|
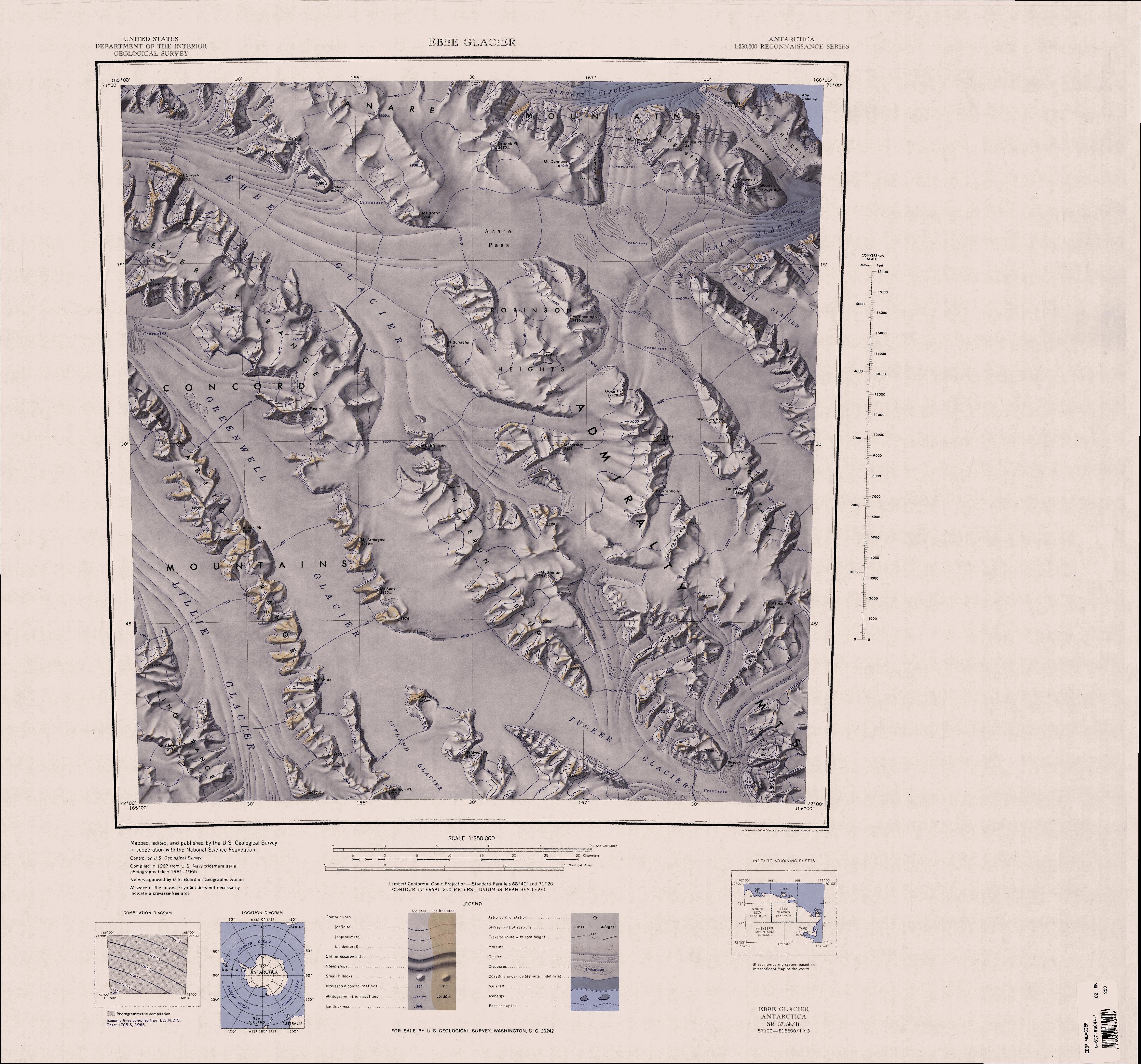
Fortenberry Glacier
Tapsell Foreland () is a borad, mostly snow-covered foreland jutting into the sea between Yule Bay and Smith Inlet, northern Victoria Land. Much of the central portion of this feature rises above . Exploration and naming The name Tapsell, applied by New Zealand Antarctic Place-Names Committee (NZ-APC) in 1969, is the surname of the Master of the barque ''Brisk'', one of the whaling vessels based on Enderby Settlement at Port Ross, Auckland Islands, 1849–52. In an exploratory voyage in February 1850, Tapsell sailed south to the Balleny Islands and then west along the parallel of 67°S as far as 143°E. No land was sighted. Location Tapsell Foreland extends eastward into the Pacific Ocean to the south of Yule Bay and the Lyall Islands, and to the north of Barnett Glacier, which empties into Smith Inlet. The Kirkby Glacier flows north past its west end. Glaciers rising on the foreland include O'Hara Glacier and Fortenberry Glacier, which flow north, and McElroy Glacier whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), the Pacific Ocean is the largest division of the World Ocean and the hydrosphere and covers approximately 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of the planet's total surface area, larger than its entire land area ().Pacific Ocean . ''Encyclopædia Britannica, Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the Land and water hemispheres, water hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere, as well as the Pole of inaccessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O'Hara Glacier
Yule Bay () is a bay indenting the coast of northern Victoria Land between Cape Hooker and Cape Dayman. An inner (western) portion of the bay is circumscribed by Bates Point and Ackroyd Point. Exploration and name Discovered by Captain James Clark Ross, 1841, who named it for Henry B. Yule, Second Master on . In 2020, a penguin colony was seen at the bay. Location Yule Bay opens into the Pacific Ocean to the south of Davis Ice Piedmont and Missen Ridge. Chapman Glacier flows into the bay from the west. O'Hara Glacier enters from the south. Ackroyd Point to the south and Bates Point at the end of Missen Ridge define the inner entrance of the bay. Cape Hooker and Cape Dayman define the outer entrance. The Lyall Islands are to the east, across the outer entrance. Features Bates Point . Ice-covered point forming the north side of the entrance to Yule Bay. Mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960-63. Name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peninsulas Of The Ross Dependency
A peninsula is a landform that extends from a mainland and is only connected to land on one side. Peninsulas exist on each continent. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula. Etymology The word ''peninsula'' derives , . The word entered English in the 16th century. Definitions A peninsula is generally defined as a piece of land surrounded on most sides by water. A peninsula may be bordered by more than one body of water, and the body of water does not have to be an ocean or a sea. A piece of land on a very tight river bend or one between two rivers is sometimes said to form a peninsula, for example in the New Barbadoes Neck in New Jersey, United States. A peninsula may be connected to the mainland via an isthmus, for example, in the Isthmus of Corinth which connects to the Peloponnese peninsula. Formation and types Peninsulas can be formed from continental drift, glacial erosion, glacial meltwater, glacial deposition, marine sediment, marine transg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Station
McMurdo Station is an American Antarctic research station on the southern tip of Ross Island. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program (USAP), a branch of the National Science Foundation. The station is the largest community in Antarctica, capable of supporting up to 1,500 residents, though the population fluctuates seasonally; during the antarctic night, there are fewer than two hundred people. It serves as one of three year-round United States Antarctic science facilities. Personnel and cargo going to or coming from Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station usually first pass through McMurdo, either by flight or by the McMurdo to South Pole Traverse; it is a hub for activities and science projects in Antarctica. McMurdo, Amundsen-Scott, and Palmer are the three non-seasonal United States stations on the continent, though by the Antarctic Treaty System the bases are not a legal claim (though the right is not forfeited); they are dedicated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horlick Mountains
The Horlick Mountains () are a mountain group in the Transantarctic Mountains of Antarctica, lying eastward of Reedy Glacier and including the Wisconsin Range, Long Hills and Ohio Range. Discovery and naming The mountains were discovered in two observations by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition, 1933–35, one by Kennett L. Rawson from a position in about , at the end of his southeastern flight of November 22, 1934, and another by Quin Blackburn in December 1934, from positions looking up Leverett Glacier and Albanus Glacier. Portions of the Wisconsin Range are recorded in aerial photography obtained by United States Navy Operation Highjump, 1946–47. The entire mountain group was surveyed by USARP parties and was mapped from United States Navy aerial photographs, 1959–64. They were named by Admiral Richard E. Byrd for William Horlick, of the Horlick's Malted Milk Corp., a supporter of the Byrd expedition of 1933–35. Extent File:C85120s1 Ant.Map Wisconsin Range.jpg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molodyozhnaya Station (Antarctica)
Molodyozhnaya (, ''"Youth"'') (also known as "Molodezhnaya") was a Soviet, then Russian research station in East Antarctica at 67°40′S 45°50′E. After being mothballed in 1990, it was reopened in 2006 to operate on a seasonal basis. In Russian, the station is sometimes referred to as the capital of Antarctica. Location Molodyozhnaya Station is located in the Thala Hills, 500–600 meters inland from the coast on the southern shore of Alasheyev Bight in the Cosmonaut Sea, at 42 meters above sea level. The area around the station is composed mostly of rocky ridges separated by snow-covered depressions and lakes. The sea near the station is covered in pack ice for much of the year, out to a distance of as much as 100 km at the end of winter. The rise to the summit of the massive East Antarctic Ice Sheet (Dome A) begins 1.5-2.0 km from the shore. Kheis Glacier is located in 15 km east of the station, and Campbell Glacier is roughly the same distance to the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Clark Ross
Sir James Clark Ross (15 April 1800 – 3 April 1862) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer of both the northern and southern polar regions. In the Arctic, he participated in two expeditions led by his uncle, Sir John Ross, John Ross, and in four led by Sir William Parry, William Edward Parry: in the Antarctic, he led Ross expedition, his own expedition from 1839 to 1843. Biography Early life Ross was born in London, the son of George Ross and nephew of Sir John Ross, John Ross, under whom he entered the Royal Navy on 5 April 1812. Ross was an active participant in the Napoleonic Wars, being present at an action where HMS Briseis (1808), HMS ''Briseis'', commanded by his uncle, captured ''Le Petit Poucet'' (a French privateer) on 9 October 1812. Ross then served successively with his uncle on HMS Acteon (1805), HMS ''Actaeon'' and HMS Driver (1840), HMS ''Driver''. Arctic exploration Ross participated in John's unsuccessful first Arctic voyage in search o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ackroyd Point
Yule Bay () is a bay indenting the coast of northern Victoria Land between Cape Hooker and Cape Dayman. An inner (western) portion of the bay is circumscribed by Bates Point and Ackroyd Point. Exploration and name Discovered by Captain James Clark Ross, 1841, who named it for Henry B. Yule, Second Master on . In 2020, a penguin colony was seen at the bay. Location Yule Bay opens into the Pacific Ocean to the south of Davis Ice Piedmont and Missen Ridge. Chapman Glacier flows into the bay from the west. O'Hara Glacier enters from the south. Ackroyd Point to the south and Bates Point at the end of Missen Ridge define the inner entrance of the bay. Cape Hooker and Cape Dayman define the outer entrance. The Lyall Islands are to the east, across the outer entrance. Features Bates Point . Ice-covered point forming the north side of the entrance to Yule Bay. Mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960-63. Named by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McElroy Glacier
Barnett Glacier () is a large glacier in the Anare Mountains that flows east along the south side of Tapsell Foreland into Smith Inlet, northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Exploration and naming Barnett Glacier was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and from United States Navy air photos, 1960–63. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) after Donald C. Barnett, USGS topographic engineer, a member of USGS Topo East and West, 1962–63, in which the expedition extended geodetic control from the area of Cape Hallett to the Wilson Hills (Topo West) and from the foot of Beardmore Glacier through the Horlick Mountains (Topo East). Location Barnett Glacier rises in the Anare Mountains to the northeast of Drabek Peak, and flows east. It passes Mount Dalmeny, Hedgpeth Heights, the Douglas Gap and Quam Heights to the south. It is fed by McElroy Glacier from Tapsell Foreland Tapsell Foreland () is a borad, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkby Glacier
Kirkby Glacier () is a glacier, in length, that drains the central Anare Mountains of Antarctica and flows northwest to the sea just north of Arthurson Bluff, northern Victoria Land. Name Kirkby Glacier was named by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) for Sydney L. Kirkby, a surveyor on the ANARE '' Thala Dan'' cruise of 1962, led by Phillip Law, which explored the area along this coast. Location The Kirkby Glacier forms in the Anare Mountains to the west of the head of Barnett Glacier. It flows north past Mount Elliot and Richardson Bluff to the east, and Frecker Ridge to the west, which terminates in Mount Gale. The Ludvig Glacier joins it from the west where it flows past Arthurson Bluff. To the south of Missen Ridge the Chapman Glacier flows east from the Kirkby Glacier to Yule Bay. The Kirkby Glacier continues northwest to enter the Pacific Ocean just east of Nielsen Fjord, and west of Davis Ice Piedmont. Features Richardson Bluff . A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |