|
Fort Langley National Historic Site
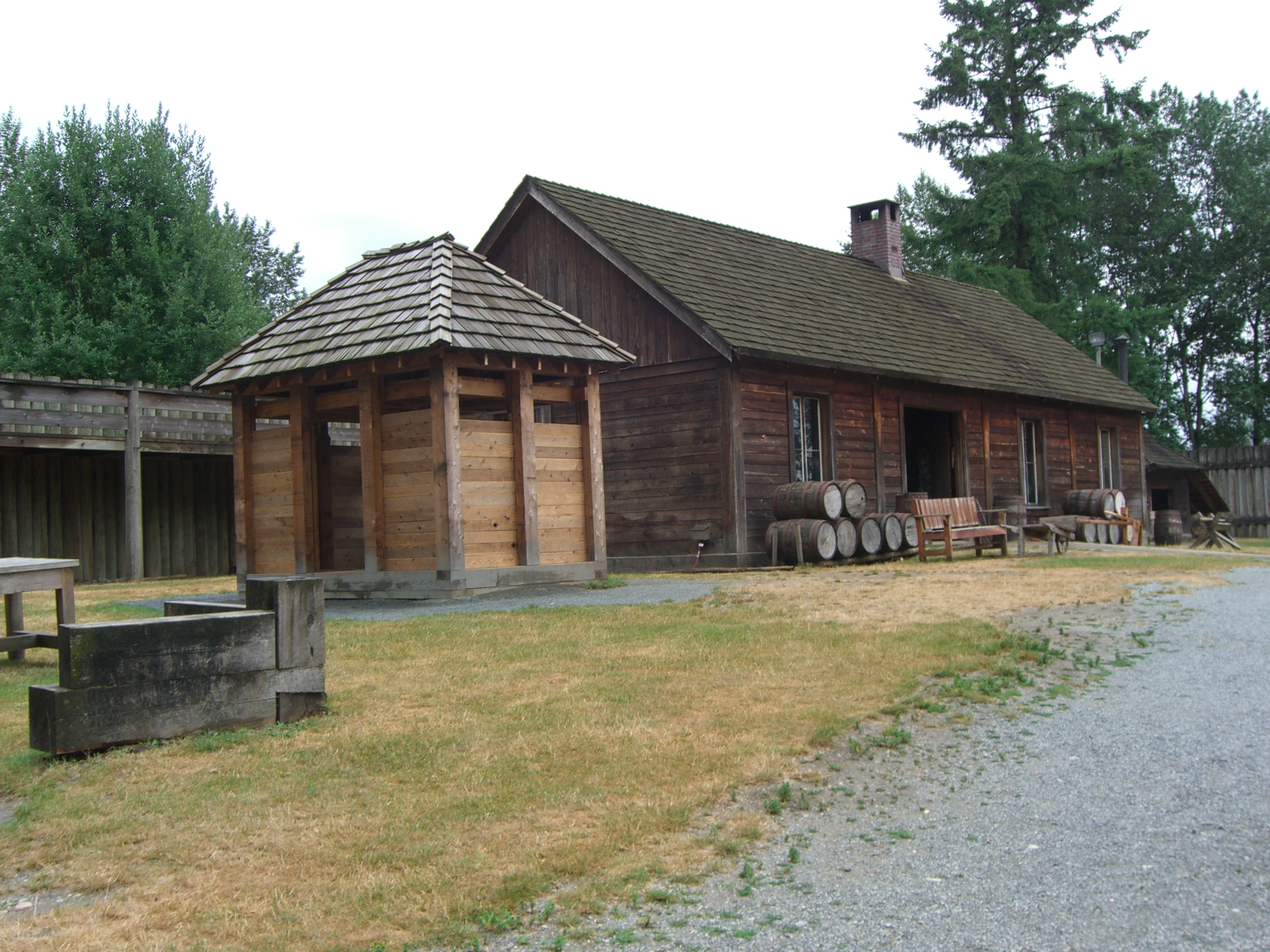
Fort Langley National Historic Site, commonly shortened to Fort Langley, is a former fur trading post of the Hudson's Bay Company in the community of Fort Langley of Langley, British Columbia, Canada. The national historic site sits above the banks of the Bedford Channel across McMillan Island. The national historic site contains a visitor centre and a largely reconstructed trading post that contains ten structures surrounded by wooden palisades. Fort Langley was initially established in 1827 in present-day Derby. The fort's operations were later relocated to present-day Langley with the new fort completed in 1839. However, the new fort would be rebuilt in the following year, after a fire ravaged the trading post. The fort continued to see use by the Hudson's Bay Company until 1886, when the company ceased to operate the site as a trading post. By the 1920s, only one building remained at the site, the fort's storehouse. The site was later was designated as a National Historic S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langley, British Columbia (district Municipality)
The Township of Langley is a district municipality immediately east of the Surrey, British Columbia, City of Surrey in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It extends south from the Fraser River to the Canada–United States border, and west of the City of Abbotsford. Langley Township is not to be confused with the City of Langley, which is adjacent to the township but politically is a separate entity. Langley is located in the eastern part of Metro Vancouver. History First Nations Throughout the last several millennia, the area that is now Langley Township was inhabited by various Stó꞉lō nations, including the Katzie and Kwantlen First Nation, Kwantlen. There is limited recorded history from this time, as much was passed down through oral tradition rather than written documents. The Kwantlen were a major factor in the salmon trade that later operated out of the Fort Langley. Simon Fraser, while traveling through the Sto:lo territory in 1808 recorded the image of a Kwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraser River
The Fraser River () is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain (Canada), Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of Vancouver. The river's annual discharge at its mouth is or , and each year it discharges about 20 million tons of sediment into the ocean. Naming The river is named after Simon Fraser (explorer), Simon Fraser, who led an expedition in 1808 on behalf of the North West Company from the site of present-day Prince George, British Columbia, Prince George almost to the mouth of the river. The river's name in the Halqemeylem (Upriver Halkomelem) language is , often seen archaically as Staulo, and has been adopted by the Halkomelem-speaking peoples of the Lower Mainland as their collective name, . The river's name in the Dakelh language is . The Chilcotin language, ''Tsilhqot'in'' name for the river, not dissimilar to the ''Dakelh'' name, is , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Alexandria
Alexandria or Fort Alexandria was a general area encompassing a trading post, ferry site, and steamboat landing in the North Cariboo region of central British Columbia. The present unincorporated community is on the eastern side of the Fraser River. On BC Highway 97, the locality is by road about northwest of Williams Lake and south of Quesnel. Name origin The name honours Alexander Mackenzie, who in 1793 on his Peace River to Pacific Ocean expedition was the first European to visit the Alexandria First Nation village. On being warned of the dangerous falls and rapids downstream, Mackenzie returned northward beyond the future Quesnel, before turning westward along the West Road River (Blackwater River) toward the coast. First Nations The First Nations village on the west side of the river was known as Tautin (Ltau'tenne, "sturgeon people"), part of the Takulli ( Carrier), which originally numbered in the hundreds. In 1826, when the Chilcotin attacked this village opp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Caledonia (Canada)
New Caledonia was a fur-trading district of the Hudson's Bay Company that comprised the territory of the north-central portions of present-day British Columbia, Canada. Though not a British colony, New Caledonia was part of the British claim to North America. Its administrative centre was Fort St. James. The rest of what is now mainland British Columbia was called the Columbia Department by the British, and the Oregon Country by the Americans. Even before the partition of the Columbia Department by the Oregon Treaty in 1846, New Caledonia was often used to describe anywhere on the mainland not in the Columbia Department, such as Fort Langley in the Fraser Valley. Fur-trading district The explorations of James Cook and George Vancouver, and the concessions of Spain in 1792 established the British claim to the coast north of California. Similarly, British claims were established inland via the explorations of such men as Sir Alexander Mackenzie, Simon Fraser, Samuel Black, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued. Historically the trade stimulated the exploration and colonization of Siberia, northern North America, and the South Shetland Islands, South Shetland and South Sandwich Islands. Today the importance of the fur trade has diminished; it is based on pelts produced at fur farms and regulated fur-bearer trapping, but has become controversial. Animal rights organizations oppose the fur trade, citing that animals are brutally killed and sometimes skinned alive. Fur has been replaced in some clothing by synthetic fiber, synthetic imitations, for example, as in ruffs on hoods of parkas. Continental fur trade Russian fur trade Before the European colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major supplier of fur pelts to W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (PNW; ) is a geographic region in Western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common conception includes the U.S. states of Oregon, Washington (state), Washington, Idaho, and the Canadian province of British Columbia. Some broader conceptions reach north into Alaska and Yukon, south into Northern California, and east into western Montana. Other conceptions may be limited to the coastal areas west of the Cascade Mountains, Cascade and Coast Mountains, Coast mountains. The Northwest Coast is the coastal region of the Pacific Northwest, and the Northwest Plateau (also commonly known as "British Columbia Interior, the Interior" in British Columbia), is the inland region. The term "Pacific Northwest" should not be confused with the Northwest Territory (also known as the Great Northwest, a historical term in the United States) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
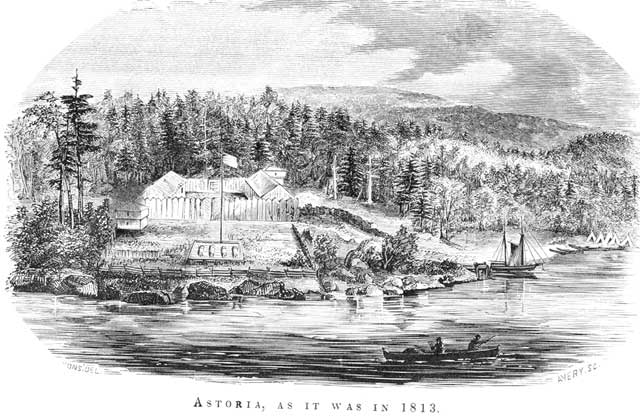
Fort Astoria
Fort Astoria (also named Fort George) was the primary Fur trade, fur trading post of John Jacob Astor's Pacific Fur Company (PFC). A maritime contingent of PFC staff was sent on board the ''Tonquin (1807 ship), Tonquin'', while another party traveled overland from St. Louis. This land based group later became known as the Astor Expedition. Built at the entrance of the Columbia River in 1811, Fort Astoria was the first American-owned settlement on the Pacific coast of North America. The inhabitants of the fort differed greatly in background and position, and were structured into a corporate hierarchy. The fur trading partners of the company were at the top, with clerks, craftsmen, hunters, and laborers in descending order. Nationalities included Americans, Scots, French Canadians, French Canadian voyageurs, Native Hawaiians, Native Hawaiian Kanaka (Pacific Island worker), Kanakas, and various Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous North Americans, including Iroquois and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of 1812
The War of 1812 was fought by the United States and its allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom and its allies in North America. It began when the United States United States declaration of war on the United Kingdom, declared war on Britain on 18 June 1812. Although peace terms were agreed upon in the December 1814 Treaty of Ghent, the war did not officially end until the peace treaty was ratified by the 13th United States Congress, United States Congress on 17 February 1815. AngloAmerican tensions stemmed from long-standing differences over territorial expansion in North America and British support for Tecumseh's confederacy, which resisted U.S. colonial settlement in the Old Northwest. In 1807, these tensions escalated after the Royal Navy began enforcing Orders in Council (1807), tighter restrictions on American trade with First French Empire, France and Impressment, impressed sailors who were originally British subjects, even those who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North West Company
The North West Company was a Fur trade in Canada, Canadian fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in the regions that later became Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great wealth at stake, tensions between the companies increased to the point where several minor armed skirmishes broke out, and the two companies were forced by the British government to merge. Before the Company After the French landed in Quebec in 1608, independent French-Canadian traders commonly known as spread out and built a fur trade empire in the St. Lawrence River, St. Lawrence basin. The French competed with the Dutch (from 1614) and English (1664) in New York and the English in Hudson Bay (1670). Unlike the French who traveled into the northern interior and traded with First Nations in their camps and villages, the English made bases at trading posts on Hudson Bay, inviting the indigenous people t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long Oregon boundary dispute, dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been demarcated by the Treaty of 1818, consisted of the land north of 42nd parallel north, 42° N latitude, south of 54°40′ N latitude, and west of the Rocky Mountains down to the Pacific Ocean and east to the Continental Divide of the Americas, Continental Divide. Article III of the 1818 treaty gave joint control to both nations for ten years, allowed land to be claimed, and guaranteed free navigation to all mercantile trade. However, both countries disputed the terms of the international treaty. Oregon Country was the American name, while the British used Columbia District for the British Empire, region. British North America, British and French Canadians, French History of Canada (1763–1867), Canadian North American fur trade, fur tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Fur Company
The Pacific Fur Company (PFC) was an American fur trade venture wholly owned and funded by John Jacob Astor that functioned from 1810 to 1813. It was based in the Pacific Northwest, an area contested over the decades among the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, the Spanish Empire, the United States of America and the Russian Empire. Management, clerks and fur trappers were sent both by land and by sea to the Pacific Coast in the Autumn of 1810. The base of operations was constructed at the mouth of the Columbia River in 1811, Fort Astoria (present-day Astoria, Oregon). The destruction of the company vessel the '' Tonquin'' later that year off the shore of Vancouver Island took with it the majority of the annual trading goods. Commercial competition with the British-Canadian North West Company began soon after the foundation of Fort Astoria. The Canadian competitors maintained several stations in the interior, primarily Spokane House, Kootanae House and Saleesh House. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
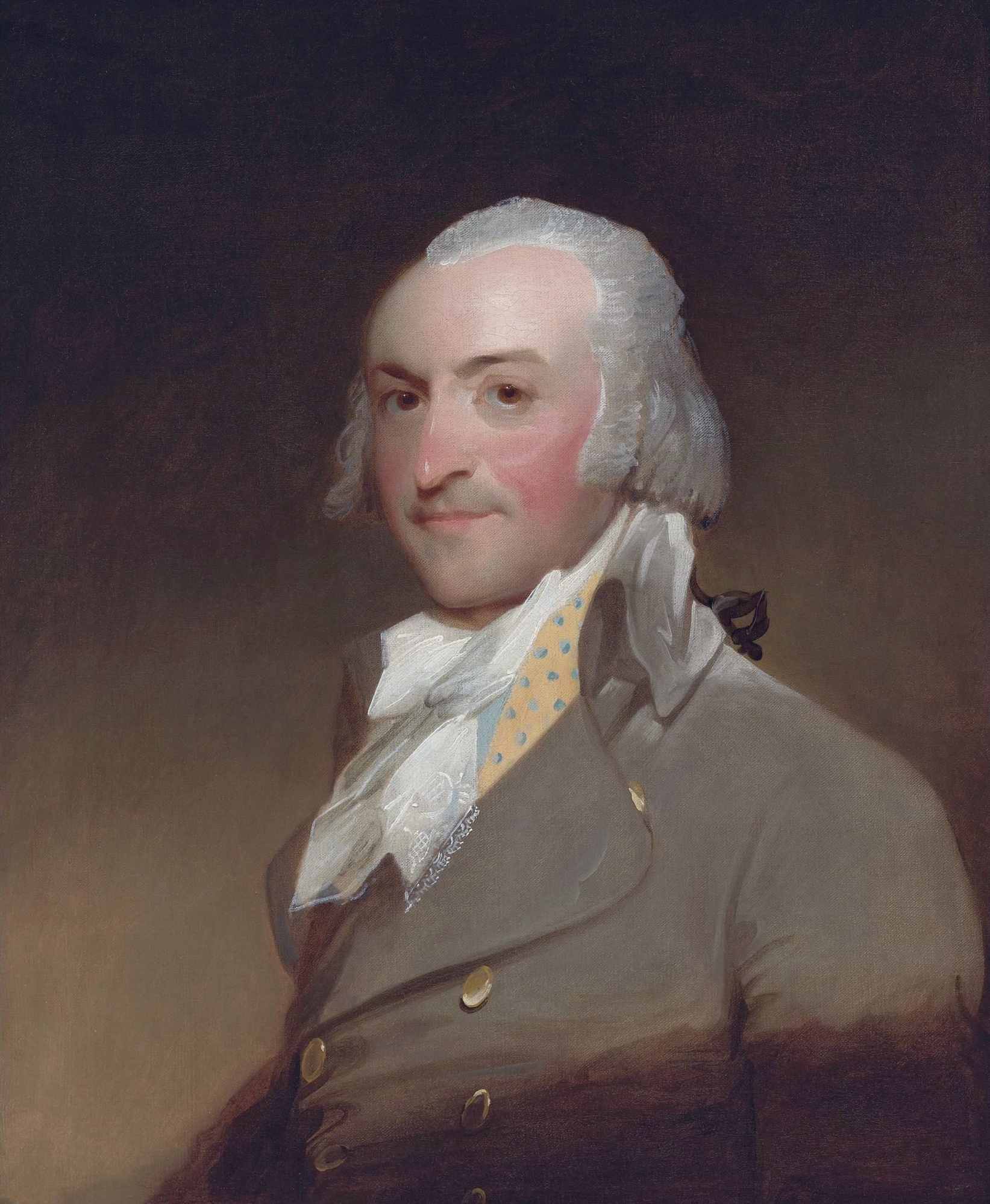
John Jacob Astor
John Jacob Astor (born Johann Jakob Astor; July 17, 1763 – March 29, 1848) was a German-born American businessman, merchant, real estate mogul, and investor. Astor made his fortune mainly in a fur trade monopoly, by exporting History of opium in China, opium into the Qing dynasty, Chinese Empire, and by investing in real estate in or around New York City History of New York City (1784–1854), during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. He was the first prominent member of the Astor family and the first multi-millionaire in the United States. Born in Holy Roman Empire, Germany, Astor immigrated to England as a teenager and worked as a musical instrument manufacturer. He moved to the United States after the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783). Seeing the expansion of population to the west, Astor entered the fur trade and built a monopoly, managing a business empire that extended to the Great Lakes region and north into British North America (future Canada, Dominion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |