|
Foula Airfield
Foula Airfield is an airfield located on the remote island of Foula, part of the Shetland Islands in the north of Scotland. History The airstrip opened in the 1970s and is run by the Foula Airstrip Trust, Scottish charity number SC021728. Foula is also served by a ferry service running three times a week but many tourists prefer the short flight to the 135 min crossing. Also, the ferry is based on Foula, so a day trip to the island is possible only by air. The flights are used to transport essentials, such as medical prescriptions, to the island, which has a population of 38. The airfield also provides the island's only public toilet and telephone. Airline and destination Foula is served by a PSO service from Tingwall Airport run by Airtask Group and funded by Shetland Islands Council The Shetland Islands Council is the local authority for the Shetland Islands, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. It was established in 1975 by the Local Government (Scotland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foula
Foula (), located in the Shetland archipelago of Scotland, is one of the United Kingdom's most remote permanently inhabited islands. The liner RMS ''Oceanic'' was wrecked on the Shaalds of Foula in 1914. Foula was the location for the film '' The Edge of the World'' (1937). Toponym The name "Foula" comes from the Old Norse ''Fugley'' 'bird island'. On some early Modern maps (such as Willem Blaeu's 1654 map of Orkney and Shetland), it is called Fule or Thule. The former – pronounced "foo-lay"– is just an alternative spelling of Foula. The latter is due to ancient sources – notably Tacitus' ''Agricola'' – often locating the mythical land of Thule in the Shetland Islands region, and the phonetic closeness of the island's name. However, the Ancient Norse name post-dates the Thule narrative and is not connected to it. Geography Foula lies in the Atlantic Ocean, west of Walls on Mainland, Shetland. It was part of Walls civil parish and now is in the parish of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shetland Islands
Shetland (until 1975 spelled Zetland), also called the Shetland Islands, is an archipelago in Scotland Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ... lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands, and Norway, marking the northernmost region of the United Kingdom. The islands lie about to the northeast of Orkney, from mainland Scotland and west of Norway. They form part of the border between the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the North Sea to the east. The island's area is and the population totalled in . The islands comprise the Shetland (Scottish Parliament constituency), Shetland constituency of the Scottish Parliament. The islands' administrative centre, largest settlement and only burgh is Lerwick, which has been the capital of Shetland since 1708, before which time the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
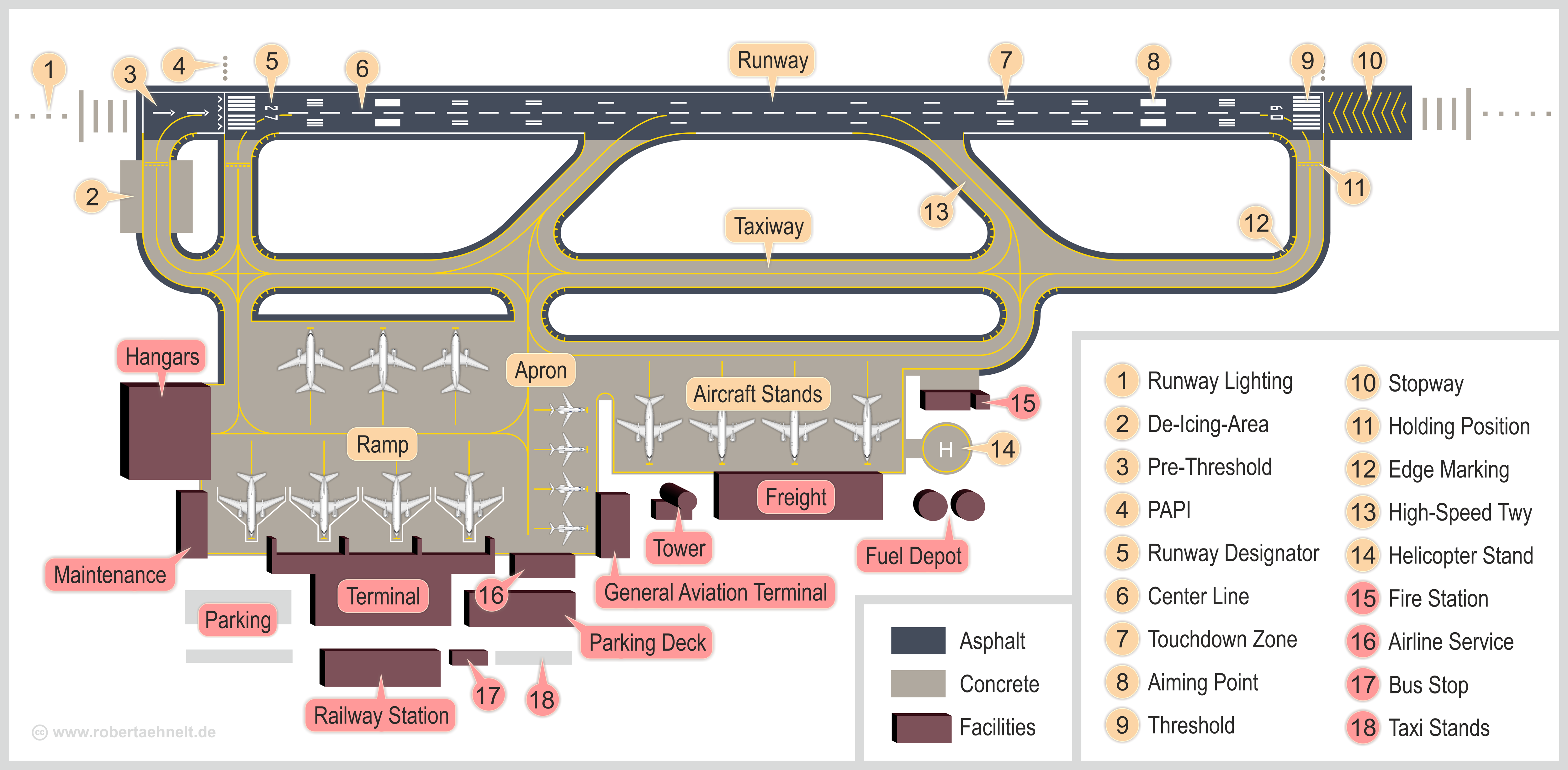
Airfield
An aerodrome, airfield, or airstrip is a location from which aircraft flight operations take place, regardless of whether they involve air cargo, passengers, or neither, and regardless of whether it is for public or private use. Aerodromes include small general aviation airfields, large commercial airports, and military air bases. The term ''airport'' may imply a certain stature (having satisfied certain certification criteria or regulatory requirements) that not all aerodromes may have achieved. That means that all airports are aerodromes, but not all aerodromes are airports. Usage of the term "aerodrome" (or "airfield") remains more common in Commonwealth English, and is conversely almost unknown in American English, where the term "airport" is applied almost exclusively. A water aerodrome is an area of open water used regularly by seaplanes, floatplanes or amphibious aircraft for landing and taking off. In formal terminology, as defined by the International Civil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of The Scottish Charity Regulator
The Scottish Charity Regulator (OSCR; ) is a non-ministerial department of the Scottish Government with responsibility for the regulation of charities in Scotland. OSCR is the independent regulator and registrar for more than 25,000 Scottish charities. OSCR is charged with developing a regulatory framework for Scottish charities, where each charity is clear about its rights and responsibilities. This framework should also foster public confidence in charities. OSCR is directly answerable to the Scottish Parliament. OSCR is based in Dundee. Background In 1981 the Law Society of Scotland announced support for a register through which all charities in Scotland could record their purposes, financial details, and accounts. Under section 6 of the Law Reform (Miscellaneous Provisions) (Scotland) Act 1990, the Lord Advocate was given the power to make inquiries either for general or specific purposes and to obtain various types of information from charities. Following the Scotland Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Service Obligation
In the context of European Union law, a public service obligation or PSO is an obligation imposed on an organisation by legislation or contract to provide a service of general interest within EU territories. PSOs may operate in any field of public service, but postal services, social services, Energy law, energy, Transport law, transport and Banking law, banking are specific sectors where the concept is relevant. Transport law In EU transport law, a PSO is an arrangement by which a governing body or other authority offers subsidy, subsidies in an auction, whereby the winning company will be obliged to operate a specified service of public transport for a specified period of time in return for the subsidy. This usually leads to the winning bidder having a monopoly on the route, as competing services would not be viable without subsidies. PSOs are aimed at routes which are unprofitable in a free market, but where there is a socially desirable advantage to transport being available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tingwall Airport
Tingwall Airport , also known as Lerwick/Tingwall Airport, is located in the Tingwall valley, near the village of Gott, northwest of Lerwick in Mainland, Shetland, Scotland. Although it is the nearest airport to Lerwick, it is not Shetland's main airport, which is Sumburgh at the south end of the main island. However, Tingwall is Shetland's inter-island flight hub. Tingwall Aerodrome has a CAA Ordinary Licence (Number P614) that allows flights for the public transport of passengers or for flying instruction as authorised by the licensee (Shetland Islands Council). It was opened in 1976. Airline and destinations Accidents and incidents In 1996, an air ambulance lost altitude while turning to final approach for Runway 02 in strong and gusting winds, crashing 1.5 km short of the runway. The pilot was killed, and the doctor and nurse in the passenger cabin were injured. (Their patient had already been delivered to Inverness Inverness (; ; from the , meaning "Mouth o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shetland Islands Council
The Shetland Islands Council is the local authority for the Shetland Islands, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. It was established in 1975 by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973 and was largely unaffected by the Scottish local government changes of 1996. It provides services in the areas of Environmental Health, Roads, Social Work, Community Development, Organisational Development, Economic Development, Building Standards, Trading Standards, Housing, Waste, Education, Burial Grounds, Port and Harbours and others. The council collects Council Tax. The Fire Service is part of the Highlands and Islands division of the Scottish Fire and Rescue Service. History Shetland had been administered by Commissioners of Supply from 1667 and then by Zetland County Council from 1890 to 1975. The county council was abolished in 1975 and replaced by the Shetland Islands Council, which also took over the functions previously exercised by Shetland's lower-tier authorities, being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britten Norman Islander
The Britten-Norman BN-2 Islander is a British light utility aircraft and regional airliner designed and originally manufactured by Britten-Norman of the United Kingdom. Still in production, the Islander is one of the best-selling commercial aircraft types produced in Europe. Although designed in the 1960s, over 750 are still in service with commercial operators around the world. The aircraft is a light transport with over 30 military aviation operators around the world. Initial aircraft were manufactured at Britten-Norman's factory in Bembridge, Isle of Wight, UK. After Fairey Aviation acquired the Britten-Norman company, its Islanders and Trislander aircraft were built in Romania, then shipped to Avions Fairey in Belgium for finishing before being flown to the UK for flight certification. The Islander has been in production for more than 50 years. In September 2023, it was announced that production of the Islander has returned to the UK, after fifty-five years of manufacturing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directflight
Directflight Limited, trading as Airtask Group, is a British airline based in Cranfield, Bedfordshire, England and operating flights mainly in the Shetland Islands Shetland (until 1975 spelled Zetland), also called the Shetland Islands, is an archipelago in Scotland Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the Uni .... It is a subsidiary of Airtask Group Ltd. Directflight (Scotland) Limited was dissolved on 12 July 2013 and merged into Directflight Limited. Destinations Scotland Shetland Island Inter Island Air Services: Fleet As of July 2017 the Shetland Island Inter Island Air Services fleet consists of the following aircraft: As of July 2017 the Directflight fleet consists of the following aircraft: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airports In Shetland
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. They usually consist of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Airport operations are extremely complex, with a complicated system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |