|
Fort Delaware
Fort Delaware is a former harbor defense facility, designed by chief engineer Joseph Gilbert Totten and located on Pea Patch Island in the Delaware River.Dobbs, Kelli W., et al. During the American Civil War (1861-1865), the Union / United States Department of War / United States Army used Fort Delaware as a prison for Confederate prisoners of war, political prisoners, miscellaneous civilians, federal convicts, and privateer officers. A three-gun concrete battery of 12-inch guns, later named Battery Torbert, was designed by Maj. Charles W. Raymond and built inside the fort in the 1890s. By 1900, the fort was part of a three fort concept, the first forts of the Coast Defenses of the Delaware, working closely with Fort Mott further upstream on the opposite shore, in Pennsville, New Jersey, and Fort DuPont downstream in Delaware City, Delaware. The fort and the island currently belong to the Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control (DNRE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
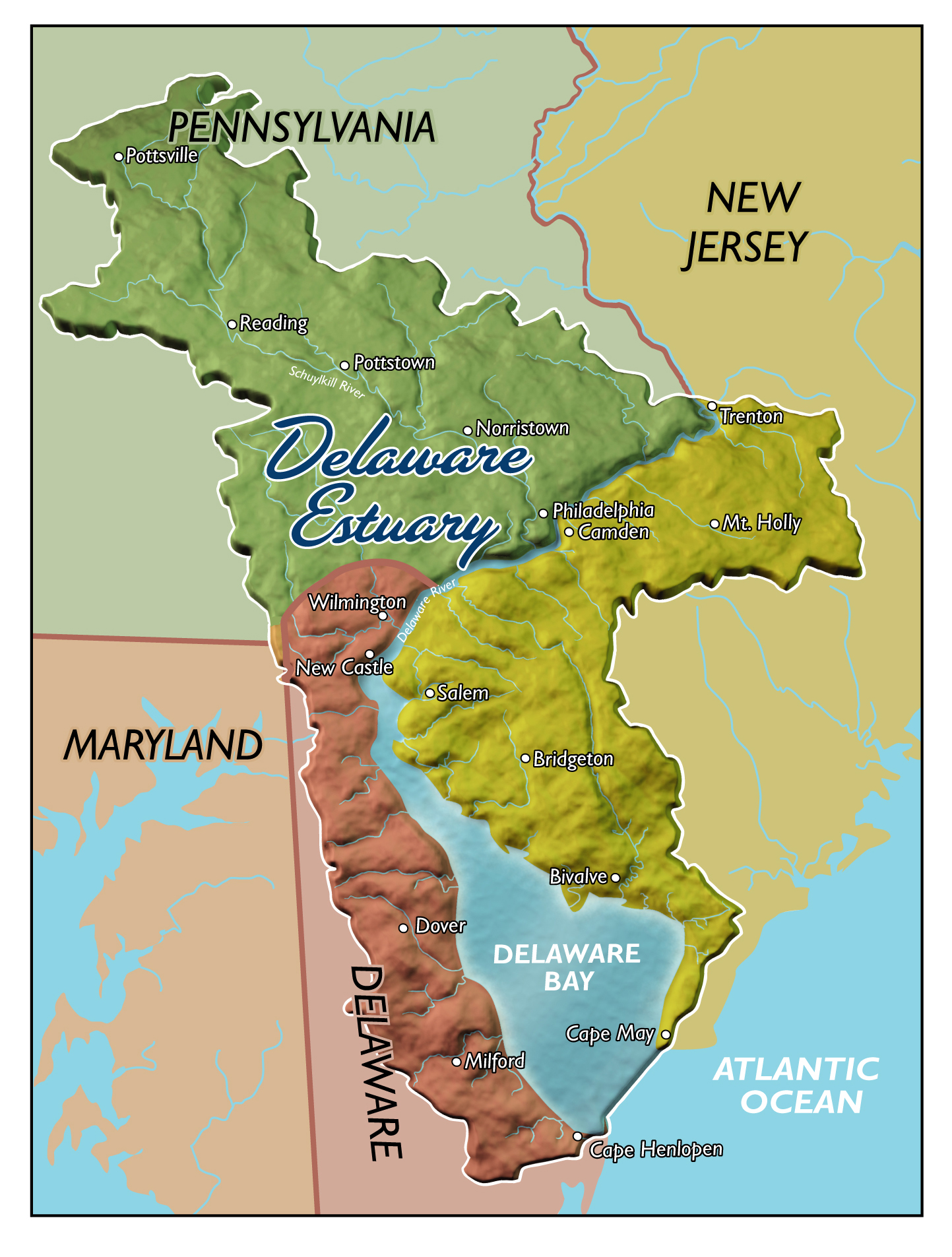
Harbor Defenses Of The Delaware
The Harbor Defenses of the Delaware was a United States Army Coast Artillery Corps Harbor Defense Command, harbor defense command. It coordinated the coastal defence and fortification, coast defenses of the Delaware River estuary from 1897 to 1950, beginning with the Board of Fortifications, Endicott program. These included both coastal artillery, coast artillery forts and Submarine mines in United States harbor defense, underwater minefields. The areas protected included the cities of Philadelphia, Camden, New Jersey, Camden, and Wilmington, Delaware, Wilmington along with the Chesapeake & Delaware Canal. The command originated circa 1896 as an Artillery District and became the Coast Defenses of the Delaware in 1913, with defenses initially at and near Fort Delaware on Pea Patch Island near Delaware City, Delaware, Delaware City. In 1925 the command was renamed as a Harbor Defense Command. During World War II the defenses were relocated to Fort Miles on Cape Henlopen at the mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pea Patch Island
Fort Delaware State Park is a , Delaware state park on Pea Patch Island in the mid channel of the Delaware River near its entrance into Delaware Bay. It is a low, marshy island in New Castle County, Delaware, facing Delaware City on the Delaware shore and Finns Point on the New Jersey shore. Fort Delaware was built on Pea Patch Island by the United States Army in 1815, near the conclusion of the War of 1812, to protect the harbors of Wilmington, Delaware and Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The fort was burned and rebuilt in the years prior to the American Civil War, and soon after the start of the war the fort was converted to a Prisoner of War camp. Fort Delaware continued to protect the mouth of the Delaware River through World War I and II. Pea Patch Island and Fort Delaware was declared surplus land by the United States Department of Defense in 1945. Fort Delaware State Park, one of the first state parks in Delaware, was established in 1951. The park, which can only be acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Defenses Of The Delaware
The Harbor Defenses of the Delaware was a United States Army Coast Artillery Corps harbor defense command. It coordinated the coast defenses of the Delaware River estuary from 1897 to 1950, beginning with the Endicott program. These included both coast artillery forts and underwater minefields. The areas protected included the cities of Philadelphia, Camden, and Wilmington along with the Chesapeake & Delaware Canal. The command originated circa 1896 as an Artillery District and became the Coast Defenses of the Delaware in 1913, with defenses initially at and near Fort Delaware on Pea Patch Island near Delaware City. In 1925 the command was renamed as a Harbor Defense Command. During World War II the defenses were relocated to Fort Miles on Cape Henlopen at the mouth of the Delaware Bay.Stanton, pp. 455-481Rinaldi, pp. 165-166Berhow, pp. 427-434 History Early forts on the Delaware River Colonial period Europeans came to the Delaware Valley in the early 17th century, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Delaware State Park
Fort Delaware State Park is a , Delaware state park on Pea Patch Island in the mid channel of the Delaware River near its entrance into Delaware Bay. It is a low, marshy island in New Castle County, Delaware, facing Delaware City on the Delaware shore and Finns Point on the New Jersey shore. Fort Delaware was built on Pea Patch Island by the United States Army in 1815, near the conclusion of the War of 1812, to protect the harbors of Wilmington, Delaware and Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The fort was burned and rebuilt in the years prior to the American Civil War, and soon after the start of the war the fort was converted to a Prisoner of War camp. Fort Delaware continued to protect the mouth of the Delaware River through World War I and II. Pea Patch Island and Fort Delaware was declared surplus land by the United States Department of Defense in 1945. Fort Delaware State Park, one of the first state parks in Delaware, was established in 1951. The park, which can only be acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Prisoner
A political prisoner is someone imprisoned for their political activity. The political offense is not always the official reason for the prisoner's detention. There is no internationally recognized legal definition of the concept, although numerous similar definitions have been proposed by various organizations and scholars, and there is a general consensus among scholars that "individuals have been sanctioned by legal systems and imprisoned by political regimes not for their violation of codified laws but for their thoughts and ideas that have fundamentally challenged existing power relations". The status of a political prisoner is generally awarded to individuals based on the declarations of non-governmental organizations like Amnesty International, on a case-by-case basis. While such statuses are often widely recognized by the international public, they are often rejected by individual governments accused of holding political prisoners, which tend to deny any bias in thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union (American Civil War)
The Union was the central government of the United States during the American Civil War. Its civilian and military forces resisted the Confederate State of America, Confederacy's attempt to Secession in the United States, secede following the 1860 United States presidential election, election of Abraham Lincoln as president of the United States. Presidency of Abraham Lincoln, Lincoln's administration asserted the permanency of the federal government of the United States, federal government and the continuity of the Constitution of the United States, United States Constitution. Nineteenth-century Americans commonly used the term Union to mean either the federal government of the United States or the unity of the states within the Federalism in the United States, federal constitutional framework. The Union can also refer to the people or territory of the states that remained loyal to the national government during the war. The loyal states are also known as the North, although fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of War
The United States Department of War, also called the War Department (and occasionally War Office in the early years), was the United States Cabinet department originally responsible for the operation and maintenance of the United States Army, also bearing responsibility for naval affairs until the establishment of the United States Department of the Navy, Navy Department in 1798, and for most land-based air forces until the creation of the United States Department of the Air Force, Department of the Air Force on September 18, 1947. The United States Secretary of War, secretary of war, a civilian with such responsibilities as finance and purchases and a minor role in directing military affairs, headed the War Department throughout its existence. The War Department existed for 158 years, from August 7, 1789, to September 18, 1947, when it split into the United States Department of the Army, Department of the Army and the United States Department of the Air Force, Department of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate States Of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), also known as the Confederate States (C.S.), the Confederacy, or Dixieland, was an List of historical unrecognized states and dependencies, unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States from 1861 to 1865. It comprised eleven U.S. states that declared Secession in the United States, secession: South Carolina in the American Civil War, South Carolina, Mississippi in the American Civil War, Mississippi, Florida in the American Civil War, Florida, Alabama in the American Civil War, Alabama, Georgia in the American Civil War, Georgia, Louisiana in the American Civil War, Louisiana, Texas in the American Civil War, Texas, Virginia in the American Civil War, Virginia, Arkansas in the American Civil War, Arkansas, Tennessee in the American Civil War, Tennessee, and North Carolina in the American Civil War, North Carolina. These states fought against the United States during the American Civil War. With Abraham Lincoln's 1860 Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prisoner Of War
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610. Belligerents hold prisoners of war for a range of legitimate and illegitimate reasons. These may include isolating them from enemy combatants still in the field (releasing and Repatriation, repatriating them in an orderly manner after hostilities), demonstrating military victory, punishment, prosecution of war crimes, labour exploitation, recruiting or even conscripting them as combatants, extracting collecting military and political intelligence, and political or religious indoctrination. Ancient times For much of history, prisoners of war would often be slaughtered or enslaved. Early Roman gladiators could be prisoners of war, categorised according to their ethnic roots as Samnites, Thracians, and Gauls (''Galli''). Homer's ''Iliad'' describes Trojan and Greek soldiers offeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War Prison Camps
Between 1861 and 1865, American Civil War prison camps were operated by the Union (American Civil War), Union and the Confederate States of America, Confederacy to detain over 400,000 captured soldiers. From the start of the American Civil War, Civil War through to 1863 a parole exchange system saw most Prisoner of war, prisoners of war swapped relatively quickly. However, from 1863 this broke down following the Confederacy's refusal to treat black and white Union prisoners equally, leading to soaring numbers held on both sides. Records indicate the capture of 211,411 Union soldiers, with 16,668 paroled and 30,218 died in captivity; of Confederate soldiers, 462,684 were captured, 247,769 paroled and 25,976 died in captivity. Just over 5.6% of the captives in Northern prisons died, compared to 14.29% for Southern prisons. Lorien Foote has noted, "the suffering of prisoners did more to inhibit postwar reconciliation than any o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
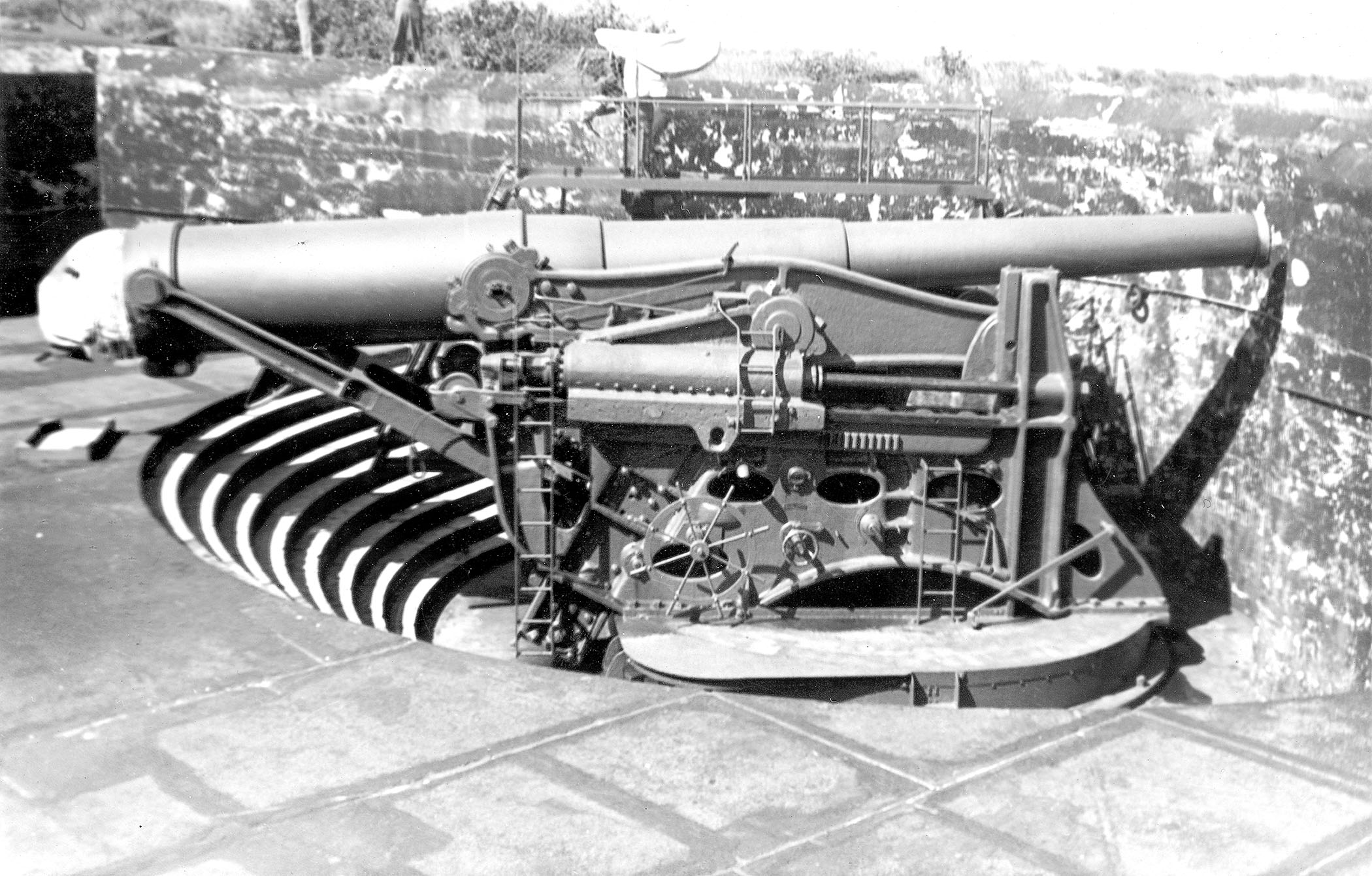
12-inch Gun M1895
The 12-inch coastal defense gun M1895 (305 mm) and its variants the M1888 and M1900 were large coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1895 and 1945. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. Most were installed on disappearing carriages, with early installations on low-angle barbette mountings. From 1919, 19 long-range two-gun batteries were built using the M1895 on an M1917 long-range barbette carriage. Almost all of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped during and after World War II. History In 1885, William C. Endicott, President Grover Cleveland's secretary of war, was tasked with creating the Board of Fortifications to review seacoast defenses. The findings of the board illustrated a grim picture of existing defenses, and in its 1886 report recommended a massive $127 million construction program of breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles W
The F/V ''Charles W'', also known as Annie J Larsen, is a historic fishing schooner anchored in Petersburg, Alaska. At the time of its retirement in 2000, it was the oldest fishing vessel in the fishing fleet of Southeast Alaska, and the only known wooden fishing vessel in the entire state still in active service. Launched in 1907, she was first used in the halibut fisheries of Puget Sound and the Bering Sea as the ''Annie J Larsen''. In 1925 she was purchased by the Alaska Glacier Seafood Company, refitted for shrimp trawling, and renamed ''Charles W'' in honor of owner Karl Sifferman's father. The company was one of the pioneers of the local shrimp fishery, a business it began to phase out due to increasing competition in the 1970s. The ''Charles W'' was the last of the company's fleet of ships, which numbered twelve at its height. The boat was acquired in 2002 by the nonprofit Friends of the ''Charles W''. The boat was listed on the National Register of Historic Place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |