|
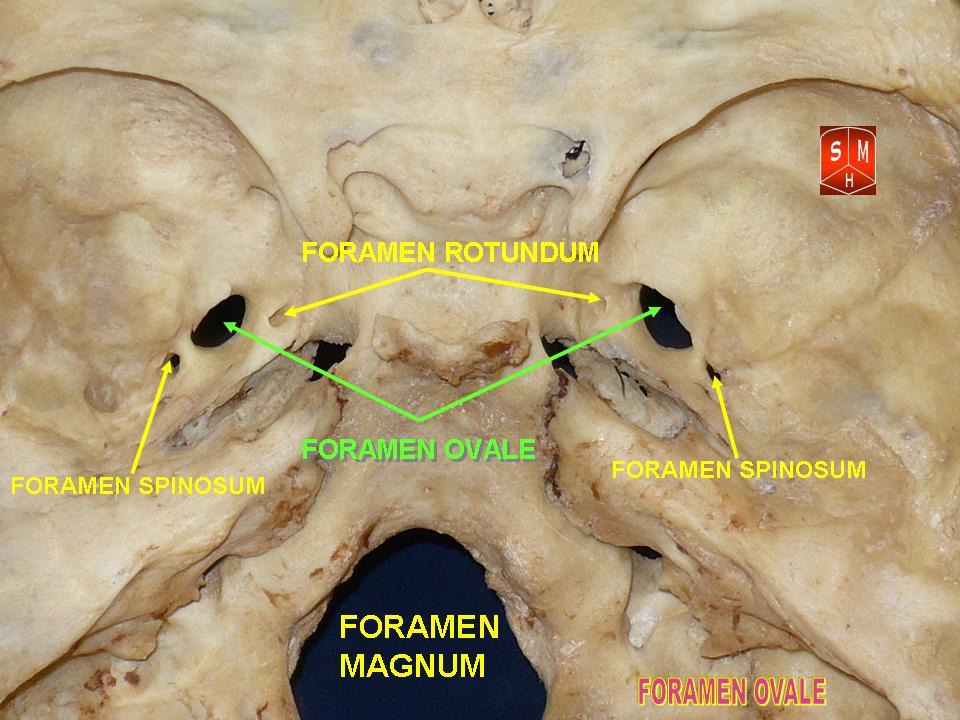
Foramen Ovale (skull)
The foramen ovale (En: oval window) is a hole in the posterior part of the sphenoid bone, posterolateral to the foramen rotundum. It is one of the larger of the several holes (the foramina) in the skull. It transmits the mandibular nerve, a branch of the trigeminal nerve. Structure The foramen ovale is an opening in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. The foramen ovale is one of two cranial foramina in the greater wing, the other being the foramen spinosum. The foramen ovale is posterolateral to the foramen rotundum and anteromedial to the foramen spinosum. Posterior and medial to the foramen is the opening for the carotid canal. Contents The following structures pass through foramen ovale: * mandibular nerve (CN V) (a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)) *accessory meningeal artery * lesser petrosal nerve (a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve) * an emissary vein connecting the cavernous sinus with the pterygoid plexus * (occasionally) meningeal branch o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoid Bone
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit (anatomy), orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly, bat or wasp with its wings extended. The name presumably originates from this shape, since () means in Ancient Greek. Structure It is divided into the following parts: * a median portion, known as the body of sphenoid bone, containing the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland as well as the paired paranasal sinuses, the sphenoidal sinuses * two Greater wing of sphenoid bone, greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two Lesser wing of sphenoid bone, lesser wings from the anterior side. * Pterygoid processes of the sphenoides, directed downwards from the junction of the body and the greater wings. Two sphenoidal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Meningeal Artery
Accessory may refer to: * Accessory (legal term), a person who assists a criminal In anatomy * Accessory bone * Accessory breast * Accessory kidney * Accessory muscle * Accessory nucleus, in anatomy, a cranial nerve nucleus * Accessory nerve * Accessory spleen In arts and entertainment * Accessory (band), with members Dirk Steyer and Ivo Lottig * Video game accessory, a piece of hardware used in conjunction with a video game console for playing video games * Accessories (album), ''Accessories'' (album), a compilation album from Dutch alternative rock band The Gathering * Accessory, a type of List of Dungeons & Dragons rulebooks, rulebook in ''Dungeons & Dragons'' and other role-playing games Other uses * Fashion accessory, an item used to complement a fashion or style * Accessory suite, a secondary dwelling on a parcel of land * Rental accessories and attachments, accessories used in the rental industry * Cable accessories for connecting and terminating cables * Accessory fruit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, language comprehension, and emotion association. ''Temporal'' refers to the head's temples. Structure The temporal lobe consists of structures that are vital for declarative or long-term memory. Declarative (denotative) or explicit memory is conscious memory divided into semantic memory (facts) and episodic memory (events). The medial temporal lobe structures are critical for long-term memory, and include the hippocampal formation, perirhinal cortex, parahippocampal, and entorhinal neocortical regions. The hippocampus is critical for memory formation, and the surrounding medial temporal cortex is currently theorized to be critical f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN or TGN), also called Fothergill disease, tic douloureux, trifacial neuralgia, is a chronic pain, long-term pain disorder that affects the trigeminal nerve, the nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing. It is a form of neuropathic pain. There are two main types: typical and atypical trigeminal neuralgia. The typical form results in episodes of severe, sudden, shock-like pain in one side of the face that lasts for seconds to a few minutes. Groups of these episodes can occur over a few hours. The atypical form results in a constant burning pain that is less severe. Episodes may be triggered by any touch to the face. Both forms may occur in the same person. Pain from the disease has been linked to mental health issues, especially depression (mood), depression. The exact cause is unknown, but believed to involve loss of the myelin of the trigeminal nerve. This might occur due to Nerve compression syndrome, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningeal Branch Of The Mandibular Nerve
The meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve (also known as the nervus spinosus) is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that enters the middle cranial fossa through either the foramen spinosum or foramen ovale to innervate the meninges of this fossa as well as the mastoid air cells. Anatomy Branches It divides into two branches - anterior and posterior - which accompany the main divisions of the middle meningeal artery and supply the dura mater: * The ''anterior branch'' communicates with the meningeal branch of the maxillary nerve. * The ''posterior branch'' also supplies the mucous lining of the mastoid cells The mastoid cells (also called air cells of Lenoir or mastoid cells of Lenoir) are air-filled cavities within the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the cranium. The mastoid cells are a form of skeletal pneumaticity. Infection in these cells .... References External links Overview at tufts.edu* Mandibular nerve Meninges {{Neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pterygoid Plexus
The pterygoid plexus (; in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary '. from ''pteryx'', "wing" and ''eidos'', "shape") is a fine venous plexus upon and within the . It drains by a short maxillary vein. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavernous Sinus
The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica. Structure The cavernous sinus is one of the dural venous sinuses of the head. It is a network of veins that sit in a cavity. It sits on both sides of the sphenoidal bone and pituitary gland, approximately 1 × 2 cm in size in an adult. The carotid siphon of the internal carotid artery, and cranial nerves III, IV, V (branches V1 and V2) and VI all pass through this blood filled space. Both sides of cavernous sinus are connected to each other via intercavernous sinuses. The cavernous sinus lies in between the inner and outer layers of dura mater. Nearby structures * Above: optic tract, optic chiasma, internal carotid artery. * Inferiorly: foramen lacerum, and the junction of the body and greater wing of sphenoid bone. * Medially: p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emissary Vein
The emissary veins connect the extracranial venous system with the intracranial venous sinuses. They connect the veins outside the cranium to the venous sinuses inside the cranium. They drain from the scalp, through the skull, into the larger meningeal veins and dural venous sinuses. They may also connect to diploic veins within the skull. Emissary veins have an important role in selective cooling of the head. They also serve as routes where infections are carried into the cranial cavity from the extracranial veins to the intracranial veins. There are several types of emissary veins including the posterior condyloid, mastoid, occipital and parietal emissary veins. Structure There are also emissary veins passing through the foramen ovale, jugular foramen, foramen lacerum, and hypoglossal canal. Function Because the emissary veins are valveless, they are an important part in selective brain cooling through bidirectional flow of cooler blood from the evaporating surface of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foramen Petrosum
The lesser petrosal nerve (also known as the small superficial petrosal nerve) is the general visceral efferent (GVE) nerve conveying pre-ganglionic parasympathetic secretomotor fibers for the parotid gland from the tympanic plexus to the otic ganglion (where they synapse). It passes out of the tympanic cavity through the petrous part of the temporal bone into the middle cranial fossa of the cranial cavity, then exits the cranial cavity through its own canaliculus to reach the infratemporal fossa. Cell bodies of the lesser petrosal nerve are situated in the inferior salivatory nucleus, and are conveyed first by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) and then by the tympanic nerve to the tympanic plexus. Structure Course The nucleus of the lesser petrosal nerve is the inferior salivatory nucleus. The lesser petrosal nerve may be considered a continuation of the tympanic nerve. After arising in the tympanic plexus, the lesser petrosal nerve passes anterior-ward, then through th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossopharyngeal Nerve
The glossopharyngeal nerve (), also known as the ninth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IX, or simply CN IX, is a cranial nerve that exits the brainstem from the sides of the upper Medulla oblongata, medulla, just anterior (closer to the nose) to the vagus nerve. Being a mixed nerve (sensorimotor), it carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the Basal plate (neural tube), basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, whereas the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest. Structure From the anterior portion of the medulla oblongata, the glossopharyngeal nerve passes laterally across or below the Flocculus (cerebellar), flocculus, and leaves the skull through the central part of the jugular foramen. From the superior and inferior ganglia in jugular foramen, it has its own sheath of dura mater. The inferior ganglion on the inferior surface of petrous part of temporal is related with a tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Petrosal Nerve
The lesser petrosal nerve (also known as the small superficial petrosal nerve) is the general visceral efferent (GVE) nerve conveying pre-ganglionic parasympathetic secretomotor fibers for the parotid gland from the tympanic plexus to the otic ganglion (where they synapse). It passes out of the tympanic cavity through the petrous part of the temporal bone into the middle cranial fossa of the cranial cavity, then exits the cranial cavity through its own canaliculus to reach the infratemporal fossa. Cell bodies of the lesser petrosal nerve are situated in the inferior salivatory nucleus, and are conveyed first by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) and then by the tympanic nerve to the tympanic plexus. Structure Course The nucleus of the lesser petrosal nerve is the inferior salivatory nucleus. The lesser petrosal nerve may be considered a continuation of the tympanic nerve. After arising in the tympanic plexus, the lesser petrosal nerve passes anterior-ward, then through th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Canal
The carotid canal is a passage in the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull through which the internal carotid artery and its internal carotid (nervous) plexus pass from the neck into (the middle cranial fossa of) the cranial cavity. Observing the trajectory of the canal from exterior to interior, the canal is initially directed vertically before curving anteromedially to reach its internal opening. Anatomy The carotid canal has two openings, namely internal and external openings. It is divided in three parts, namely, ascending petrous, transverse petrous, and ascending cavernous parts. Boundaries The carotid canal opens into the middle cranial fossa, at the petrous part of the temporal bone. Anteriorly, it is limited by posterior margin of the greater wing of sphenoid bone. Posteromedially, it is limited by basilar part of occipital bone. Relations The external opening of carotid canal (Latin: "''apertura externa canalis carotici''") is located upon the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |