|
Fourier Transform Spectroscopy
Fourier-transform spectroscopy (FTS) is a measurement technique whereby Spectrum (physics), spectra are collected based on measurements of the coherence (physics), coherence of a Radiation, radiative source, using time-domain or space-domain measurements of the radiation, electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic or not. It can be applied to a variety of types of ''spectroscopy'' including optical spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy (Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, FTIR, FT-NIRS), Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI), mass spectrometry and electron spin resonance spectroscopy. There are several methods for measuring the temporal coherence of the light (see: Optical autocorrelation#Field autocorrelation, field-autocorrelation), including the continuous-wave and the pulsed Fourier-transform spectrometer or Fourier-transform spectrograph. The term "Fourier-transform spectroscopy" refl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Spectrum (physics)
In the physical sciences, the term ''spectrum'' was introduced first into optics by Isaac Newton in the 17th century, referring to the range of colors observed when white light was dispersed through a prism. Soon the term referred to a plot of light intensity or power as a function of frequency or wavelength, also known as a ''spectral density plot''. Later it expanded to apply to other waves, such as sound waves and sea waves that could also be measured as a function of frequency (e.g., noise spectrum, sea wave spectrum). It has also been expanded to more abstract "signals", whose power spectrum can be analyzed and processed. The term now applies to any signal that can be measured or decomposed along a continuous variable, such as energy in electron spectroscopy or mass-to-charge ratio in mass spectrometry. Spectrum is also used to refer to a graphical representation of the signal as a function of the dependent variable. Etymology Electromagnetic spectrum Electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Wiener–Khinchin Theorem
In applied mathematics, the Wiener–Khinchin theorem or Wiener–Khintchine theorem, also known as the Wiener–Khinchin–Einstein theorem or the Khinchin–Kolmogorov theorem, states that the autocorrelation function of a wide-sense-stationary random process has a spectral decomposition given by the power spectral density of that process. History Norbert Wiener proved this theorem for the case of a deterministic function in 1930; Aleksandr Khinchin later formulated an analogous result for stationary stochastic processes and published that probabilistic analogue in 1934. Albert Einstein explained, without proofs, the idea in a brief two-page memo in 1914. Continuous-time process For continuous time, the Wiener–Khinchin theorem says that if x is a wide-sense-stationary random process whose autocorrelation function (sometimes called autocovariance) defined in terms of statistical expected value r_(\tau) = \mathbb\big (t)^* x(t - \tau)\big< \infty, \quad \forall \tau,t \i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Electron Paramagnetic Resonance
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy is a method for studying materials that have unpaired electrons. The basic concepts of EPR are analogous to those of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), but the spins excited are those of the electrons instead of the atomic nuclei. EPR spectroscopy is particularly useful for studying metal complexes and organic radicals. EPR was first observed in Kazan State University by Soviet physicist Yevgeny Zavoisky in 1944, and was developed independently at the same time by Brebis Bleaney at the University of Oxford. Theory Origin of an EPR signal Every electron has a magnetic moment and spin quantum number s = \tfrac , with magnetic components m_\mathrm = + \tfrac or m_\mathrm = - \tfrac . In the presence of an external magnetic field with strength B_\mathrm , the electron's magnetic moment aligns itself either antiparallel ( m_\mathrm = - \tfrac ) or parallel ( m_\mathrm = + \tfrac ) to the fie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Sine And Cosine Transforms
In mathematics, the Fourier sine and cosine transforms are integral equations that decompose arbitrary functions into a sum of sine waves representing the Even and odd functions#Even–odd decomposition, odd component of the function plus cosine waves representing the even component of the function. The modern Fourier transform concisely Sine and cosine transforms#Relation with complex exponentials, contains both the sine and cosine transforms. Since the sine and cosine transforms use sine and cosine waves instead of Euler's formula#Relationship to trigonometry, complex exponentials and don't require complex numbers or negative frequency, they more closely correspond to Joseph Fourier's original transform equations and are still preferred in some signal processing and statistics applications and may be better suited as an introduction to Fourier analysis. Definition The Fourier sine transform of f(t) is: If t means time, then \xi is frequency in cycles per unit time, but in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Wavenumber
In the physical sciences, the wavenumber (or wave number), also known as repetency, is the spatial frequency of a wave. Ordinary wavenumber is defined as the number of wave cycles divided by length; it is a physical quantity with dimension of reciprocal length, expressed in SI units of cycles per metre or reciprocal metre (m−1). Angular wavenumber, defined as the wave phase divided by time, is a quantity with dimension of angle per length and SI units of radians per metre. They are analogous to temporal frequency, respectively the '' ordinary frequency'', defined as the number of wave cycles divided by time (in cycles per second or reciprocal seconds), and the ''angular frequency'', defined as the phase angle divided by time (in radians per second). In multidimensional systems, the wavenumber is the magnitude of the '' wave vector''. The space of wave vectors is called ''reciprocal space''. Wave numbers and wave vectors play an essential role in optics and the physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
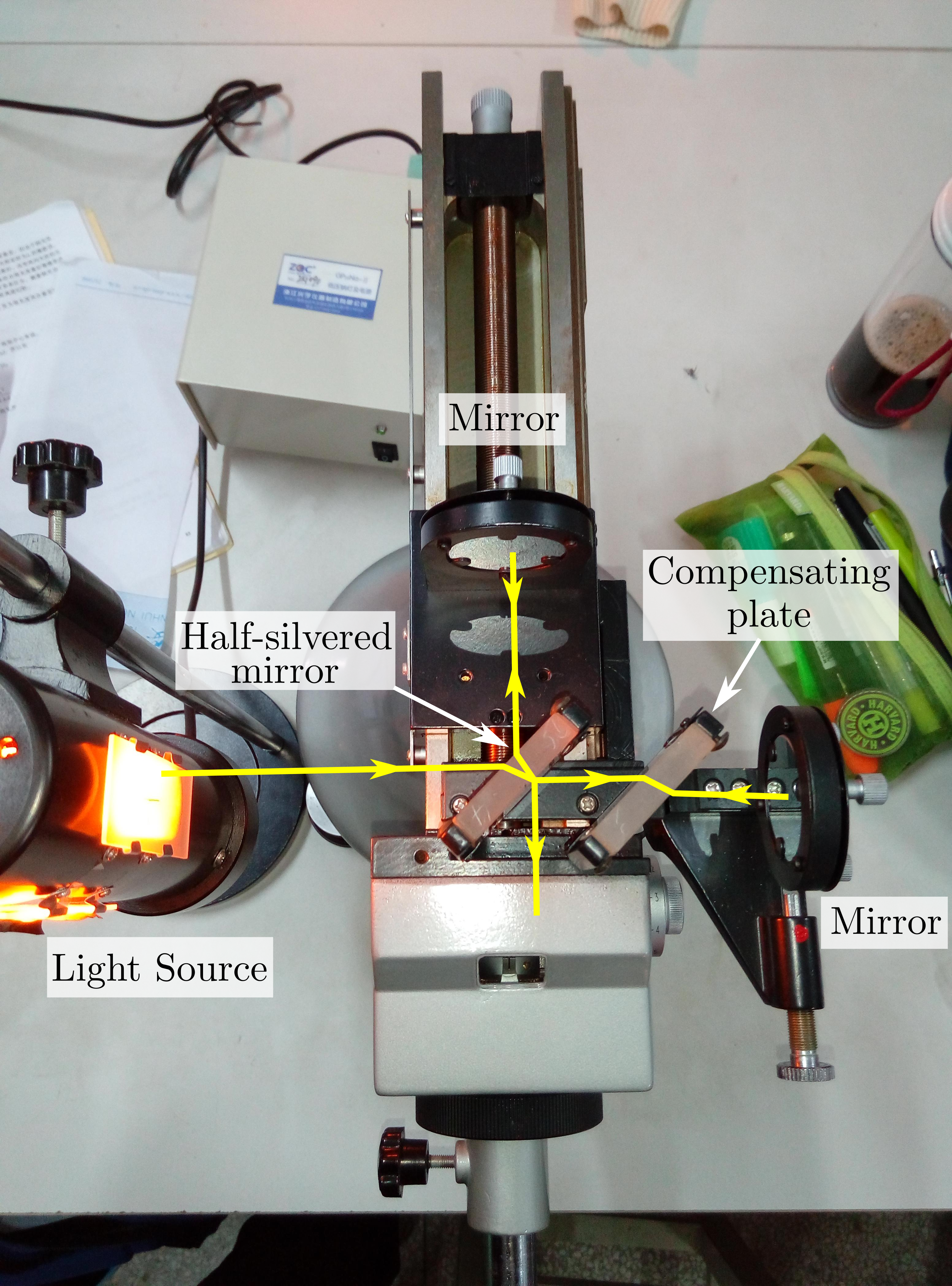 |
Michelson Interferometer
The Michelson interferometer is a common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by the American physicist Albert Abraham Michelson in 1887. Using a beam splitter, a light source is split into two arms. Each of those light beams is reflected back toward the beamsplitter which then combines their amplitudes using the superposition principle. The resulting interference pattern that is not directed back toward the source is typically directed to some type of photoelectric detector or camera. For different applications of the interferometer, the two light paths can be with different lengths or incorporate optical elements or even materials under test. The Michelson interferometer is employed in many scientific experiments and became well known for its use by Michelson and Edward Morley in the famous Michelson–Morley experiment (1887) in a configuration which would have detected the Earth's motion through the supposed luminiferous aether that most physicists a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Michelson–Morley Experiment
The Michelson–Morley experiment was an attempt to measure the motion of the Earth relative to the luminiferous aether, a supposed medium permeating space that was thought to be the carrier of light waves. The experiment was performed between April and July 1887 by American physicists Albert A. Michelson and Edward W. Morley at what is now Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio, and published in November of the same year. The experiment compared the speed of light in perpendicular directions in an attempt to detect the relative motion of matter, including their laboratory, through the luminiferous aether, or "aether wind" as it was sometimes called. The result was negative, in that Michelson and Morley found no significant difference between the speed of light in the direction of movement through the presumed aether, and the speed at right angles. This result is generally considered to be the first strong evidence against some aether theories, as well as initiating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Fourier Transform Spectrometer
Fourier-transform spectroscopy (FTS) is a measurement technique whereby spectra are collected based on measurements of the coherence of a radiative source, using time-domain or space-domain measurements of the radiation, electromagnetic or not. It can be applied to a variety of types of ''spectroscopy'' including optical spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy ( FTIR, FT-NIRS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI), mass spectrometry and electron spin resonance spectroscopy. There are several methods for measuring the temporal coherence of the light (see: field-autocorrelation), including the continuous-wave and the pulsed Fourier-transform spectrometer or Fourier-transform spectrograph. The term "Fourier-transform spectroscopy" reflects the fact that in all these techniques, a Fourier transform is required to turn the raw data into the actual spectrum, and in many of the cases in optics involving interferometers, is based on the Wie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Absorption Spectroscopy
Absorption spectroscopy is spectroscopy that involves techniques that measure the absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this variation is the absorption spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is performed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is employed as an analytical chemistry tool to determine the presence of a particular substance in a sample and, in many cases, to quantify the amount of the substance present. Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy are particularly common in analytical applications. Absorption spectroscopy is also employed in studies of molecular and atomic physics, astronomical spectroscopy and remote sensing. There is a wide range of experimental approaches for measuring absorption spectra. The most commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Wave Interference
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two coherent waves are combined by adding their intensities or displacements with due consideration for their phase difference. The resultant wave may have greater amplitude (constructive interference) or lower amplitude (destructive interference) if the two waves are in phase or out of phase, respectively. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves as well as in loudspeakers as electrical waves. Etymology The word ''interference'' is derived from the Latin words ''inter'' which means "between" and ''fere'' which means "hit or strike", and was used in the context of wave superposition by Thomas Young in 1801. Mechanisms The principle of superposition of waves states that when two or more propagating waves of the same type are incident on the same point, the resultant amplitude at that point is equal to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |