|
Foscari
The House of Foscari () was an ancient Venice, Venetian patrician family, which reached its peak in the 14th–15th centuries, culminating in the Doge of Venice, dogeship of Francesco Foscari (1423–1457). History According to family tradition, they originated from the area of Mestre, and had settled in Venice proper in the late 10th century, and the first members of the family are attested in written sources in the early 11th century. The Foscari were not very important during the subsequent centuries, but in the 13th century, after the Fourth Crusade, they became rulers of the Greek island of Lemnos, along with the Navagero family, until 1276. The family's real rise to prominence began in the early 14th century, when they managed to be included among the patrician families that held the hereditary right to be members of the Great Council of Venice following the so-called "''Serrata del Maggior Consiglio, Serrata''" ("Closing"). As membership in the Great Council was a prereq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Foscari
Francesco Foscari (19 June 1373 – 1 November 1457) was the 65th Doge of the Republic of Venice from 1423 to 1457. His reign, the longest of all Doges in Venetian history, lasted 34 years, 6 months and 8 days, and coincided with the inception of the Italian Renaissance. Biography Francesco Foscari was born in 1373, as the oldest son of Nicolò Foscari and his wife Cateruzia Michiel. The Foscari family had been of only moderate importance, but had managed to become one of the few noble families that secured a hereditary place in the Great Council of Venice after the so-called '' Serrata'' ("Closing") of the Great Council, and had begun to rise in prominence throughout the 14th century. Francesco's ancestors began holding high public office, and his father Nicolò even became a member of the powerful Council of Ten. Francesco served the Republic of Venice in numerous official capacities—as ambassador, president of the Council of Forty, member of the Council of Ten, inquis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paolo Foscari
Paolo Foscari was a Venetian noble and churchman, who rose to become Bishop of Castello in 1367–1375, and Latin Archbishop of Patras from 1375 until his death in 1393/4. In the latter capacity he played a leading role in the affairs of the Principality of Achaea. Biography Early life and career He was a son of Giovanni Foscari, a member of the noble Foscari family. Nothing is known about his early life, except that he studied civil and canon law in the University of Padua, where he may also have taught as a professor for a time. He chose an ecclesiastical career, and on 19 August 1365 the Venetian Senate recommended him for the position of Latin Archbishop of Patras in the Morea in southern Greece. The Archbishop of Patras was a powerful figure in Latin Greece: he was not only the pre-eminent Catholic prelate of the Morea, but also, having acquired the secular barony of Patras in and added its 24 fiefs to the Archbishopric's eight, the most important territorial feudatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
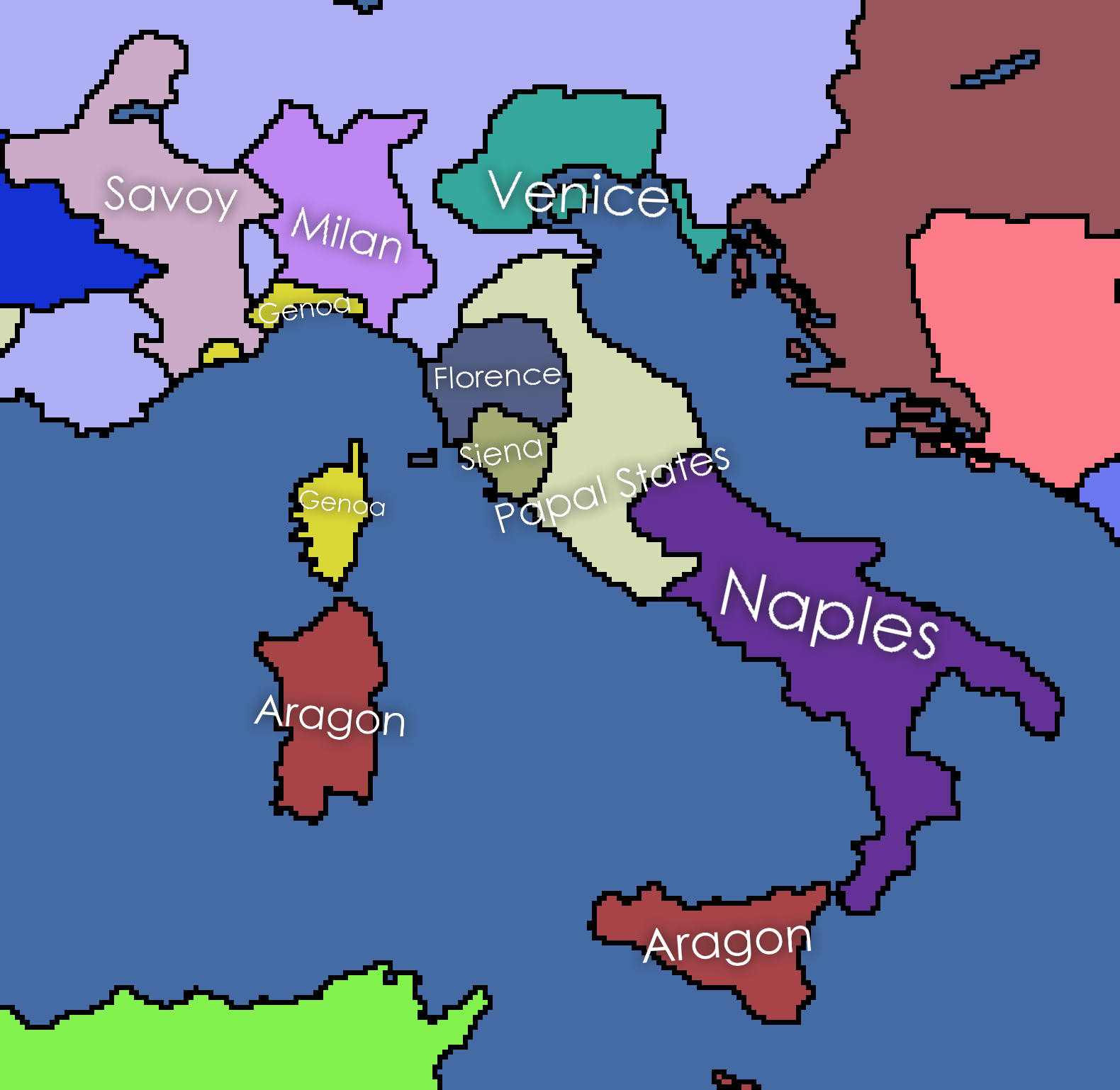
Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are linked by 438 bridges. The islands are in the shallow Venetian Lagoon, an enclosed bay lying between the mouths of the Po River, Po and the Piave River, Piave rivers (more exactly between the Brenta (river), Brenta and the Sile (river), Sile). As of 2025, 249,466 people resided in greater Venice or the Comune of Venice, of whom about 51,000 live in the historical island city of Venice (''centro storico'') and the rest on the mainland (''terraferma''). Together with the cities of Padua, Italy, Padua and Treviso, Italy, Treviso, Venice is included in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area (PATREVE), which is considered a statistical metropolitan area, with a total population of 2.6 million. The name is derived from the ancient Adr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
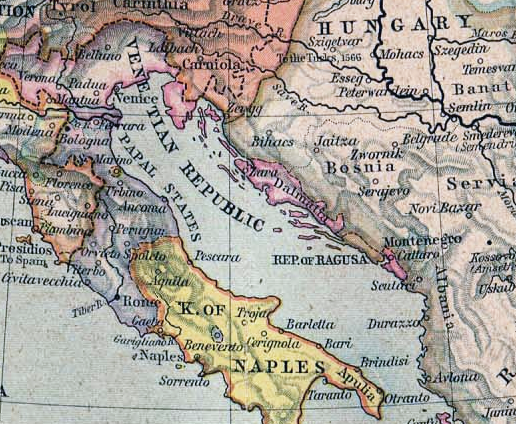
Republic Of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 by Paolo Lucio Anafesto, over the course of its History of the Republic of Venice, 1,100 years of history it established itself as one of the major European commercial and naval powers. Initially extended in the ''Dogado'' area (a territory currently comparable to the Metropolitan City of Venice), during its history it annexed a large part of Northeast Italy, Istria, Dalmatia, the coasts of present-day Montenegro and Albania as well as numerous islands in the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and eastern Ionian Sea, Ionian seas. At the height of its expansion, between the 13th and 16th centuries, it also governed Crete, Cyprus, the Peloponnese, a number of List of islands of Greece, Greek islands, as well as several cities and ports in the eastern Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wars In Lombardy
The Wars in Lombardy were a series of conflicts between the Republic of Venice and the Duchy of Milan and their respective allies, fought in four campaigns in a struggle for hegemony in Northern Italy that ravaged the economy of Lombardy. They lasted from 1423 until the signing of the Treaty of Lodi in 1454. During their course, the political structure of Italy was transformed: out of a competitive congeries of communes and city-states emerged the five major Italian territorial powers that would make up the map of Italy for the remainder of the 15th century and the beginning of the Italian Wars at the turn of the 16th century. They were Venice, Milan, Florence, the Papal States and Naples. Important cultural centers of Tuscany and Northern Italy—Siena, Pisa, Urbino, Mantua, Ferrara—became politically marginalized. The wars, which were both a result and cause of Venetian involvement in the power politics of mainland Italy, found Venetian territory extended to the ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doge Of Venice
The Doge of Venice ( ) – in Italian, was the doge or highest role of authority within the Republic of Venice (697–1797). The word derives from the Latin , meaning 'leader', and Venetian Italian dialect for 'duke', highest official of the republic of Venice for over 1,000 years. In standard Italian, the cognate is '' duce'' ( , ), one of National Fascist Party leader Benito Mussolini's titles. Originally referring to any military leader, it became in the Late Roman Empire the title for a leader of an expeditionary force formed by detachments () from the frontier army (), separate from, but subject to, the governor of a province, authorized to conduct operations beyond provincial boundaries. The Doge of Venice acted as both the head of state and head of the Venetian oligarchy. Doges were elected for life through a complex voting process. History The office and title of doge, in relation to Venetia (region) and Venice (city), emerged from older ducal offices (lat. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Zara
The Archdiocese of Zadar (; ) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic church in Croatia."Archdiocese of Zadar" ''GCatholic.org.'' Gabriel Chow. Retrieved February 29, 2016 The diocese was established in the 3rd century AD and was made an archdiocese by the in 1154. Today, it is not part of any of Croatia, rather it is the only Croatian archdiocese directly subject to the |
Latin Archbishop Of Patras
The Latin Archbishopric of Patras was the see of Patras in the period in which its incumbents belonged to the Latin Church. This period began in 1205 with the installation in the see of a Catholic archbishop following the Fourth Crusade. The Latin archbishop was the senior-most of the seven ecclesiastic barons of the Principality of Achaea, which comprised the entire Peloponnese. From the late 13th century, the archbishops also purchased the secular Barony of Patras from its holders, becoming the most important vassals of the entire principality. It had five suffragans, Andravida, Amyclae, Modon, Coron, and Cephalonia-Zante. The archbishopric survived as a Latin residential see until 1430, when the city of Patras fell to the Byzantine Greeks of the Despotate of the Morea. From 1475 on, Latin archbishops continued to be appointed, but for them the bishopric was only a titular see. It continues to be included in the Catholic Church's list of such sees, but since the Second Vat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terraferma
The () or () was the hinterland territories of the Republic of Venice beyond the Adriatic coast in Northeast Italy. They were one of the three subdivisions of the Republic's possessions, the other two being the original '' Dogado'' (Duchy) and the '' Stato da Màr'' (maritime territories). Geography At its greatest extent, it included the present-day Italian regions of Veneto, Western and Central Friuli-Venezia Giulia and the eastern parts of Lombardy (i.e. the present-day Bergamo and Brescia provinces) up to the Adda River, where it bordered on the Imperial Duchy of Milan. In the south the lower Po River (Polesine) formed the border with the Papal States. The ''Terraferma'' comprised the western and central parts of the historic Friuli region, except for the easternmost part along the Isonzo River, which was held by the Imperial counts of Gorizia. In the north, the Carnic and Julian Alps marked the border with the Inner Austrian duchies of Carinthia and Carniola. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of The House Of Foscari
A coat is typically an outer garment for the upper body, worn by any gender for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front, and closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners (AKA velcro), toggles, a belt, or a combination of some of these. Other possible features include collars, shoulder straps, and hoods. Etymology ''Coat'' is one of the earliest clothing category words in English, attested as far back as the early Middle Ages. (''See also'' Clothing terminology.) The Oxford English Dictionary traces ''coat'' in its modern meaning to , when it was written ''cote'' or ''cotte''. The word coat stems from Old French and then -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... and then Latin ''cottus.'' It originates from the Proto-Indo-European language">Proto-Indo-European word for woolen clothes. An early use of ''coat'' in English is Mail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franzi Foscari
The Valigeria Franzi was an Italian manufacturer of leather bags and luggage founded in Milan in 1864 by Rocco Franzi. By the early 20th century, it was a supplier to royalty and nobility. It was listed on the Milan stock exchange from 1905 to 1909. Guccio Gucci worked for the company until he set up Gucci in 1921. The company mostly used English leather, but also produced some at the Conceria Monzese in Monza, which it owned. This was marketed as "Cuoio Franzi". In 1967 Franzi manufactured a suitcase, "Partner", designed by Cini Boeri and made from two half-shells of aluminium and ABS resin. The company went into liquidation Liquidation is the process in accounting by which a Company (law), company is brought to an end. The assets and property of the business are redistributed. When a firm has been liquidated, it is sometimes referred to as :wikt:wind up#Noun, w ... in 1978, and a new company, Oreste Franzi & Co., was set up. It finally closed in 1998. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niccolò Foscari (died 1412)
Niccolò is an Italian male given name, derived from the Greek Nikolaos meaning "Victor of people" or "People's champion". There are several male variations of the name: Nicolò, Niccolò, Nicolas, and Nicola. The female equivalent is Nicole. The female diminutive Nicoletta is used although seldom. Rarely, the letter "C" can be followed by a "H" (ex. Nicholas). As the letter "K" is not part of the Italian alphabet, versions where "C" is replaced by "K" are even rarer. People with the name include: Given name In literature: * Niccolò Ammaniti (born 1966), Italian writer * Niccolò Machiavelli (1469–1527), Italian political philosopher, musician, poet, and romantic comedic playwright * Niccolò Massa (1485–1569), Italian anatomist who wrote an early anatomy text ''Anatomiae Libri Introductorius'' in 1536 In music: * Niccolò Castiglioni (1932–1996), Italian composer and pianist * Niccolò da Perugia, 14th-century Italian composer of the trecento * Niccolò Jommelli ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |