|
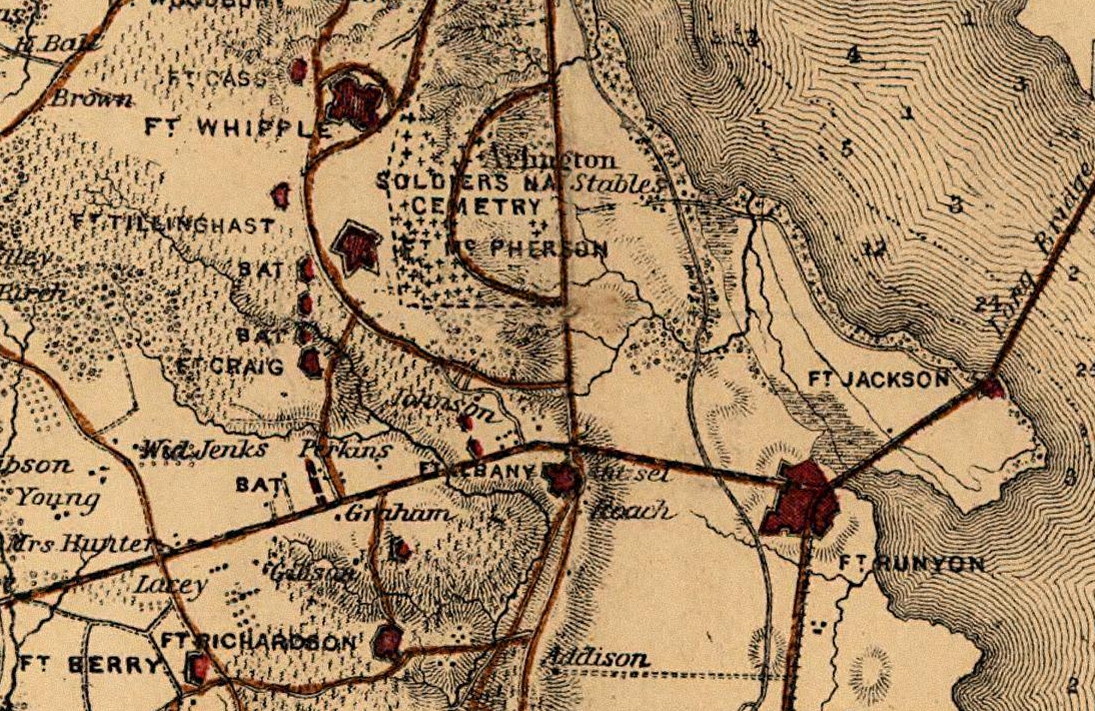
Fort Woodbury
Fort Woodbury was a Lunette (fortification), lunette fortification built in 1861 by the 4th Michigan Infantry Regiment during the early American Civil War. It was part of the larger Arlington Line, an extensive network of fortifications erected in present-day Arlington County, Virginia designed to protect Washington, D.C. from Confederate States of America, Confederate attack. Like the other 3 lunettes in the Arlington Line, Fort Woodbury occupied highlands in Arlington that had a direct line of sight towards Washington DC. Construction and use In 1861, four earthen lunettes, including Forts Cass, Fort Craig (Virginia), Craig, Fort Tillinghast, Tillinghast, and Woodbury, were built in the heights of Arlington overlooking Washington.Rose Jr. p. 15 Colonel Barton S. Alexander, B. S. Alexander and Major Daniel_Phineas_Woodbury, D. P. Woodbury were charged with the design and engineering of all the lunettes. Fort Woodbury was constructed in August 1861 by the 4th Michigan Infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil War Defenses Of Washington, D
Civil may refer to: *Civility, orderly behavior and politeness *Civic virtue, the cultivation of habits important for the success of a society *Civil (journalism) ''The Colorado Sun'' is an online news outlet based in Denver, Colorado. It launched on September 10, 2018, to provide long-form, in-depth coverage of news from all around Colorado. It was started with two years of funding from blockchain ventu ..., a platform for independent journalism * Civil (surname) See also * {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Phineas Woodbury
Daniel Phineas Woodbury (December 16, 1812 – August 15, 1864) was an American soldier and an engineer during the American Civil War. Birth and early years Woodbury was born at New London, New Hampshire. He graduated at West Point in 1836, entered the artillery as a second lieutenant, and until 1840 served as assistant engineer in building the Cumberland Road. He superintended the construction of Forts Kearney and Laramie (1847–50), but in 1851 he was recalled to the East. He published works on ''Sustaining Walls'' (1845) and the ''Theory of the Arch'' (1858). Woodbury supervised construction of Fort Jefferson and the Dry Tortugas Light. Civil War In 1861 he was appointed to be major of engineers and lieutenant colonel on the staff. He fought at the First Battle of Bull Run, afterward was engaged until 1862 upon the defenses of Washington, D.C.. He then commanded the Engineer Brigade during the Peninsula Campaign and the Northern Virginia Campaign, as well as during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
16th Maine Infantry Regiment
The 16th Maine Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The regiment was one of five raised in answer to the July 2, 1862, call by Lincoln for 300,000 volunteers for three years. The state of Maine's quota was 9,609. It was particularly noted for its service during the 1863 Battle of Gettysburg. Organization and assignments The 16th Maine was organized at Augusta, Maine, and mustered into Federal service for a three-year enlistment on August 14, 1862. It departed for Washington, D.C. in 1862. It was assigned to: * 3rd Brigade, 2nd Division, III Corps, Army of Virginia (AoV), to September, 1862. * 3rd Brigade, 2nd Division, I Corps, Army of the Potomac (AoP), to May, 1863. * 1st Brigade, 2nd Division, I Corps, AoP, to March, 1864. * 1st Brigade, 2nd Division, V Corps, AoP, to June, 1864. * 1st Brigade, 3rd Division, V Corps, AoP, to August, 1864 or later. * 2nd Brigade, 3rd Division, V Corps, AoP, by February 7, 1865 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th New York Heavy Artillery Regiment
The 4th New York Heavy Artillery Regiment, U.S. Volunteers was a heavy artillery regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. The regiment operated as both heavy artillery and infantry beginning in February 1862 while serving in the defenses of Washington, D.C., and continued in both capacities until the end of the war. Service The regiment was organized at New York City, New York, beginning November 1861 through February 1862 and mustered in at Port Richmond, Staten Island, for three years service under the command of Colonel Thomas Donnelly Doubleday. The regiment was designated as the 1st New York Heavy Artillery on January 27, 1862, and soon renamed 4th New York Heavy Artillery on February 8, 1862. Four batteries from the 11th New York Heavy Artillery were assigned to the regiment on July 25, 1863, as Batteries I, K, L, and M. Battery A – mustered in November 1861 Battery B – mustered in November 1861 Battery C – mustered in December 1861 Bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
88th Pennsylvania Infantry Regiment
The 88th Regiment, Pennsylvania Volunteer Infantry was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Service The 88th Pennsylvania Infantry was organized at Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and mustered in for a three-year enlistment in September 1861 under the command of Colonel George P. McLean. The regiment was attached to 1st Brigade, Ord's 2nd Division, Department of the Rappahannock, to June 1862. 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, III Corps, Army of Virginia, to September 1862. 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, I Corps, Army of the Potomac, to March 1863. 3rd Brigade, 2nd Division, I Corps, to May 1863. 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, I Corps, to March 1864. 2nd Brigade, 2nd Division, V Corps, to June 1864. 2nd Brigade, 3rd Division, V Corps, to March 1865. 3rd Brigade, 3rd Division, V Corps, to June 1865. The 88th Pennsylvania Infantry mustered out of service June 30, 1865. Detailed service Left Pennsylvania for Washington, D.C., October 1. At Kendall Green ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Massachusetts Heavy Artillery Regiment
The 1st Massachusetts Volunteer Heavy Artillery Regiment was a unit that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was originally raised as the 14th Massachusetts Volunteer Infantry Regiment. History 14th Mass Infantry The 14th Massachusetts Infantry began its recruitment in spring 1861, with most of its members coming from Essex County. They were mustered in on 5 July 1861, and left the state on 7 August for Washington, DC, where it would serve in its defenses until the end of the year. Colonel William B. Greene, a West Point graduate and a veteran of the Florida Indian Wars, resigned in October, and was replaced as leader of the unit by Colonel Thomas R. Tannatt, who transferred over from the 16th Regiment Massachusetts Volunteer Infantry. Reorganization as artillery On 1 January 1862, the regiment was reorganized and became a heavy artillery regiment. As artillery units required more men, fifty additional soldiers were added to each company and two a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlington, Virginia
Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the national capital. Arlington County is coextensive with the United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau's census-designated place of Arlington. Arlington County is the eighth-most populous county in the Washington metropolitan area with a population of 238,643 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. If Arlington County were incorporated as a city, it would rank as the third-most populous city in the state. With a land area of , Arlington County is the geographically smallest Administrative divisions of Virginia, self-governing county in the nation. Arlington County is home to the Pentagon, the world's second-largest office structure, which houses the headquarters of the United States Department of Defense, U.S. Department of Defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgetown (Washington, D
Georgetown or George Town may refer to: Places Africa *George, South Africa, formerly known as Georgetown * Janjanbureh, Gambia, formerly known as Georgetown *Georgetown, Ascension Island, main settlement of the British territory of Ascension Island Asia * Georgetown, Prayagraj, India * George Town, Chennai, India * George Town, Penang, capital city of the Malaysian state of Penang Europe * Georgetown, Blaenau Gwent, now part of the town of Tredegar in Wales * Georgetown, Dumfries and Galloway, a location in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland * Es Castell in Minorca, Spain, originally called Georgetown North and Central America Canada * Georgetown, Alberta * Georgetown, Newfoundland and Labrador * Georgetown, Ontario * Georgetown, Prince Edward Island Caribbean * George Town, Bahamas, a village in Exuma District, Bahamas * George Town, Belize, a village in Stann Creek District, Belize * George Town, Cayman Islands, the capital city on Grand Cayman * Georgetown, Saint Vincent and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Albany (Arlington, Virginia)
Fort Albany was a bastioned earthwork that the Union Army built in Arlington County, Virginia, Arlington County (known at the time as Alexandria County) in Virginia. The Army constructed the fort during May 1861 as part of its Civil War Defenses of Washington, Civil War defenses of Washington (see Washington, D.C., in the American Civil War). The fort was built by New York troops, and therefore named after Albany, New York, the state capital of New York. It had a perimeter of 429 yards and emplacements for 12 guns. Fort Richardson (Arlington, Virginia), Fort Richardson, Fort Craig (Virginia), Fort Craig and Fort Tillinghast provided supporting fire for the fort. A May 17, 1864, report from the Union Army's Inspector of Artillery (see Field artillery in the American Civil War#Union artillery, Union Army artillery organization) noted the following:''Fort Albany, Captain Rhodes commanding.''–Garrison, one company First Massachusetts Volunteers–5 commissioned officers, 1 ordnan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Richardson (Arlington, Virginia)
Fort Richardson was a detached redoubt that the Union Army constructed in September 1861 as part of the Civil War defenses of Washington (see Washington, D.C., in the American Civil War).Cooling, pp. 85-90 : Filler Forts — Forts Berry and Richardson: Fort Richardson. The Army built the fort shortly after its rout at the First Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in late July 1861. The Army named the fort after General Israel B. Richardson, whose division had been deployed to defend the City of Washington against attack by way of the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coehorn
A Coehorn (also spelled ''cohorn'') is a lightweight mortar originally designed by Dutch military engineer Menno van Coehoorn. Concept and design Van Coehoorn came to prominence during the 1688–1697 Nine Years War, whose tactics have been summarised by historian John Childs: "The majority of infantrymen never fired their muskets in anger; ... armies were consciously geared towards the dominant forms of warfare: manoeuvre and the siege." This emphasis on siege warfare led to many developments in the use and design of artillery. Fortifications were vulnerable to vertical trajectory or plunging fire, and the concept of mortars was well understood, but large-scale mortars were initially used only to provide close support for infantry assaults on fortified positions. Van Coehoorn demonstrated them in May 1701 to William III of England, and they were first used in action at the siege of Kaiserswerth in 1702. The original Coehorn was light enough to be moved by as few as two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parrott Rifles
The Parrott rifle was a type of muzzle-loading rifled artillery weapon used extensively in the American Civil War. Parrott rifle The gun was invented by Captain Robert Parker Parrott, a West Point graduate. He was an American soldier and inventor of military ordnance. He resigned from the service in 1836 and became the superintendent of the West Point Foundry in Cold Spring, New York. He created the first Parrott rifle (and corresponding projectile) in 1860 and patented it in 1861.. Daniel Treadwell, who developed a method for making built-up guns in the early 1840s, tried to claim that his patent infringed on an earlier one, but in 1866 United States District Court court dismissed it, deciding that Treadwell's claim was invalidated by a 1843 British patent to John Frith. Parrotts were manufactured with a combination of cast and wrought iron. The cast iron made for an accurate gun, but was brittle enough to suffer fractures. Hence, a large wrought iron reinforcing band was ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |