|
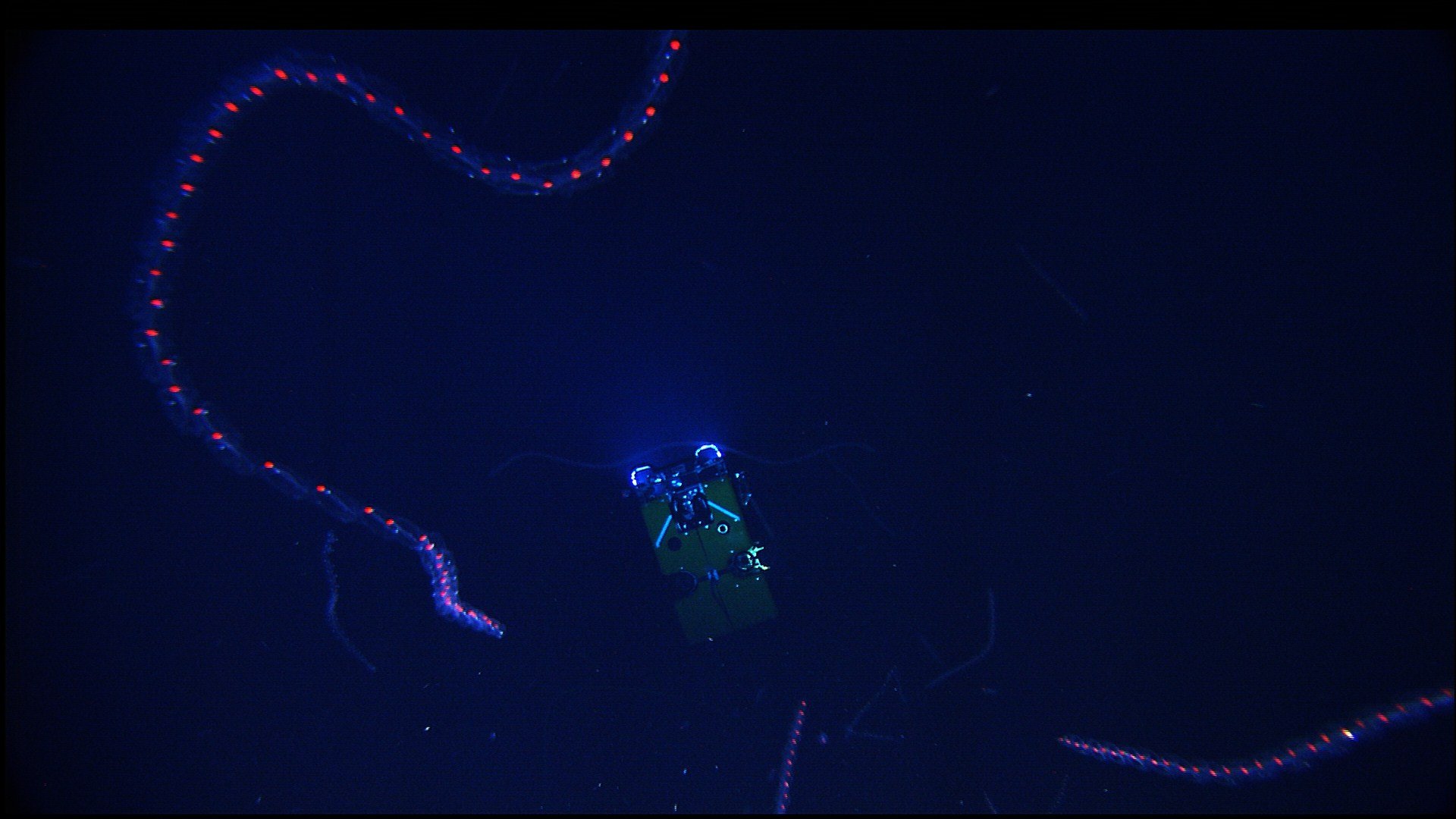
Forskalia Edwardsi
''Forskalia'' is a genus of siphonophores. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Forskaliidae. Species The following species are classified within the genus'' Forskalia'': * ''Forskalia asymmetrica'' Pugh, 2003 * ''Forskalia contorta'' (Milne-Edwards, 1841) * '' Forskalia edwardsi'' Kölliker, 1853 * '' Forskalia formosa'' Keferstein & Ehlers, 1860 * '' Forskalia saccula'' Pugh, 2003 * '' Forskalia tholoides'' Haeckel Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new sp ..., 1888 References Bioluminescent cnidarians Physonectae Cnidarian families {{Siphonophorae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Haeckel
Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new species, mapped a genealogical tree relating all life forms and coined many terms in biology, including ''ecology'', ''phylum'', ''phylogeny'', and '' Protista.'' Haeckel promoted and popularised Charles Darwin's work in Germany and developed the influential but no longer widely held recapitulation theory ("ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny") claiming that an individual organism's biological development, or ontogeny, parallels and summarises its species' evolutionary development, or phylogeny. The published artwork of Haeckel includes over 100 detailed, multi-colour illustrations of animals and sea creatures, collected in his '' Kunstformen der Natur'' ("Art Forms of Nature"), a book which would go on to influence the Art Nouveau artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Von Kölliker
Albert von Kölliker (born Rudolf Albert Kölliker'';'' 6 July 18172 November 1905) was a Swiss anatomist, physiologist, and histologist. Biography Albert Kölliker was born in Zurich, Switzerland. His early education was carried on in Zurich, and he entered the university there in 1836. After two years, however, he moved to the University of Bonn, and later to that of Berlin, becoming a pupil of noted physiologists Johannes Peter Müller and of Friedrich Gustav Jakob Henle. He graduated in philosophy at Zurich in 1841, and in medicine at Heidelberg in 1842. The first academic post which he held was that of prosector of anatomy under Henle, but his tenure of this office was briefin 1844 he returned to Zurich University to occupy a chair as professor extraordinary of physiology and comparative anatomy. His stay here was also brief; in 1847 the University of Würzburg, attracted by his rising fame, offered him the post of professor of physiology and of microscopical and compara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphonophore
Siphonophorae (from Greek ''siphōn'' 'tube' + ''pherein'' 'to bear') is an order within Hydrozoa, which is a class of marine organisms within the phylum Cnidaria. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the order contains 175 species thus far. Although a siphonophore may appear to be an individual organism, each specimen is in fact a colonial organism composed of medusoid and polypoid zooids that are morphologically and functionally specialized. Zooids are multicellular units that develop from a single fertilized egg and combine to create functional colonies able to reproduce, digest, float, maintain body positioning, and use jet propulsion to move. Most colonies are long, thin, transparent floaters living in the pelagic zone. Like other hydrozoans, some siphonophores emit light to attract and attack prey. While many sea animals produce blue and green bioluminescence, a siphonophore in the genus '' Erenna'' was only the second life form found to produce a red ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda.' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forskalia Asymmetrica
''Forskalia'' is a genus of siphonophores. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Forskaliidae. Species The following species are classified within the genus'' Forskalia'': * '' Forskalia asymmetrica'' Pugh, 2003 * ''Forskalia contorta'' (Milne-Edwards, 1841) * '' Forskalia edwardsi'' Kölliker, 1853 * '' Forskalia formosa'' Keferstein & Ehlers, 1860 * '' Forskalia saccula'' Pugh, 2003 * '' Forskalia tholoides'' Haeckel Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new sp ..., 1888 References Bioluminescent cnidarians Physonectae Cnidarian families {{Siphonophorae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Milne-Edwards
Henri Milne-Edwards (23 October 1800 – 29 July 1885) was an eminent French zoologist. Biography Henri Milne-Edwards was the 27th child of William Edwards, an English planter and colonel of the militia in Jamaica and Elisabeth Vaux, a Frenchwoman. Henri was born in Bruges, in present-day Belgium, where his parents had retired; Bruges was then a part of the newborn French Republic. His father had been jailed for several years for helping some Englishmen in their escape to their country. Henri spent most of his life in France. He was brought up in Paris by his older brother Guillaume Frederic Edwards (1777–1842), a distinguished physiologist and ethnologist. His father was released after the fall of Napoleon. The whole family then moved to Paris. At first he turned his attention to medicine, in which he graduated as an MD at Paris in 1823. His passion for natural history soon prevailed, and he gave himself up to the study of the lower forms of animal life. He became a stude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forskalia Edwardsi
''Forskalia'' is a genus of siphonophores. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Forskaliidae. Species The following species are classified within the genus'' Forskalia'': * ''Forskalia asymmetrica'' Pugh, 2003 * ''Forskalia contorta'' (Milne-Edwards, 1841) * '' Forskalia edwardsi'' Kölliker, 1853 * '' Forskalia formosa'' Keferstein & Ehlers, 1860 * '' Forskalia saccula'' Pugh, 2003 * '' Forskalia tholoides'' Haeckel Ernst Heinrich Philipp August Haeckel (; 16 February 1834 – 9 August 1919) was a German zoologist, naturalist, eugenicist, philosopher, physician, professor, marine biologist and artist. He discovered, described and named thousands of new sp ..., 1888 References Bioluminescent cnidarians Physonectae Cnidarian families {{Siphonophorae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Moritz Keferstein
Wilhelm Moritz Keferstein (7 June 1833, Winsen (Luhe) – 25 January 1870) was a German naturalist. He described a number of reptiles and amphibians for the first time. He originally studied hydraulic engineering in Hanover, later becoming a lecturer and professor of zoology at the University of Göttingen. With zoologist Ernst Ehlers (1835-1925), he wrote ''Zoologische Beiträge gesammelt im Winter 1859/60 in Neapel und Messina...'' in 1861. With Karl Wilhelm von Kupffer (1829-1902) he was co-author of a study on the electric organs of '' Gymnotus'' and ''Mormyrus'' that was published in Henle and Pfeufer's ''Zeitschrift für rationelle Medicin'' (Journal of rational medicine). He also made important contributions to Heinrich Georg Bronn's ''Die Klassen und Ordnungen des Thier-Reichs'' (Classes and Orders of the Animal Kingdom). Keferstein's tree frog is named after him (a species he described in 1868), as is a genus of polychaetes, ''Kefersteinia'' (family Hesionidae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Ehlers
Ernst Heinrich Ehlers (11 November 1835 – 31 December 1925) was a German zoologist born in Lüneburg. He studied medicine and natural sciences at the University of Göttingen, earning his doctorate in 1861. Here he was influenced by Rudolf Wagner (1805–1864) and Wilhelm Moritz Keferstein (1833–1870). In 1869 he became a full professor of zoology, comparative anatomy and veterinary medicine at the University of Erlangen. From 1874 to 1919, he was a professor of zoology and comparative anatomy in Göttingen. In 1890 he was one of the founders of the ''Deutschen Zoologischen Gesellschaft'' (German Zoological Society). He was a leading authority on polychaetes, and is credited with describing many invertebrate species new to science. The polychaete genus ''Ehlersia'' ( de Quatrefages, 1866) from the family Syllidae is named after him. Selected writings * ''Die Borstenwürmer (Annelida Chaetopoda) nach systematischen und anatomischen Untersuchungen dargestellt'', (1864-68) � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |