|
Francesco Manca
Francesco Manca (born November 1966, in Milan, Italy) is an Italian amateur astronomer and discoverer of minor planets at the Sormano Astronomical Observatory in northern Italy. Manca also performs follow-up astrometry of near-Earth objects (NEOs). He acquired research and observational experience on the NEOs at professional observatories in Arizona, United States at Catalina Sky Survey (IAU Obs code 703 and G96) Non-observational work focuses on computations of orbit and close approaches of asteroids with the Earth (linked at Center for Near Earth Object Studies (CNEOS) - Jet Propulsion Laboratory) and computation of orbit identifications of asteroids (Near Earth Asteroids, Mars-crossing asteroids , Hungaria group, Trans-Neptunian object) and comets. He wrote many articles on specialistic magazines. Member of SIMCA ( it, Società Italiana Meccanica Celeste e Astrodinamica) and associated (INAF) National Institute for Astrophysics. His professional activity concerns the applic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor planet'', but that year's meeting reclassified minor planets and comets into dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies (SSSBs).Press release, IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes International Astronomical Union, August 24, 2006. Accessed May 5, 2008. Minor planets include s ( ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very Large Telescope
The Very Large Telescope (VLT) is a telescope facility operated by the European Southern Observatory on Cerro Paranal in the Atacama Desert of northern Chile. It consists of four individual telescopes, each with a primary mirror 8.2 m across, which are generally used separately but can be used together to achieve very high angular resolution. The four separate optical telescopes are known as ''Antu'', ''Kueyen'', ''Melipal'', and ''Yepun'', which are all words for astronomical objects in the Mapuche language. The telescopes form an array complemented by four movable Auxiliary Telescopes (ATs) of 1.8 m aperture. The VLT operates at visible and infrared wavelengths. Each individual telescope can detect objects roughly four billion times fainter than can be detected with the naked eye, and when all the telescopes are combined, the facility can achieve an angular resolution of about 0.002 arcsecond. In single telescope mode of operation angular resolution is about 0.05 arcs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9115 Battisti
9115 Battisti, provisional designation , is a stony Vestian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 5.5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 27 February 1997, by Italian astronomers Piero Sicoli and Francesco Manca at Sormano Astronomical Observatory in northern Italy. The asteroid was named for Italian singer-songwriter Lucio Battisti. Orbit and classification ''Battisti'' is a member of the Vestian family. It orbits the Sun in the inner main-belt at a distance of 2.2–2.6 AU once every 3 years and 9 months (1,354 days). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.09 and an inclination of 5 ° with respect to the ecliptic. In September 1980, it was first identified as at Palomar Observatory, extending the body's observation arc by 17 years prior to its official discovery observation at Sormano. Physical characteristics Rotation period In November 2010, a fragmentary rotational lightcurve of ''Battisti'' was obtained from photometric obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Marcello Pistoiese Observatory
The Pistoia Mountains Astronomical Observatory ( it, Osservatorio Astronomico della Montagna Pistoiese; obs. code: 104), also known as the ''San Marcello Observatory'' and the ''Pian dei Termini Observatory'' ( it, Osservatorio di Pian dei Termini), is an astronomical observatory in San Marcello Piteglio, Tuscany, central Italy. The observatory uses a 0.4- and 0.6-meter Newton-Cassegrain telescope and is the home of the Gruppo Astrofili Montagna Pistoiese, a group of amateur astronomers known for its members Luciano Tesi (founder), Silvano Casulli, Paolo Bacci, Vasco Cecchini and late Vittorio Goretti. List of discovered minor planets See also * List of asteroid-discovering observatories * List of astronomical observatories This is a list of astronomical observatories ordered by name, along with initial dates of operation (where an accurate date is available) and location. The list also includes a final year of operation for many observatories that are no longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luciano Tesi
Luciano Tesi (; born 10 December 1931) is an Italian veterinarian, amateur astronomer, discoverer of many minor planets, and director of the San Marcello Pistoiese Observatory. In 1980, he founded the "Amateur Group of Pistoiese Mountain" ( it, Gruppo Astrofili Montagna Pistoiese). Later on, this resulted in the construction of the Pistoia Mountains Astronomical Observatory. As the director of the observatory, he has collaborated with many discoverers in following up near-Earth objects and in finding minor planets since 1994. The near-Earth object and Amor asteroid, 15817 Lucianotesi, discovered by Andrea Boattini and Maura Tombelli at San Marcello Pistoiese in 1994, was named in his honor. Discoveries Luciano Tesi is credited by the Minor Planet Center The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrea Boattini
Andrea Boattini (born 16 September 1969) is an Italian astronomer and a prolific discoverer of minor planets and comets. Career After developing a growing interest in minor planets, he graduated in 1996 from the University of Bologna with a thesis on near-Earth objects (NEOs). He is involved in various projects related to NEO follow-up and search programs, with special interest in the NEO class known as Atens. He currently works at the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, University of Arizona after many years spent at the Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche (CNR, National Research Council) and the Astronomical Observatory in Rome. He worked for the Catalina Sky Survey project from 2007 to 2014, in Tucson, Arizona (USA). Meanwhile, he discovered the active comets C/2007 W1 (Boattini), C/2008 J1 (Boattini), C/2008 S3 (Boattini), C/2009 P2 (Boattini), C/2009 W2 (Boattini), C/2010 F1 (Boattini), C/2010 G1 (Boattini) as well as the most distant discovery of an inbound active com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15460 Manca
15460 Manca, provisional designation , is a Koronian asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 5 kilometers in diameter. The asteroid was discovered on 25 December 1998, by Italian astronomers Andrea Boattini and Luciano Tesi at Pistoia Mountains Astronomical Observatory in San Marcello Pistoiese, central Italy. It was named for Italian amateur astronomer Francesco Manca. Orbit and classification ''Manca'' belongs to the Koronis family, a family of stony asteroids in the outer main-belt with nearly ecliptical orbits. It orbits the Sun at a distance of 2.6–3.2 AU once every 4 years and 12 months (1,810 days). Its orbit has an eccentricity of 0.09 and an inclination of 3 ° with respect to the ecliptic. The asteroid's observation arc begins 48 years prior to its official discovery observation, with a precovery taken at the Palomar Observatory in March 1950. Physical characteristics ''Manca'' has also been characterized as an X-type ast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koronis Family
] The Koronis or Koronian family (), also known as the Lacrimosa family, is a very large asteroid family of stony asteroids, located in the outer region of the asteroid belt. They are thought to have been formed at least two billion years ago in a catastrophic collision between two larger bodies. The family is named after 158 Koronis, and the largest known member (208 Lacrimosa) is about in diameter. The Koronis family travels in a cluster along the same orbit. It has 5949 members. This family has two subfamilies. The Karin family () was formed remarkably recently in a catastrophic collision (destroying the parent body), with an estimated age of 5.72 million years. The Koronis(2) family () with 246 members is the other. It formed 15 million years ago by a non-catastrophic collision with 158 Koronis. On August 28, 1993, the Galileo spacecraft visited a member of this family, 243 Ida Ida, minor planet designation 243 Ida, is an asteroid in the Koronis family of the asteroid b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
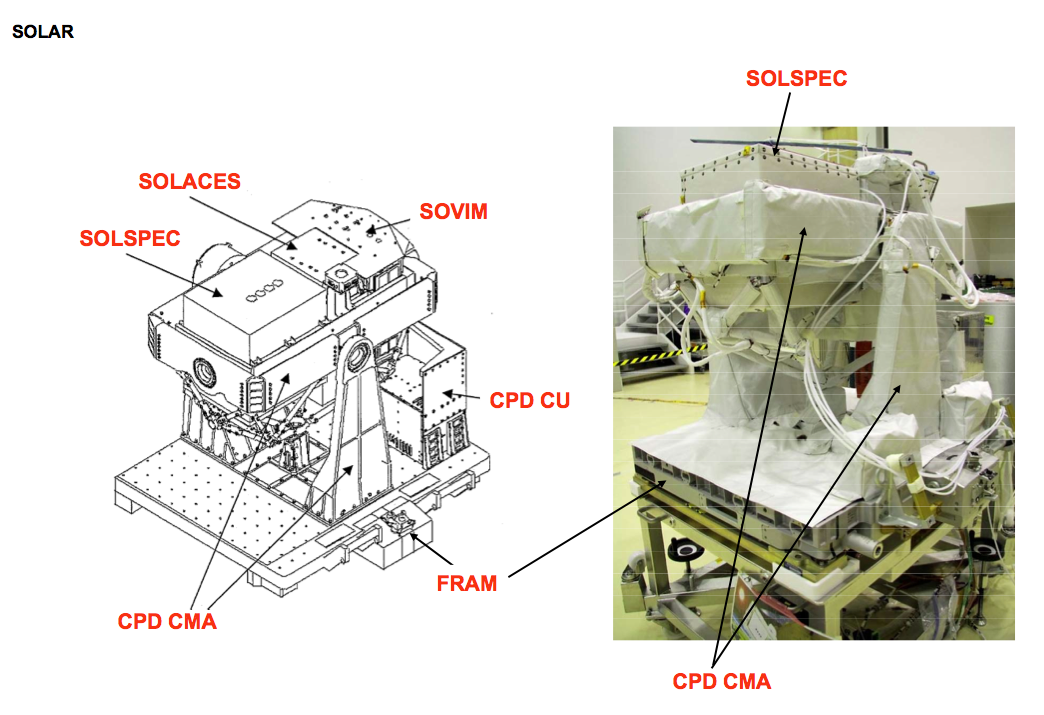
Solar Monitoring Observatory
SOLAR was an ESA science observatory on the Columbus Laboratory, which is part of the International Space Station. SOLAR was launched with Columbus on February 2008 aboard STS-122. It was externally mounted to Columbus with the European Technology Exposure Facility (EuTEF). SOLAR has three main space science instruments: SOVIMSOLSPECand SOL-ACES. Together they provide detailed measurements of the Sun's spectral irradiance. The SOLAR platform and its instruments are controlled from thBelgian User Support and Operations Centre(B.USOC), located at thBelgian Institute for Space Aeronomy(BISA) in Uccle, Belgium. Instruments *SOVIM (''So''lar ''V''ariability and ''I''rradiance ''M''onitor) instrument is based on an earlier instrument (SOVA) which flew aboard the European Retrievable Carrier, launched on STS-46 in 1992. It is designed to measure solar radiation with wavelengths from 200 nanometers - 100 micrometers. This covers near-ultraviolet, visible and infrared areas of the spect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEOSTEL
The Near Earth Object Survey TELescope (NEOSTEL - also known as "Flyeye") is an astronomical survey and early-warning system for detecting near-Earth objects sized and above a few weeks before they impact Earth. NEOSTEL is a project founded by the European Space Agency (ESA), starting with an initial prototype currently under construction at OHB in Milan, Italy. The telescope is of a new "fly-eye" design inspired by the wide field of vision from a fly's eye. The design combines a single objective reflector with multiple sets of optics and CCDs, giving a very wide field of view (around , or 220 times the area of the full moon). When complete it will have one of the widest fields of view of any telescope and be able to survey the majority of the visible sky in a single night. If the initial prototype is successful, three more telescopes are planned, in complementary positions around the globe close to the equator. In terms of light gathering power, the size of the primary m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Anatolia Observatory
Eastern Anatolia Observatory ( tr, Doğu Anadolu Gözlemevi, shortly DAG) is proposed ground-based astronomical observatory of Atatürk University in Erzurum, Turkey. The project to establish an observatory in Erzurum is conducted by the Astrophysics Research and Application Center of Atatürk University with the scientific and technical coordination of TÜBİTAK National Observatory and financial support of the Ministry of Development, Government of Erzurum Province, 40 universities and seven observatories in the region. It is the country's biggest project for astronomy, astrophysics and space science. The observatory will be built on a land of atop Karakaya Hill at above sea level within the Konaklı Ski Resort south of Erzurum. It will host Turkey's first infrared telescope. The telescope will have an active primary mirror of in diameter and will be equipped with adaptive optics (AO) technology. The contract for the construction of the telescope has been awarded to the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)