|
Foraminiferan
Foraminifera ( ; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonly an external shell (called a " test") of diverse forms and materials. Tests of chitin (found in some simple genera, and '' Textularia'' in particular) are believed to be the most primitive type. Most foraminifera are marine, the majority of which live on or within the seafloor sediment (i.e., are benthic, with different sized species playing a role within the macrobenthos, meiobenthos, and microbenthos), while a smaller number float in the water column at various depths (i.e., are planktonic), which belong to the suborder Globigerinina. Fewer are known from freshwater or brackish conditions, and some very few (nonaquatic) soil species have been identified through molecular analysis of small subunit ribosomal DNA. Foraminifera typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
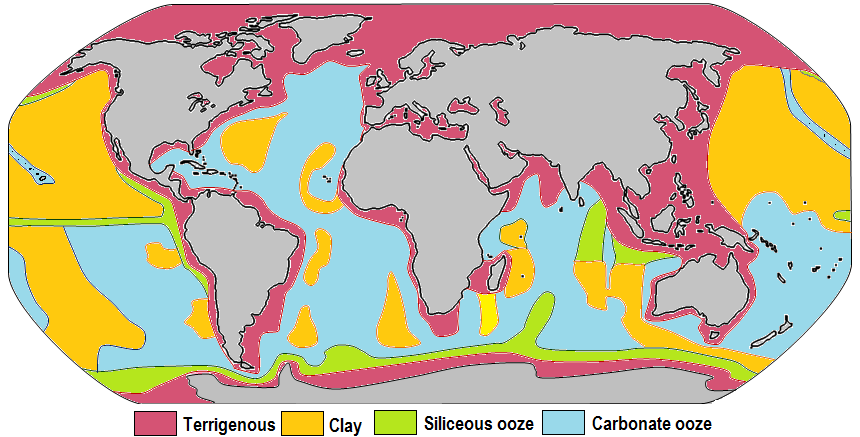
Seafloor Sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles either have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the sea, mainly by rivers but also by dust carried by wind and by the flow of glaciers into the sea, or they are biogenic deposits from marine organisms or from chemical precipitation in seawater, as well as from underwater volcanoes and meteorite debris. Except within a few kilometres of a mid-ocean ridge, where the volcanic rock is still relatively young, most parts of the seafloor are covered in sediment. This material comes from several different sources and is highly variable in composition. Seafloor sediment can range in thickness from a few millimetres to several tens of kilometres. Near the surface seafloor sediment remains unconsolidated, but at depths of hundreds to thousands of metres the sediment becomes lithified (turned to rock). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reticulomyxa
''Reticulomyxa'' is a monospecific genus of freshwater foraminiferans. The type species is the unicellular ''Reticulomyxa filosa''. It is found in freshwater environments as well as moist environments, like decomposing matter and damp soils. The heterotrophic naked foraminiferan can feed on microbes as well has larger organisms and is able to be sustained in culture by supplemented nutrients such as wheat germ and oats. The large, multinucleate foraminferan is characteristic for its lack of test and named for the network of connecting pseudopodia surrounding its central body mass. The organism has unique bidirectional cytoplasmic streaming throughout the anastomosing pseudopodia that is some of the fastest reported organelle transport observed. ''Reticulomyxa'' was first described in 1949 and is commonly used as a model organism for the unique transport of organelles throughout the cytoplasm of pseudopodia by cytoskeletal mechanisms. Only asexual reproduction of this genus has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allogromiida
The Allogromiida is an order of single-chambered, mostly organic-walled foraminiferans, including some that produce agglutinated tests (Lagynacea). Genetic studies indicate that some foraminiferans with agglutinated tests, previously included in the Textulariida or as their own order Astrorhizida, may also belong here. Allogromiids produce relatively simple tests, usually with a single chamber, similar to those of other protists such as '' Gromia''. They are found as both marine and freshwater forms, and are the oldest forms known from the fossil record. Genus * '' Allogromia'' References * * * Further reading * Foraminifera orders Monothalamea Extant Cambrian first appearances {{foram-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test (biology)
In biology, a test is the hard Seashell, shell of some spherical aquatic animals and protists, notably sea urchins and microorganisms such as testate foraminiferans, radiolarians, and testate amoebae. The term is also applied to the covering of scale insects. The related Latin term testa (botany), testa is used for the outer layer of the hard seed coat of plant seeds. Etymology The anatomical term "test" derives from the Latin word ''wikt:testa#Latin, testa'', which refers to an earthenware object, for example, a piece of pottery, a tile, or a potshard, and by extension, the mollusc shell, shell of a mollusc or a skull. Structure The test is a skeletal structure, made of hard material such as calcium carbonate, silica, chitin or composite materials. As such, it allows the protection of the internal organs and the attachment of soft flesh. The structure is notable for its Ambulacral, ambulacra, alternating in wide and narrow patterns. Small serrations, bumps, ridges or th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenophyophorea
Xenophyophorea is a clade of foraminiferans. Xenophyophores are multinucleate unicellular organisms found on the ocean floor throughout the world's oceans, at depths of . They are a kind of foraminiferan that extract minerals from their surroundings and use them to form an exoskeleton known as a Test (biology), test. They were first described by Henry Bowman Brady in 1883. They are abundant on abyssal plains, and in some regions are the dominant species. Fifteen genus, genera and 75 species have been described, varying widely in size. The largest, ''Syringammina fragilissima'', is among the largest known coenocytes, reaching up to in diameter. Naming and classification The name Xenophyophora means "bearer of foreign bodies", from the Greek language , Greek. This refers to the sediments, called xenophyae, which are cemented together to construct their Test (biology) , tests. In 1883, Henry Bowman Brady classified them as primitive Foraminifera. Later they were placed within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicellular Organism
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are classified into bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular such as protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi. Unicellular organisms are thought to be the oldest form of life, with early organisms emerging 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Although some prokaryotes live in colonies, they are not specialised cells with differing functions. These organisms live together, and each cell must carry out all life processes to survive. In contrast, even the simplest multicellular organisms have cells that depend on each other to survive. Most multicellular organisms have a unicellular life-cycle stage. Gametes, for example, are reprodu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (biology)
In biological classification, class () is a taxonomic rank, as well as a taxonomic unit, a taxon, in that rank. It is a group of related taxonomic orders. Other well-known ranks in descending order of size are domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class ranking between phylum and order. History The class as a distinct rank of biological classification having its own distinctive name – and not just called a ''top-level genus'' ''(genus summum)'' – was first introduced by French botanist Joseph Pitton de Tournefort in the classification of plants that appeared in his '' Eléments de botanique'' of 1694. Insofar as a general definition of a class is available, it has historically been conceived as embracing taxa that combine a distinct ''grade'' of organization—i.e. a 'level of complexity', measured in terms of how differentiated their organ systems are into distinct regions or sub-organs—with a distinct ''type'' of construction, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagenida
Lagenida is an order of benthic foraminiferal rhizaria in which the tests (shells) are monolamellar, with walls composed of optically and ultra-structurally radiate calcite, with the crystallographic c-axes perpendicular to the surface. Lagenids first appear in the Upper Silurian and continue to the Recent. They are currently divided into two superfamilies, the older Robuloidacea which range from the Upper Silurian to the Lower Cretaceous (Albian) and the younger Nodosariacea, ranging from the Permian to Recent. Taxonomic history Lagenida (suborder Lagenina in Loeblich and Tappan 1988) is an emendation of the rotaliid superfamily Nodosariacea, removing it from the Rotaliina in the ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology'' (Loeblich and Tappan, 1964) and combining it with the Robuloidacea, named by Reiss, 1963, to form a new order Lagenida. Robuloidacea includes families previously included in the Fusulinida The Fusulinida is an extinct order within the Foraminifera in whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about eight phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships among phyla within larger clades like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectoplasm (cell Biology)
Ectoplasm (also exoplasm) is the non- granulated outer part of a cell's cytoplasm, while endoplasm is its often granulated inner layer. It is clear, and protects as well as transports things within the cell. Moreover, large numbers of actin filaments frequently occur in the ectoplasm, which form an elastic support for the cell membrane. It contains actin and myosin microfilaments. Amoebae form an outer zone of cytoplasm, known as ectoplasm, where actin and myosin association help move it forward. The term comes from the Ancient Greek words ἐκτός ''ektos'', "outside" and πλάσμα ''plasma'', "anything formed." See also * Cytoplasm The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ... * Endoplasm References Cell anatomy {{cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizaria
The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich clade of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus '' Paulinella'' in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many Foraminifera and Radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, ''Guttulinopsis vulgaris'', a cellular slime mold, has been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon. Being described mainly from rDNA sequences, they vary considerably in form, having no clear morphological distinctive characters ( synapomorphies), but for the most part they are amoeboids with filose, reticulose, or microtubule-supported pseudopods. In the absence of an apomorphy, the group is ill-defined, and its composition has been very fluid. Some Rhizaria possess mineral exoskeletons ( thecae or loricas), which are in diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |