Egypt And Syria
The French campaign in Egypt and Syria (1798–1801) was Napoleon Bonaparte's campaign in the Ottoman territories of Egypt and Syria, proclaimed to defend French trade interests, to establish scientific enterprise in the region. It was the primary purpose of the Mediterranean campaign of 1798, a series of naval engagements that included the capture of Malta and the Greek island Crete, later arriving in the Port of Alexandria. The campaign ended in defeat for Napoleon, leading to the withdrawal of French troops from the region. On the scientific front, the expedition eventually led to the discovery of the Rosetta Stone, creating the field of Egyptology. Despite early victories and an initially successful expedition into Syria, Napoleon and his Armée d'Orient were eventually defeated and forced to withdraw, especially after suffering the defeat of the supporting French fleet at the Battle of the Nile. Preparations and voyage Proposal At the time of the invasion, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Vetch
John Vetch MD (1783–1835) was a Scottish army surgeon, now known for his early work on trachoma. The variant spelling Veitch of his surname was also used. Life He was the eldest son of Robert Vetch of Caponflat, born in East Lothian; James Vetch and Hamilton Vetch were younger brothers. He graduated M.D. at the University of Edinburgh in 1804. He joined the army, in the position of hospital mate until he was commissioned in August 1806. A depot hospital had been set up in 1801 at Selsey to treat British troops returning from the fighting in the French campaign in Egypt and Syria, with the condition called "Egyptian ophthalmia". The name was not a very good fit, but its scope in severe cases is recognised as modern medicine's trachoma. Stewart Duke-Elder considered that further pathogens were involved, Weeks Koch bacillus, and some mixture of gonococcus. In 1804 Vetch observed in a battalion of the 52nd Foot at Hythe, Kent, an apparent outbreak of contagious ophthalmia, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selsey
Selsey is a seaside town and civil parish, about eight miles (12 km) south of Chichester in West Sussex, England. Selsey lies at the southernmost point of the Manhood Peninsula, almost cut off from mainland Sussex by the sea. It is bounded to the west by Bracklesham Bay, to the north by Broad Rife (''rife''Parish. A Dictionary of the Sussex Dialect. pp. 96–97 being the local word for stream or creek), to the east by Pagham Harbour and terminates in the south at Selsey Bill. There are significant rock formations beneath the sea off both of its coasts, named the Owers rocks and Mixon rocks. Coastal erosion has been an ever-present problem for Selsey.SCOPAC''Sedimentary Study from East Head to Pagham.'' Section 1.1. – The Standing Conference on Problems Associated with the Coastline (SCOPAC) was established in 1986 and consists of local authorities, the Environment agency and others. ''Archaeological evidence demonstrates that the coastline was some 2 to 3 km s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachoma
Trachoma is an infectious disease caused by bacterium '' Chlamydia trachomatis''. The infection causes a roughening of the inner surface of the eyelids. This roughening can lead to pain in the eyes, breakdown of the outer surface or cornea of the eyes, and eventual blindness. Untreated, repeated trachoma infections can result in a form of permanent blindness when the eyelids turn inward. The bacteria that cause the disease can be spread by both direct and indirect contact with an affected person's eyes or nose. Indirect contact includes through clothing or flies that have come into contact with an affected person's eyes or nose. Children spread the disease more often than adults. Poor sanitation, crowded living conditions, and not enough clean water and toilets also increase spread. Efforts to prevent the disease include improving access to clean water and treatment with antibiotics to decrease the number of people infected with the bacterium. This may include treating, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newport, Isle Of Wight
Newport is the county town of the Isle of Wight, an island county off the south coast of England. The town is slightly north of the centre of the island, and is in the civil parish of Newport and Carisbrooke. It has a quay at the head of the navigable section of the River Medina, which flows northwards to Cowes and the Solent. In 2020 it had an estimated population of 26,109. History Mousterian remains, featuring tools made by Neanderthals at least 40,000 years ago, were found at Great Pan Farm in the 1970s. There are signs of Roman settlement in the area, which was probably known as ''Medina''. They include two known Roman villas, one of which, Newport Roman Villa, has been excavated and opened to the public. Information on the area resumes after the Norman Conquest. The first charter was granted in the late 12th century. In 1377 an invading French force burnt down much of the town while attempting to take Carisbrooke Castle, then under the command of Sir Hugh Tyrill. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1588, an English fleet based in Plymouth intercepted and defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony, the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a commercial shipping port, handling impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
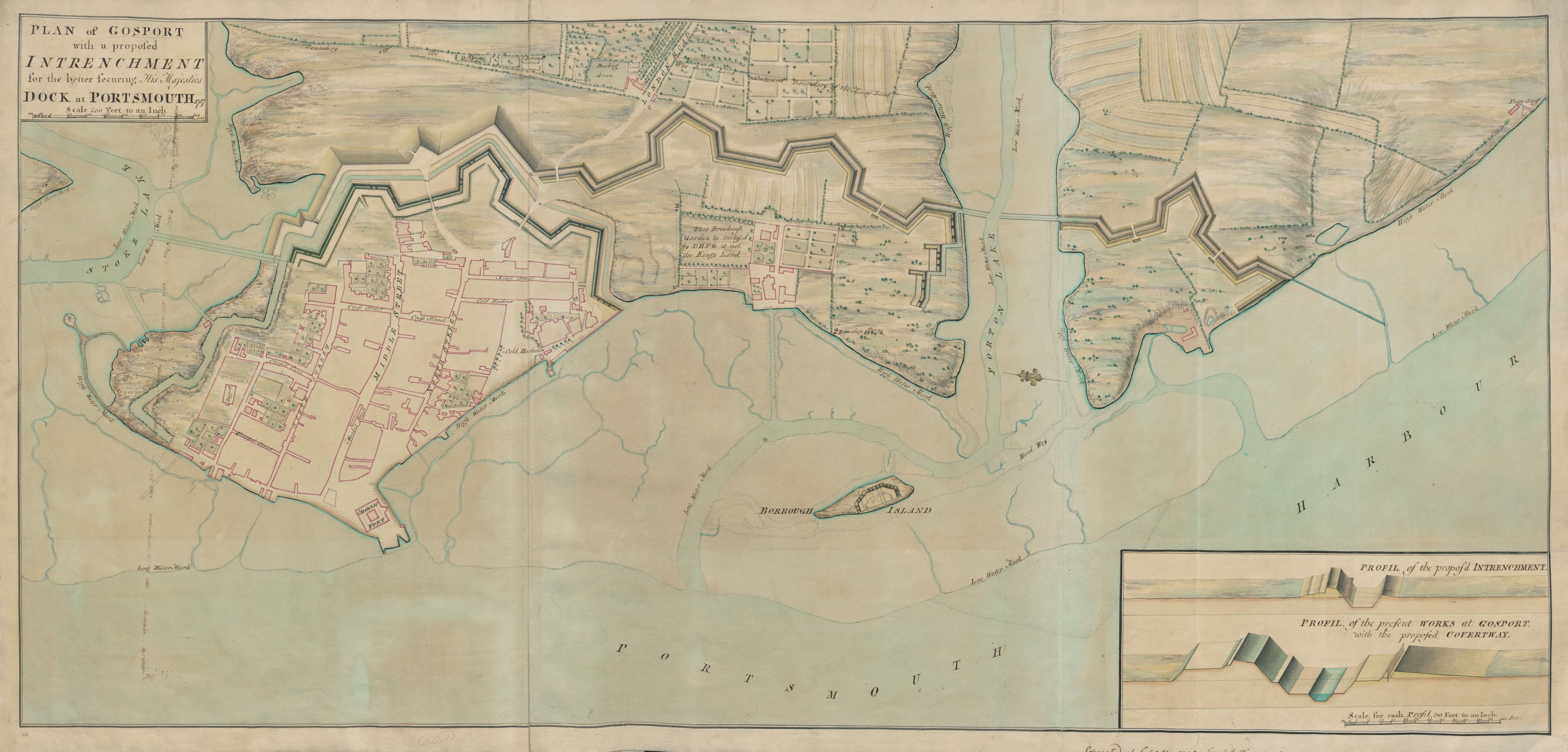
Gosport
Gosport ( ) is a town and non-metropolitan borough on the south coast of Hampshire, South East England. At the 2011 Census, its population was 82,662. Gosport is situated on a peninsula on the western side of Portsmouth Harbour, opposite the city of Portsmouth, to which it is linked by the Gosport Ferry. Gosport lies south-east of Fareham, to which it is linked by a Bus Rapid Transit route and the A32. Until the last quarter of the 20th century, Gosport was a major naval town associated with the defence and supply infrastructure of His Majesty's Naval Base (HMNB) Portsmouth. As such over the years extensive fortifications were created. Gosport is still home to and a Naval Armament Supply Facility, as well as a Helicopter Repair base. The Town area of the Borough, including Newtown, consists of the town centre, Stoke Road shopping area, Walpole Park, Royal Clarence Yard and three modern marinas: Royal Clarence, Gosport Marina and Haslar Marina. As part of the ''Renai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)