|
Formosa Expedition
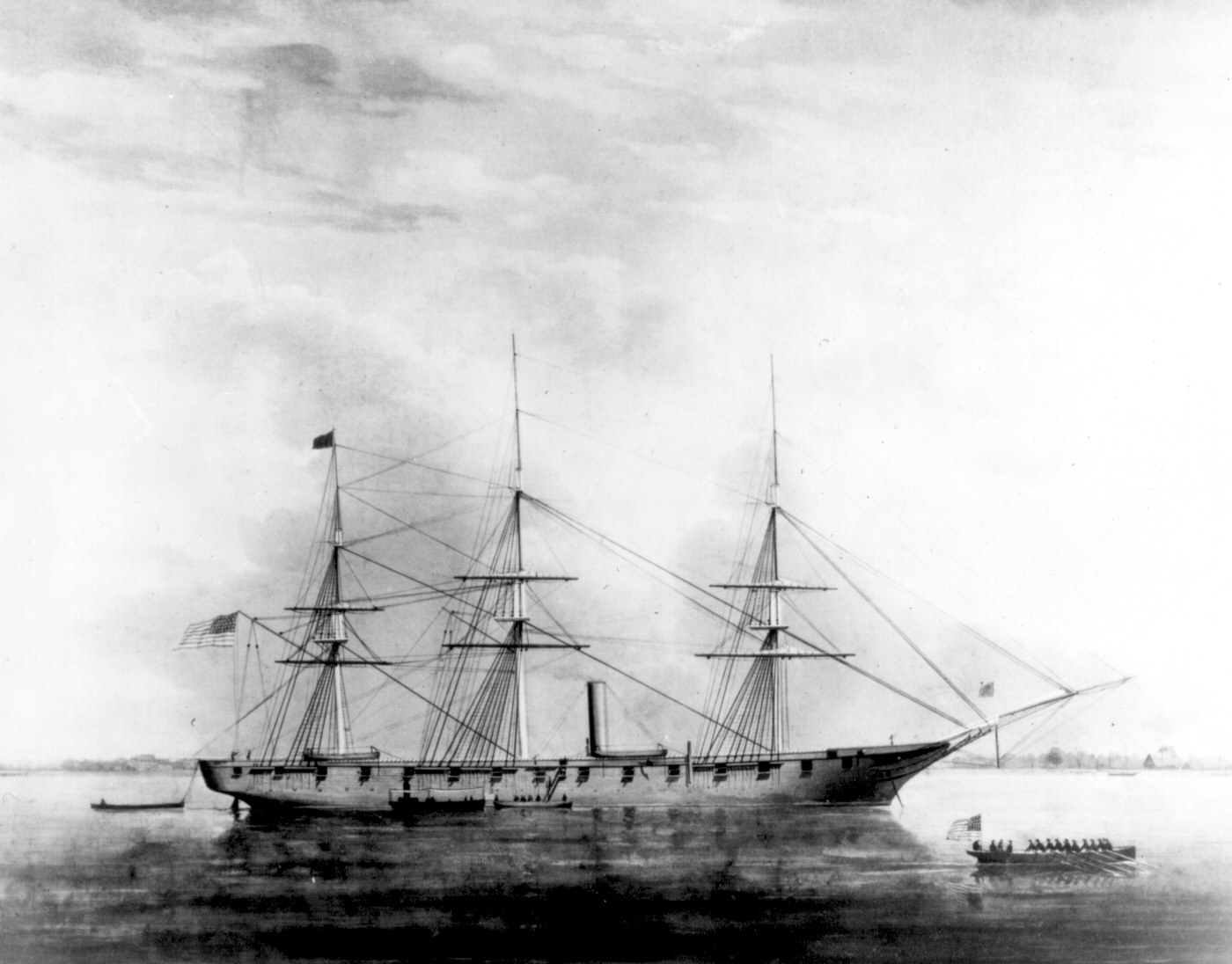
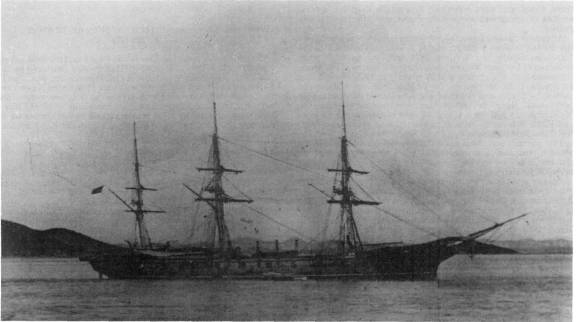
The Formosa Expedition (), or the Taiwan Expedition of 1867, was a punitive expedition launched by the United States against the Paiwan, an indigenous Taiwanese tribe. The expedition was undertaken in retaliation for the ''Rover'' incident, in which the ''Rover'', an American bark, was wrecked and its crew killed by Paiwan warriors in March 1867. A United States Navy and Marine company landed in southern Taiwan and attempted to advance into the Paiwan village. The Paiwan responded with guerrilla warfare, repeatedly ambushing, skirmishing, disengaging and retreating. Eventually, the Marines' commander was killed and they retreated to their ship due to fatigue and heat exhaustion, and the Paiwan dispersed and retreated into the jungle. The action is regarded as an American failure. Background On 12 March 1867, the United States merchantman ''Rover'' was sailing off Cape Eluanbi, the southernmost point of Taiwan, when she wrecked on an uncharted reef and began drifting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harper's Weekly
''Harper's Weekly, A Journal of Civilization'' was an American political magazine based in New York City. Published by Harper (publisher), Harper & Brothers from 1857 until 1916, it featured foreign and domestic news, fiction, essays on many subjects, and humor, alongside illustrations. It carried extensive coverage of the American Civil War, including many illustrations of events from the war. During its most influential period, it was the forum of the political cartoonist Thomas Nast. History Inception Along with his brothers James, John, and Wesley, Fletcher Harper began the publishing company Harper (publisher), Harper & Brothers in 1825. Following the successful example of ''The Illustrated London News'', Harper started publishing ''Harper's Magazine'' in 1850. The monthly publication featured established authors such as Charles Dickens and William Makepeace Thackeray, and within several years, demand for the magazine was great enough to sustain a weekly edition.Palmquis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Eluanbi
Cape Eluanbi or Oluanpi, also known by other names, is the southernmost point on the island of Taiwan. It is located in within the Hengchun Township in Pingtung County. Names ''Éluánbí'' is the pinyin romanization of the Mandarin pronunciation of its Chinese name These characters literally mean "Goose Bell Nose", but actually transcribe the local Hokkien pronunciation ''Gô-lôan'', used as a transliteration of the Paiwan ' ("sail"). This may be a reference to nearby Sail Rock. The "nose" in the name is a dialectical term for a cape, as in nearby Cape Maobitou. Under the Qing, it was sometimes known as "Linhaishan". Under Japanese rule, the cape was known as or Garanbi from the Japanese pronunciation of characters in Eluanbi. It is also sometimes known as or Oluanpi; as Gaw-loan-phi, Ngoluanpi, or from its Hokkien pronunciation; or as from its position. Geography Eluanbi is the southernmost point of the Hengchun Peninsula, making it the southernmost point on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloop-of-war
During the 18th and 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship of the Royal Navy with a single gun deck that carried up to 18 guns. The rating system of the Royal Navy covered all vessels with 20 or more guns; thus, the term encompassed all unrated warships, including List of gun-brigs of the Royal Navy, gun-brigs and Cutter (boat), cutters. In technical terms, even the more specialised bomb vessels and fire ships were classed by the Royal Navy as sloops-of-war, and in practice these were employed in the role of a sloop-of-war when not carrying out their specialised functions. In World War I and World War II, the Royal Navy reused the term "sloop" for specialised convoy-defence vessels, including the of the First World War and the highly successful of the Second World War, with anti-aircraft and anti-submarine capabilities. They performed similar duties to the destroyer escorts of the United States Navy, and also performed similar duties to the smaller corvettes of the Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screw Sloop
A screw sloop is a propeller-driven sloop-of-war. They were popularized in the mid-19th century, during the introduction of the steam engine and the transition of fleets to this new technology. The sailing sloop The British sloop in the Age of Sail In the Age of Sail, there was a large variety of terms to describe sailing vessels. In British English, the meaning of the term 'sloop' depends on the context. The main source of confusion about the term sloop, is that for commercial vessels, 'sloop' referred and refers to a vessel with a single mast rigged fore-and-aft. If the term referred to a British warship, its meaning was heavily dependent on the number of officers and men on the vessel. Under the rating system of the Royal Navy, any vessel that did not require a post-captain as commander was a sloop. This generally referred to all vessels with fewer than 20 guns. By this system, small frigates that lost most of their guns and sailors so they could be used as transports would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles William Le Gendre
Charles William or Guillaum Joseph Émile Le Gendre (August 26, 1830– September 1, 1899) was a French-born American officer and diplomat who served as advisor to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Empire of Japan from 1872 to 1875 and as advisor to Emperor Gojong of the Korean Empire from 1890 to 1899. Biography Early life Le Gendre was born in Oullins, France. He was the son of Jean-François Legendre-Héral, a noteworthy painter, sculptor and professor at the École de Beaux-Arts. Le Gendre was educated at the Royal College of Reims, but he eventually graduated from the University of Paris. At the age of 24, he married Clara Victoria Mulock in Brussels. She was the daughter of a well-known New York lawyer and soon after their marriage Le Gendre moved to the United States and became a naturalized citizen. Civil War military career With the outbreak of the American Civil War in 1861, Le Gendre helped recruit the 51st New York Volunteer Infantry; he was commissioned a maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiamen
Xiamen,), also known as Amoy ( ; from the Zhangzhou Hokkien pronunciation, zh, c=, s=, t=, p=, poj=Ē͘-mûi, historically romanized as Amoy, is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six District of the People's Republic of China, districts: Huli District, Huli, Siming District, Siming, Jimei District, Jimei, Tong'an, Haicang District, Haicang, and Xiang'an. All together, these cover an area of with a population of 5,163,970 as of 2020 Chinese census, 2020 and estimated at 5.35 million as of 31 December 2024. The urbanization in China, urbanized area of the city has spread from its original island to include most parts of all six of its District of the People's Republic of China, districts, as well as 4 Zhangzhou districts (Xiangcheng District, Zhangzhou, Xiangcheng, Longwen, Longhai District, Longhai and Changtai), which form a built-up area of 7,284,148 inhabitants. This area also connects with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuzhou
Fuzhou is the capital of Fujian, China. The city lies between the Min River (Fujian), Min River estuary to the south and the city of Ningde to the north. Together, Fuzhou and Ningde make up the Eastern Min, Mindong linguistic and cultural region. Fuzhou's population was 8,291,268 as of the 2020 Chinese census. Like other prefecture-level city, prefecture-level cities in China, its administrative area contains both urban and rural areas: in 2020, 72.49% of inhabitants (6,010,242) were urban, while 27.51% (2,281,026) were rural. As of 31 December 2018, the total population was estimated at 7,740,000 whom 4,665,000 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of five urban districts plus Minhou County. In 2015, Fuzhou was ranked as the 10th fastest growing metropolitan area in the world by Brookings Institution. Fuzhou is listed as No. 20 in the China Integrated City Index 2016's total ranking, a study conducted by the National Development and Reform Commission. Fuzhou is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies. History Pre-steam era In the age of sail, a gunboat was usually a small undecked vessel carrying a single smoothbore cannon in the bow, or just two or three such cannons. A gunboat could carry one or two masts or be oar-powered only, but the single-masted version of about length was most typical. Some types of gunboats carried two cannon, or else mounted a number of swivel guns on the railings. The small gunboat had advantages: if it only carried a single cannon, the boat could manoeuvre in shallow or restricted areas – such as rivers or lakes – where larger ships could sail only with difficulty. The gun that such boats carried could be quite heavy; a 32-pounder for instance. As such boats were cheap and quick to build, naval forces favoured swarm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Carson Febiger
John Carson Febiger (14 February 1821 – 9 October 1898) was a rear admiral of the United States Navy who served with the Union Navy during the American Civil War. Biography Febiger's father was the adopted son of American Revolutionary War soldier Christian Febiger. Febiger entered the United States Navy from Ohio as a midshipman on 14 September 1838, and was in the , of the Brazil Squadron, when she was wrecked in the Mozambique Channel off the eastern coast of Africa on 2 October 1842. He became passed midshipman on 20 May 1844, and lieutenant on 30 April 1853. He was on the of the East India Squadron 1858–1860, and on the sloop in 1861. On 11 August 1862, he was commissioned commander, and assigned to the steamer of the Western Gulf Blockading Squadron. After commanding various vessels in that and the Mississippi River Squadron, in 1864 he was given the , of the North Atlantic Squadron. In that steamer on 5 May 1864, he took part in the fight between the little flee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank as well as a job title in many army, armies. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries, this naval rank is termed as a frigate captain. Commander is also a generic term for an officer commanding any armed forces unit, such as "platoon leader, platoon commander", "brigade commander" and "Squadron (army), squadron commander". In the police, terms such as "borough commander" and "incident commander" are used. Commander as a naval and air force rank Commander is a rank used primarily in Navy, navies, and is very rarely used as a rank in army, armies. In most armies, the term "commander" is used as a job title. For example, in the US Army, an officer with the rank of captain (armed forces), captain (Ranks and insignia of NATO, NATO rank code OF-2) may hold the title of "company (military unit), company commander (United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a flag officer rank used by English-speaking navies. In most European navies, the equivalent rank is called counter admiral. Rear admiral is usually immediately senior to commodore and immediately below vice admiral. It is usually equivalent to the rank of major general in armies. In the U.S. Navy and some other navies, there are two rear admiral ranks. The term originated in the days of naval sailing squadrons and can trace its origins to the British Royal Navy. Each naval squadron was assigned an admiral as its head, who commanded from the centre vessel and directed the squadron's activities. The admiral would in turn be assisted by a vice admiral, who commanded the lead ships that bore the brunt of a battle. In the rear of the squadron, a third admiral commanded the remaining ships and, as this section was considered to be in the least danger, the admiral in command of it was typically the most junior. This has continued into the modern age, with rear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |