|
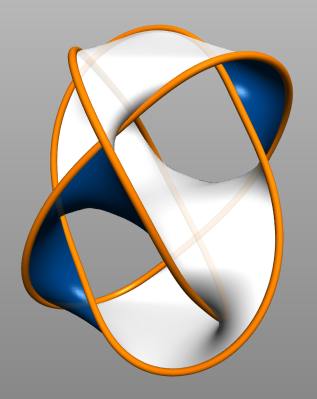
Fox–Artin Arc
In geometric topology, a wild arc is an embedding of the unit interval into 3-dimensional space not equivalent to the usual one in the sense that there does not exist an ambient isotopy taking the arc to a straight line segment. found the first example of a wild arc. found another example, called the Fox-Artin arc, whose complement is not simply connected. Fox-Artin arcs Two very similar wild arcs appear in the article. Example 1.1 (page 981) is most generally referred to as the Fox-Artin wild arc. The crossings have the regular sequence over/over/under/over/under/under when following the curve from left to right. The left end-point 0 of the closed unit interval ,1/math> is mapped by the arc to the left limit point of the curve, and 1 is mapped to the right limit point. The range of the arc lies in the Euclidean space \mathbb^3 or the 3-sphere S^3. Fox-Artin arc variant Example 1.1* has the crossing sequence over/under/over/under/over/under. According to , pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Mathematics
The ''Annals of Mathematics'' is a mathematical journal published every two months by Princeton University and the Institute for Advanced Study. History The journal was established as ''The Analyst'' in 1874 and with Joel E. Hendricks as the founding editor-in-chief. It was "intended to afford a medium for the presentation and analysis of any and all questions of interest or importance in pure and applied Mathematics, embracing especially all new and interesting discoveries in theoretical and practical astronomy, mechanical philosophy, and engineering". It was published in Des Moines, Iowa, and was the earliest American mathematics journal to be published continuously for more than a year or two. This incarnation of the journal ceased publication after its tenth year, in 1883, giving as an explanation Hendricks' declining health, but Hendricks made arrangements to have it taken over by new management, and it was continued from March 1884 as the ''Annals of Mathematics''. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prentice Hall
Prentice Hall was a major American publishing#Textbook_publishing, educational publisher. It published print and digital content for the 6–12 and higher-education market. It was an independent company throughout the bulk of the twentieth century. In its last few years it was owned by, then absorbed into, Savvas Learning Company. In the Web era, it distributed its technical titles through the Safari Books Online e-reference service for some years. History On October 13, 1913, law professor Charles Gerstenberg and his student Richard Ettinger founded Prentice Hall. Gerstenberg and Ettinger took their mothers' maiden names, Prentice and Hall, to name their new company. At the time the name was usually styled as Prentice-Hall (as seen for example on many title pages), per an orthographic norm for Dash#Relationships and connections, coordinate elements within such compounds (compare also ''McGraw-Hill'' with later styling as ''McGraw Hill''). Prentice-Hall became known as a publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Horned Sphere
The Alexander horned sphere is a pathological object in topology discovered by . It is a particular topological embedding of a two-dimensional sphere in three-dimensional space. Together with its inside, it is a topological 3-ball, the Alexander horned ball, and so is simply connected; i.e., every loop can be shrunk to a point while staying inside. However, the exterior is ''not'' simply connected, unlike the exterior of the usual round sphere. Construction The Alexander horned sphere is the particular (topological) embedding of a sphere in 3-dimensional Euclidean space obtained by the following construction, starting with a standard torus:. #Remove a radial slice of the torus. #Connect a standard punctured torus to each side of the cut, interlinked with the torus on the other side. #Repeat steps 1–2 on the two tori just added ''ad infinitum''. By considering only the points of the tori that are not removed at some stage, an embedding of the sphere with a Cantor set remov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Knot
In the mathematical theory of knots, a knot is tame if it can be "thickened", that is, if there exists an extension to an embedding of the solid torus S^1\times D^2 into the 3-sphere. A knot is tame if and only if it can be represented as a finite closed polygonal chain. In knot theory and 3-manifold theory, often the adjective "tame" is omitted. Smooth knots, for example, are always tame. Knots that are not tame are called wild and can have pathological behavior. Every closed curve containing a wild arc is a wild knot. It has been conjectured that every wild knot has infinitely many quadrisecants. As well as their mathematical study, wild knots have also been studied for their potential for decorative purposes in Celtic-style ornamental knotwork. See also * Wild arc In geometric topology, a wild arc is an embedding of the unit interval into 3-dimensional space not equivalent to the usual one in the sense that there does not exist an ambient isotopy taking the arc to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knitting
Knitting is a method for production of textile Knitted fabric, fabrics by interlacing yarn loops with loops of the same or other yarns. It is used to create many types of garments. Knitting may be done Hand knitting, by hand or Knitting machine, by machine. Knitting creates Stitch (textile arts), stitches: loops of yarn in a row; they can be either on straight flat needles or in ''the round'' on needles with (often times plastic) tubes connected to both ends of the Knitting needle, needles. There are usually many ''active stitches'' on the knitting needle at one time. Knitted fabric consists of a number of consecutive rows of connected loops that intermesh with the next and previous rows. As each row is formed, each newly created loop is pulled through one or more loops from the prior row and placed on the ''gaining needle so'' that the loops from the prior row can be pulled off the other needle without unraveling. Differences in yarn (varying in fibre type, Yarn weight, ''w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Stitch
Chain stitch is a sewing and embroidery technique in which a series of looped stitches form a chain-like pattern. Chain stitch is an ancient craft – examples of surviving Chinese chain stitch embroidery worked in silk thread have been dated to the Warring States period (5th – 3rd century BC). Handmade chain stitch embroidery does not require that the needle pass through more than one layer of fabric. For this reason the stitch is an effective surface embellishment near seams on finished fabric. Because chain stitches can form flowing, curved lines, they are used in many surface embroidery styles that mimic "drawing" in thread. Chain stitches are also used in making tambour lace, needlelace, macramé and crochet. In Azerbaijan, in the Sheki region, this ancient type of needlework is called ''tekeldus''. History The earliest archaeological evidence of chain stitch embroidery dates from 1100 BC in China. Excavated from royal tombs, the embroidery was made using thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-sphere
In mathematics, a hypersphere or 3-sphere is a 4-dimensional analogue of a sphere, and is the 3-dimensional n-sphere, ''n''-sphere. In 4-dimensional Euclidean space, it is the set of points equidistant from a fixed central point. The interior of a 3-sphere is a 4-ball. It is called a 3-sphere because topologically, the surface itself is 3-dimensional, even though it is curved into the 4th dimension. For example, when traveling on a 3-sphere, you can go north and south, east and west, or along a 3rd set of cardinal directions. This means that a 3-sphere is an example of a 3-manifold. Definition In coordinates, a 3-sphere with center and radius is the set of all points in real, Four-dimensional space, 4-dimensional space () such that :\sum_^3(x_i - C_i)^2 = ( x_0 - C_0 )^2 + ( x_1 - C_1 )^2 + ( x_2 - C_2 )^2+ ( x_3 - C_3 )^2 = r^2. The 3-sphere centered at the origin with radius 1 is called the unit 3-sphere and is usually denoted : :S^3 = \left\. It is often convenient to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Topology
In mathematics, geometric topology is the study of manifolds and Map (mathematics)#Maps as functions, maps between them, particularly embeddings of one manifold into another. History Geometric topology as an area distinct from algebraic topology may be said to have originated in the 1935 classification of lens spaces by Reidemeister torsion, which required distinguishing spaces that are homotopy equivalent but not homeomorphic. This was the origin of simple homotopy, ''simple'' homotopy theory. The use of the term geometric topology to describe these seems to have originated rather recently. Differences between low-dimensional and high-dimensional topology Manifolds differ radically in behavior in high and low dimension. High-dimensional topology refers to manifolds of dimension 5 and above, or in relative terms, embeddings in codimension 3 and above. Low-dimensional topology is concerned with questions in dimensions up to 4, or embeddings in codimension up to 2. Dimensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Space
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space. Originally, in Euclid's ''Elements'', it was the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics there are ''Euclidean spaces'' of any positive integer dimension ''n'', which are called Euclidean ''n''-spaces when one wants to specify their dimension. For ''n'' equal to one or two, they are commonly called respectively Euclidean lines and Euclidean planes. The qualifier "Euclidean" is used to distinguish Euclidean spaces from other spaces that were later considered in physics and modern mathematics. Ancient Greek geometers introduced Euclidean space for modeling the physical space. Their work was collected by the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid in his ''Elements'', with the great innovation of '' proving'' all properties of the space as theorems, by starting from a few fundamental properties, called '' postulates'', which either were considered as evid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |