|
Francesca French
Francesca Law French (; 12 December 1871 – 2 August 1960) was a British Protestant Christian missionary in China. She served with the China Inland Mission. Early career French was born in Bruges, Belgium, the second daughter of English parents John Erington French and his first cousin Frances Elizabeth French. She was educated at the secondary school in Geneva, Switzerland. Her older sister, Evangeline F. French had gone to China as a missionary in 1893. Francesca wanted to go to China also, but she remained in England to care for her aging mother. After her mother died, in 1908 she joined her sister in China. The French sisters were stationed with Mildred Cable in Huozhou, Shanxi and travelled constantly in the surrounding area. They became known as the "trio." Francesca was the quietest of the three and described as sensitive, sympathetic, bookish, and artistic. After 20 years in Huozhou, the trio believed that the mission should be turned over to Chinese leaders and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to be growing Criticism of the Catholic Church, errors, abuses, and discrepancies within it. Protestantism emphasizes the Christian believer's justification by God in faith alone (') rather than by a combination of faith with good works as in Catholicism; the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by Grace in Christianity, divine grace or "unmerited favor" only ('); the Universal priesthood, priesthood of all faithful believers in the Church; and the ''sola scriptura'' ("scripture alone") that posits the Bible as the sole infallible source of authority for Christian faith and practice. Most Protestants, with the exception of Anglo-Papalism, reject the Catholic doctrine of papal supremacy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
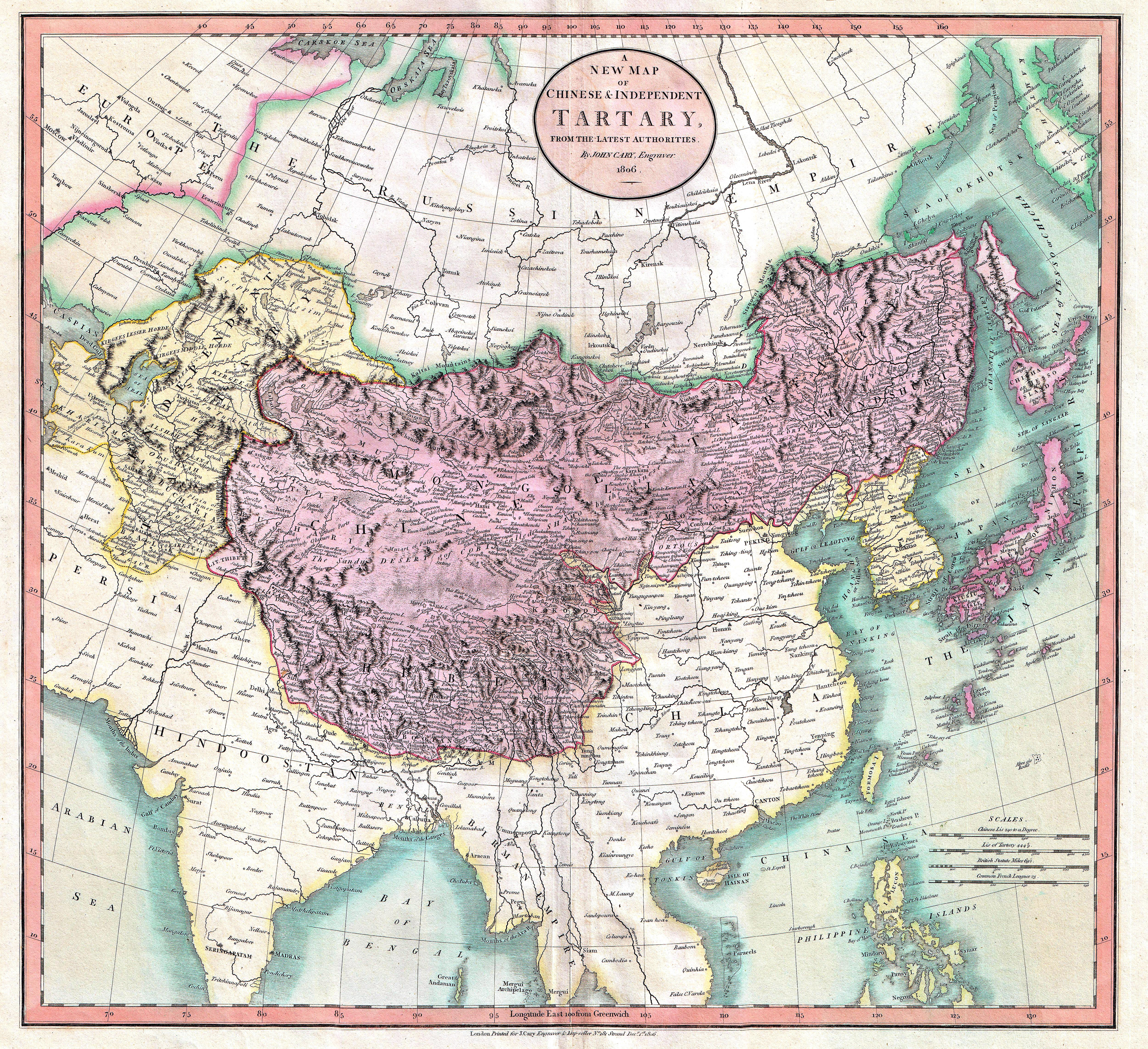
Tartars
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bounded by the Caspian Sea, the Ural Mountains, the Pacific Ocean, and the northern borders of China, India and Persia, at a time when this region was largely unknown to European geographers. The active use of the toponym (place name) can be traced from the 13th to the 19th centuries. In European sources, Tartary became the most common name for Central Asia that had no connection with the real polities or ethnic groups of the region; until the 19th century, European knowledge of the area remained extremely scarce and fragmentary. In modern English-speaking tradition, the region formerly known as Tartary is usually called Inner or Central Eurasia. Much of this area consists of arid plains, the main nomadic population of which in the past was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instituted by Jesus Christ during the Last Supper; giving his disciples bread and wine during a Passover meal, he commanded them to "do this in memory of me" while referring to the bread as "my body" and the cup of wine as "the blood of my covenant, which is poured out for many". The elements of the Eucharist, sacramental bread ( leavened or unleavened) and wine (or non-alcoholic grape juice), are consecrated on an altar or a communion table and consumed thereafter, usually on Sundays. Communicants, those who consume the elements, may speak of "receiving the Eucharist" as well as "celebrating the Eucharist". Christians generally recognize a special presence of Christ in this rite, though they differ about exactly how, where, and when Chri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uighur Language
The Uyghur or Uighur language (; , , , or , , , , CTA: Uyğurçä; formerly known as Eastern Turki), is a Turkic language written in a Uyghur Perso-Arabic script with 8-11 million speakers, spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of Western China. Significant communities of Uyghur speakers are located in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan, and various other countries have Uyghur-speaking expatriate communities. Uyghur is an official language of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region; is widely used in both social and official spheres, as well as in print, television, and radio; and is used as a common language by other ethnic minorities in Xinjiang. Uyghur belongs to the Karluk branch of the Turkic language family, which includes languages such as Uzbek. Like many other Turkic languages, Uyghur displays vowel harmony and agglutination, lacks noun classes or grammatical gender, and is a left-branching language with subject–ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Manchu Relations in Five Phases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan People
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans live in the Chinese provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Sichuan, and Yunnan, as well as in India, Nepal, and Bhutan. Tibetan languages belong to the Tibeto-Burman language group. The traditional or mythological explanation of the Tibetan people's origin is that they are the descendants of the human Pha Trelgen Changchup Sempa and rock ogress Ma Drag Sinmo. It is thought that most of the Tibeto-Burman speakers in Southwest China, including Tibetans, are direct descendants from the ancient Qiang people. Most Tibetans practice Tibetan Buddhism, although some observe the indigenous Bon religion and there is a small Muslim minority. Tibetan Buddhism influences Tibetan art, drama and architecture, while the harsh geography of Tibet has produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexi Corridor
The Hexi Corridor (, Xiao'erjing: حْسِ ظِوْلاْ, IPA: ), also known as the Gansu Corridor, is an important historical region located in the modern western Gansu province of China. It refers to a narrow stretch of traversable and relatively arable plain west of the Yellow River's Ordos Loop, flanked between the much more elevated and inhospitable terrains of the Mongolian and Tibetan Plateaus. The name ''Hexi'', refers to "west of the river". As part of the Northern Silk Road, running northwest from the western section of the Ordos Loop between Yinchuan and Lanzhou, the Hexi Corridor was the most important trade route in Northwest China. It linked China ''proper'' to the historic Western Regions for traders and military incursions into Central Asia. It is a string of oases along the northern edges of the Qilian Mountains and Altyn-Tagh, with the high and desolate Tibetan Plateau further to the south. To the north are the Longshou, Heli and Mazong Mountains se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhangye
Zhangye (), formerly romanized as Changyeh or known as Kanchow, is a prefecture-level city in central Gansu Province in the People's Republic of China. It borders Inner Mongolia on the north and Qinghai on the south. Its central district is Ganzhou, formerly a city of the Western Xia and one of the most important outposts of western China. Name The city was formerly also known as Ganzhou, named after the sweet waters () of its oasis. An alternative theory states that "Gan" was from the Ganjun Hill () near the city. The name of province came from a contraction of Ganzhou and Suzhou (modern Jiuquan). The name appears in Marco Polo's '' Travels'' under the name Campichu. Zhangye Commandery was established by Western Han in 111 BC, with the seat at the site of modern Wuwei, Gansu. Etymology of Zhangye is unclear. A popular theory interprets the name Zhangye as "Extending Arm", excerpted from a phrase "to extend the arm of the country through to the Western Realm" () document ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evangelizing
In Christianity, evangelism (or witnessing) is the act of preaching the gospel with the intention of sharing the message and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians who specialize in evangelism are often known as evangelists, whether they are in their home communities or living as missionaries in the field, although some Christian traditions refer to such people as ''missionaries'' in either case. Some Christian traditions consider evangelists to be in a leadership position; they may be found preaching to large meetings or in governance roles. In addition, Christian groups who encourage evangelism are sometimes known as evangelistic or ''evangelist''. Etymology The word ''evangelist'' comes from the Koine Greek word (transliterated as ''euangelion'') via Latinised ''evangelium'' as used in the canonical titles of the Four Gospels, authored by (or attributed to) Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John (also known as the Four Evangelists). The Greek word originally meant a reward given to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former Soviet republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, which are colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as the countries all have names ending with the Persian suffix " -stan", meaning "land of". The current geographical location of Central Asia was formerly part of the historic region of Turkistan, also known as Turan. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Chorasmians and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. After expansion by Turkic peoples, Central Asia also became the homeland for the Kazakhs, Uzbeks, Tatars, Turkmen, Kyrgyz, and Uyghurs; Turkic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuguchak
TachengThe official spelling according to (), as the official romanized name, also transliterated from Mongolian as Qoqak, is a county-level city (1994 est. pop. 56,400) and the administrative seat of Tacheng Prefecture, in northern Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang. The city was sometimes called Tarbaghatay or Tarbagatai (Mongolian: 'having marmots') and in European languages as Chuguchak (based on its name in the Mongolian language). The current official Chinese name Tacheng is an abbreviation of "Tarbaghatay City". The current Uyghur name is Qöqäk transliterated from Mongolian. It is located in the Dzungarian Basin, some from the Chinese border with Kazakhstan. For a long time it has been a major center for trade with Central Asia because it is an agricultural hub. Its industries include food processing, textiles, and utilities. History In the mid-19th century, Chuguchak was considered the most important commercial center of Western China after Ghulja (Yining), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.png)