|
Fort Sully (South Dakota)
Fort Sully was one of the main military posts located on the east bank of the Missouri River in central Dakota built for use in the Indian Wars. There were two forts named Sully—old Fort Sully, which was in existence and occupied from 1863 to 1866, and the later, or new Fort Sully, which was established in 1866 and was continuously occupied as a military fort until its abandonment in the fall of 1894. Old Fort Sully Old Fort Sully , in present-day Hughes County, was built by the orders of Major General Alfred Sully in September 1863 and was named for him. It was located about eighty rods from the left (east) bank of the Missouri River, a short distance above the head of Farm Island and about four and one-half miles southeast of what is now the city of Pierre, South Dakota. It was square and was built of cottonwood timber taken from Farm Island. A portion of the command of General Sully in the campaigns of 1863-4 and 1865 against the Sioux was garrisoned at old Fort Sully. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hughes County, South Dakota
Hughes County is a county in the U.S. state of South Dakota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 17,765, making it the least populous capital county in the nation, and the 12th most populous county in South Dakota. Its county seat is Pierre, which is also the state capital. The county was created in 1873, and was organized in 1880. It was named for Alexander Hughes, a legislator. On June 4, 1891, the county's area was increased by the addition of Farm Island, in the Missouri River downstream of Pierre. Hughes County is part of the Pierre, SD Micropolitan Statistical Area. Geography The Missouri River forms the southwestern boundary line of Hughes County. The county's terrain consists of rolling hills cut by gullies and drainages. The area is partially dedicated to agriculture, including the use of center pivot irrigation. The county terrain generally slopes to the southeast, although the hills along the west fall off into the river valley. The county's highest point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
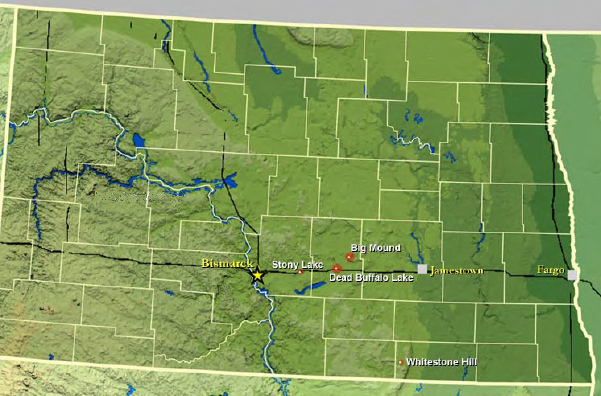
Battle Of Whitestone Hill
The Battle of Whitestone Hill (known also as Whitestone Hill Massacre by the Dakota) was a battle of the Sioux Wars in 1863 in the Dakota Territory as punishment against the Sioux in the aftermath of the Dakota War of 1862. From September 3-5, 1863, Brigadier General Alfred Sully led U.S. Army troops against a village of Yanktonai, Santee, and Teton (Lakota) Sioux. The reported casualties vary, but U.S. Army troops killed somewhere between 150 and 300 Sioux and captured between 150 and 250 Sioux, including women and children, and they suffered approximately 22 killed and 38 wounded. Background In the Dakota War of 1862, a faction of the Santee Dakota, or Sioux, in Minnesota rose up in rebellion against the United States because of the non-payment by the U.S. government to the Sioux of food and money as agreed to by treaties. The Sioux killed more than 600 whites, mostly unarmed civilians. The Sioux were defeated, the leaders of the rebellion executed, and, in April 1863, nea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Benton, Montana
Fort Benton is a city in and the county seat of Chouteau County, Montana, United States. Established in 1846, Fort Benton is the oldest continuously occupied settlement in Montana. Fort Benton was the most upstream navigable port on the Mississippi River System, and is considered "the world’s innermost port". The city's waterfront area, the most important aspect of its 19th century growth, was designated the Fort Benton Historic District, a National Historic Landmark, in 1961. The population was 1,449 at the 2020 census. History Established in 1846 as Fort Lewis and relocated 15 miles downstream in 1847 by Alexander Culbertson, who worked for Auguste Chouteau and Pierre Chouteau, Jr. of St. Louis, the original fort was the last fur trading post on the Upper Missouri River, Chouteau County Courthouse, 2009 which soon made it an important economic center. For 30 years, the port attracted steamboats carrying goods, merchants, gold miners and settlers, coming from New O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Rice
Fort Rice (Lakota: ''Psíŋ Otȟúŋwahe''; "Wild Rice Village") was a frontier military fort in the 19th century named for American Civil War General James Clay Rice in what was then Dakota Territory and what is now North Dakota. The 50th Wisconsin Infantry Regiment became the garrison in October 1865. Foundation and History The fort was originally established in 1864 by General Alfred H. Sully and was built by him and the 30th Wisconsin Infantry Regiment. This regiment would later be replaced by the 1st US volunteer infantry, consisting mainly of ex-confederate soldiers who had joined the Union. Its location was placed north of the mouth of Cannonball River, and south of Heart River's mouth. The buildings within the fort were made of materials that could be found locally, including cottonwood logs for walls and support, and prairie sod for roofing. The fort was reconstructed in 1868, with the old buildings being torn down and new ones constructed in their stead. The fort b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of Missouri
The Department of the Missouri was a command echelon of the United States Army in the 19th century and a sub division of the Military Division of the Missouri that functioned through the Indian Wars. History Background Following the successful conclusion of the Mexican–American War, the administration of the United States Army was theoretically directed, under the President of the United States, by the Secretary of War and the general in chief. In practice the Secretary of War and the heads of the army's staff agencies—who reported directly to him (adjutant general, quartermaster general, commissary general, inspector general, paymaster general, surgeon general, chief engineer, colonel of topographical engineers, and colonel of ordnance)—exercised full authority, leaving the general-in-chief a figurehead. With a lack of central direction, policy and strategy were ''de facto'' developed by the commanders of the numbered geographical departments and three division headquart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Dakota
A subdivision of the Division of the Missouri, the Department of Dakota was established by the United States Army on August 11, 1866, to encompass all military activities and forts within Minnesota, Dakota Territory and Montana Territory. The Department of Dakota was initially headquartered at Fort Snelling, Minnesota, and then moved to Saint Paul in March 1867. The 18th Infantry Regiment (United States) would serve in Dakota several times. From 1869-1877 the 20th Infantry Regiment (United States) was posted to the Department. In 1879 the Department returned to the Fort until 1886 at which time it moved back to downtown Saint Paul. The department was discontinued in 1911. Commanders *Brevet Major General Alfred H. Terry, (Sept. 18, 1866-May 17, 1869) *Major General Winfield S. Hancock, (May 17, 1869-Jan. 2, 1873) *Brigadier General Alfred H. Terry, (Jan. 2, 1873–1886) *Major General Thomas Howard Ruger, (1886–1891) *Brigadier General James F. Wade, (1899-1901) *Brigadier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of The Platte
The Department of the Platte was a military administrative district established by the U.S. Army on March 5, 1866, with boundaries encompassing Iowa, Nebraska, Dakota Territory, Utah Territory and a small portion of Idaho. With headquarters in Omaha, the district commander oversaw the army's role initially along the Overland route (or Oregon Trail) to Salt Lake City, then later the construction route of the Union Pacific Railroad. The district also included the Montana road (or Bozeman Trail) through eastern Wyoming. The district was discontinued when the Army's command was reorganized in 1898. Headquarters The Headquarters of the Department of the Platte was located in downtown Omaha, Nebraska for many years. When the headquarters was transferred to Fort Omaha in 1878, the building it was located in was found unsuitable, and the headquarters were again transferred downtown. Notable Campaigns * Powder River Expedition (1865), Powder River Expedition (1865), against the Lakota, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloody Knife
Bloody Knife (Sioux: ''Tȟamila Wewe''; Arikara: ''NeesiRAhpát''; ca. 1840 – June 25, 1876) was an American Indian who served as a scout and guide for the U.S. 7th Cavalry Regiment. He was the favorite scout of Lieutenant Colonel George Armstrong Custer and has been called "perhaps the most famous Native American scout to serve the U.S. Army." Bloody Knife was born to a Hunkpapa Sioux father and an Arikara mother around 1840. He was abused and discriminated against by the other Sioux in his village because of his background, in particular by Gall, a future chief. When Bloody Knife was a teenager, he left his village with his mother to live with the Arikara tribe. His brothers were killed during a Sioux raid led by Gall in 1862. Bloody Knife found employment as a courier and hunter for the American Fur Company and later served under Alfred Sully before scouting for George Custer on several military expeditions. He died from a bullet wound to the head on June 25, 1876, durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th Regiment Iowa Volunteer Cavalry
{{Infobox military unit , unit_name= 7th Iowa Cavalry Regiment , image=Flag of Iowa.svg , image_size=100px , caption=Iowa state flag , dates= April 27, 1863, to June 22, 1866 , country= United States , allegiance= Union , branch= Cavalry , equipment= , battles= American Indian Wars * Battle of Killdeer Mountain * Battle of the Badlands * Battle of Julesburg * Powder River Expedition The 7th Iowa Cavalry Regiment was a cavalry regiment that served in the Union Army during the Indian Wars. In Chapter IX of MacKinlay Kantor's Pulitzer Prize-winning novel "Andersonville" (1955), the father of one of the main characters is commissioned as a lieutenant in Company G of the Seventh Iowa Cavalry. Service The 7th Iowa Cavalry was mustered into Federal service at Davenport, Iowa, for a three-year enlistment between April 27 to July 13, 1863. On September 19, 1863, it was deployed to Omaha en route to the west. In 1864, three companies of the regiments were part of Lieutenant Colonel Samu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Pope (general)
John Pope (March 16, 1822 – September 23, 1892) was a career United States Army officer and Union Army, Union general in the American Civil War. He had a brief stint in the Western Theater of the American Civil War, Western Theater, but he is best known for his defeat at the Second Battle of Bull Run (Second Manassas) in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War, East. Pope was a graduate of the United States Military Academy in 1842. He served in the Mexican–American War and had numerous assignments as a topographical engineer and surveyor in Florida, New Mexico, and Minnesota. He spent much of the last decade before the Civil War surveying possible southern routes for the proposed first transcontinental railroad. He was an early appointee as a Union Brigadier general (United States), brigadier general of volunteers and served initially under Maj. Gen. John C. Frémont. He achieved initial success against Brig. Gen. Sterling Price in Missouri, then led a successful campa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farm Island State Recreation Area
A farm (also called an agricultural holding) is an area of land that is devoted primarily to agricultural processes with the primary objective of producing food and other crops; it is the basic facility in food production. The name is used for specialized units such as Arable land, arable farms, vegetable farms, fruit farms, dairy, pig and poultry farms, and land used for the production of Fiber, natural fiber, biofuel, and other biobased Product (business), products. It includes ranches, feedlots, orchards, plantations and estates, smallholdings, and hobby farms, and includes the farmhouse and agricultural buildings as well as the land. In modern times, the term has been extended to include such industrial operations as wind farms and aquaculture, fish farms, both of which can operate on land or at sea. There are about 570 million farms in the world, most of which are small and family-operated. Small farms with a land area of fewer than 2 hectares operate on about 12% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
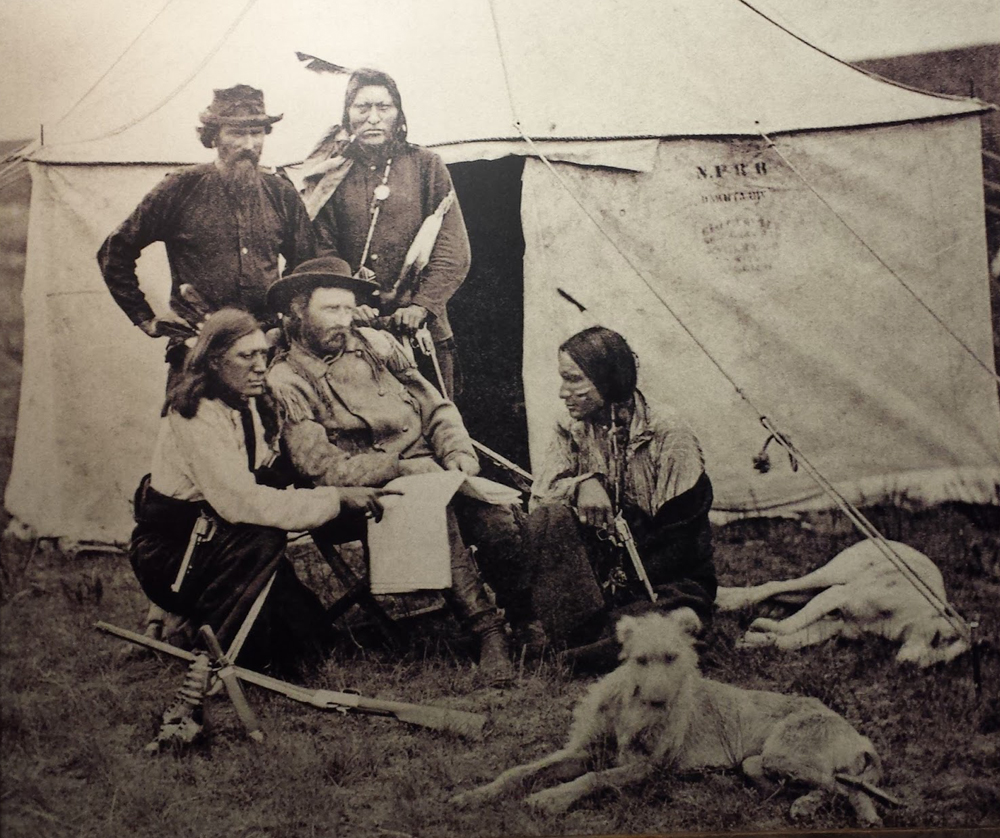
Alfred Sully
Alfred Sully (May 22, 1820 or 1821 – April 27, 1879) was an American military officer who served in the United States Army during the Mexican-American War and the American Indian Wars. He served as Brevet Brigadier General in the Union army during the American Civil War but was removed from command by John Gibbon for failure to suppress a mutiny by the 34th New York Infantry Regiment. He was cleared by a court of inquiry of any wrongdoing and sent to command the District of Iowa (including the Territory of North Dakota) in the Department of the Northwest during the Sioux Wars. After the Civil War, he served as major in the United States Army and continued to fight in the Indian Wars including the Nez Perce War and out of Fort Dodge, Fort Harker and Fort Vancouver. He served as Superintendent of Indian Affairs for Montana in 1869 and as colonel of the 21st Infantry Regiment in 1873. Early life and education Sully was born in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, on May 22, 1820 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |