|
Folkung
In modern Swedish, Folkung has two meanings, which appear to be opposites: # The medieval " House of Bjälbo" in Sweden Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ..., which produced several Swedish statesmen and kings. # A group of people (singular ''Folkunge'', plural ''Folkungar''), who were at times in political opposition to the same House of Bjälbo. This "political party" fought for the ancient right of free men to elect the kings in Sweden. Until the 17th century, ''Folkunge'' was used only with the second meaning. However, many of these political opponents were also said to have been descendants of Jarl Folke the Fat (from the House of Bjälbo), who lived before the family became royal. Hence, in the 17th century, the whole family, then already extinct and without a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Folkung Uprising
The Second Folkung Uprising ( Swedish: ''Andra Folkungaupproret,'' Danish: ''Andet Folkungsoprør,'' German: ''Zweiter Folkung-Aufstand''; 1251) was a revolt performed by the Folkungs with support from Danish and German soldiers. A dissatisfaction had built up among the insurgents, and after most likely failing the first uprising against Sweden the Folkungs, led by Filip Knutsson, made a second attempt. Unfortunately, the uprising was defeated once again. After the attempt of recruiting soldiers from Norway which wasn’t appreciated, Filip Knutsson and Knut Magnusson requested German and Danish knights to join their revolt against Sweden and the regent, Birger Jarl. In the Battle of Herrevadsbro'','' the insurgents met Birger Jarl in desire of defeating him. The leaders of the uprising eventually were executed on demand by Birger. Prelude Even though Birger Jarl was good at not bringing jealously to the Folkung league over his power and authority as a regent, it still tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Folkung Uprising
The Third Folkung Uprising ( Swedish: ''Tredje'' ''Folkungaupproret''; 1278–1280) was the last uprising known for the political power of the Folkungs. The insurgents, who were led by the known Folkung Johan Filipsson, started the revolt in hopes to end the leadership of Sweden's current King, Magnus Ladulås. At first the uprising was successful. Queen Helvig was forced to seek refuge in a monastery and the queen’s father was taken prisoner and brought to a Folkung castle. A knight who had a good relation to the Swedish king had also been killed at the castle in Jönköping. It's also said that troops of the Folkungs attacked Norway during the period, which resulted in the Norwegians Norwegians () are an ethnic group and nation native to Norway, where they form the vast majority of the population. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegians are descended from the Norsemen, Norse of the Early ... summoning their fleet. The rebelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
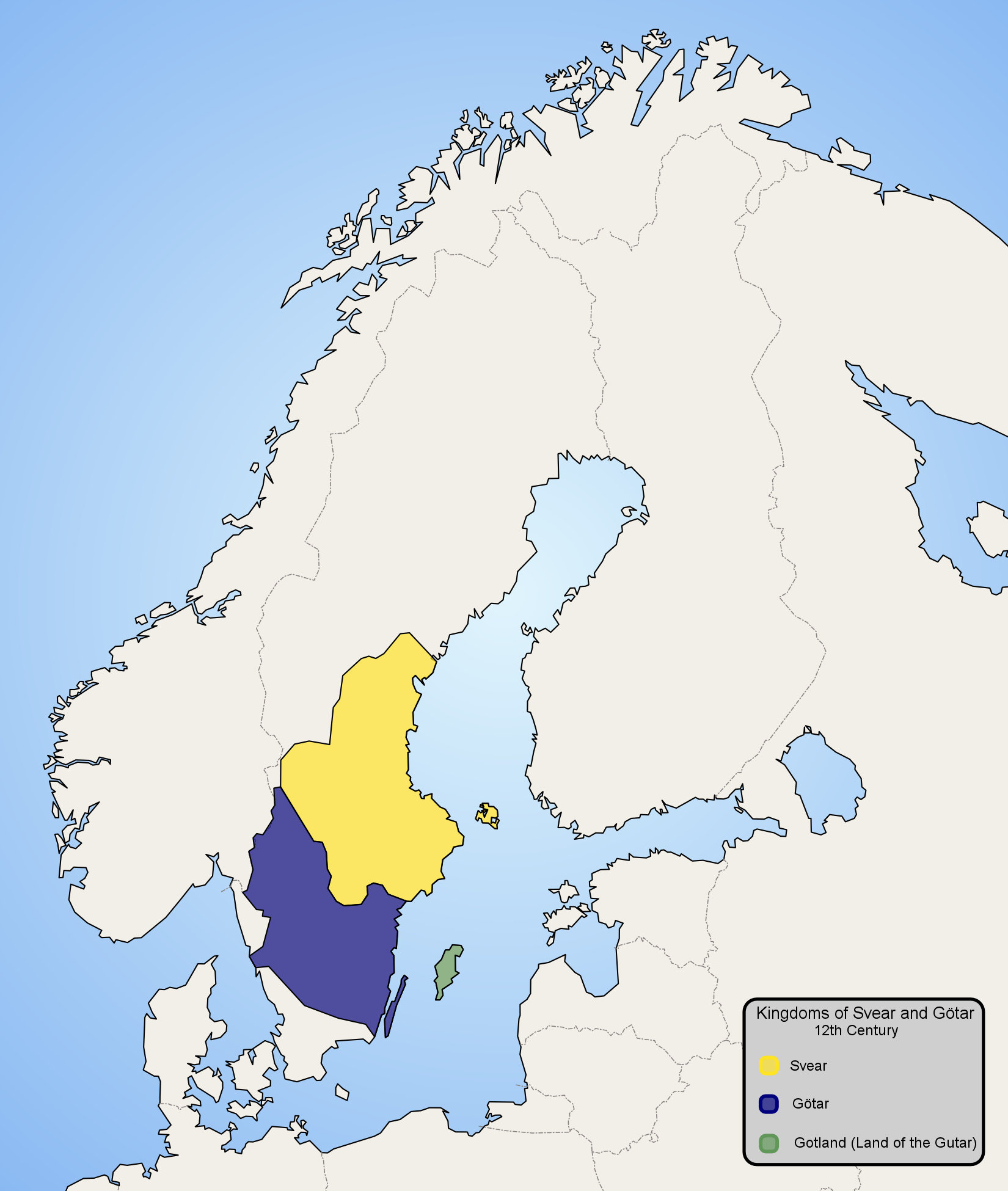
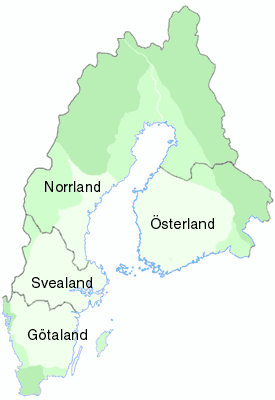
Götaland
Götaland (; also '' Gothia'', ''Gothland'', ''Gothenland'' or ''Gautland'') is one of three lands of Sweden and comprises ten provinces. Geographically it is located in the south of Sweden, bounded to the north by Svealand, with the deep woods of Tiveden, Tylöskog and Kolmården marking the border. Götaland once consisted of petty kingdoms, and their inhabitants were called ''Gautar'' in Old Norse. However, the term mainly referred to the population of modern Västergötland. It is agreed that these were the same as the ''Geats'', the people of the hero Beowulf in England's national epic, ''Beowulf''. The modern state of Sweden started forming when some provinces of Götaland gradually became more and more politically intertwined with those of Svealand. This process can be traced back to at least the 10th century, and would continue for several hundred years. Other parts of modern Götaland were at that time either Danish or Norwegian. The province of Småland, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th Century In Sweden
In music or music theory, a thirteenth is the Musical note, note thirteen scale degrees from the root (chord), root of a chord (music), chord and also the interval (music), interval between the root and the thirteenth. The thirteenth is most commonly major or minor . A thirteenth chord is the stacking of six (major third, major or minor third, minor) thirds, the last being above the 11th of an eleventh chord. Thus a thirteenth chord is a tertian (built from thirds) chord containing the interval of a thirteenth, and is an extended chord if it includes the ninth and/or the eleventh. "The jazzy thirteenth is a very versatile chord and is used in many genres." Since 13th chords tend to become unclear or confused with other chords when Inverted chord, inverted, they are generally found in root position. For example, depending on voicing (music), voicing, a major triad with an added major sixth (chord), sixth is usually called a sixth chord , because the sixth serves as a sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consolidation Of Sweden
Consolidation may refer to: In science and technology * Consolidation (computing), the act of linkage editing in computing * Consolidation (locomotive), popular name of a steam locomotive with a 2-8-0 wheel arrangement * Consolidation (soil), a geological process whereby a soil decreases in volume * Consolidation ratio, the number of virtual servers that can run on each physical host machine * Mathematical consolidation, the fusion of diverse theories into one * Memory consolidation, the process in the brain by which recent memories are crystallised into long-term memory * Pulmonary consolidation, a clinical term for solidification into a firm dense mass * Semiconductor consolidation, the trend of semiconductor companies collaborating * Ultrasonic consolidation, a manufacturing technique for metals In economics * Consolidation (business), the mergers or acquisitions of many smaller companies into much larger ones ** Consolidation (media), consolidation of United States me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sparrsätra
The Battle of Sparrsätra was fought in 1247 between the forces of King Eric XI of Sweden and rebels led by Holmger Knutsson near Enköping in Sweden. It occurred during a poorly documented period in Swedish history; as a result, many details are uncertain and conjectural. Although it was not the end of the Folkung rebellion, many scholars consider it to have marked the end of the old order, leading to the Uppland Swedes' loss of their semi-aristocratic status, and to the beginning of taxation by the King. Background Since pre-historic times the Swedes of Uppland had elected the king of Sweden, and their responsibility towards him lay not in paying taxes, but in providing warriors and ships for the leidang organization. Many scholars consider the reasons for the battle to have been the abolition of the leidang organization and its replacement with monetary taxes. The people of Uppland also appear to have refused to pay tithes to the church.Lindström & Lindström 2006, p.151 T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canute II Of Sweden
Cnut ( ; ; – 12 November 1035), also known as Canute and with the epithet the Great, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norway from 1028 until his death in 1035. The three kingdoms united under Cnut's rule are referred to together as the North Sea Empire by historians. As a Danish prince, Cnut won the throne of England in 1016 in the wake of centuries of Viking activity in northwestern Europe. His later accession to the Danish throne in 1018 brought the crowns of England and Denmark together. Cnut sought to keep this power base by uniting Danes and English under cultural bonds of wealth and custom. After a decade of conflict with opponents in Scandinavia, Cnut claimed the crown of Norway in Trondheim in 1028. In 1031, Malcolm II of Scotland also submitted to him, though Anglo-Norse influence over Scotland was weak and ultimately did not last by the time of Cnut's death.ASC, Ms. D, s.a. 1031. Dominion of England lent the Danes an importa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svealand
Svealand (), or Swealand, is the historical core region of Sweden. It is located in south-central Sweden and is one of the three historical lands of Sweden, bounded to the north by Norrland and to the south by Götaland. Deep forests, Tiveden, Tylöskog, and Kolmården, separated Svealand from Götaland. Historically, its inhabitants were called , from which is derived the English 'Swedes'. Svealand consists of the capital region Mälardalen in the east, Roslagen in the north-east, the former mining district Bergslagen in the center, and Dalarna and Värmland in the west. It includes an extensive archipelago of thousands of small islands in Södermanland and Uppland and has lakeshores on the four largest lakes in the country. In the interior, there are several ski resorts in the southern parts of the Scandinavian Mountains. Two large rivers run through Svealand. Klarälven originates in Norway and enters lake Vänern through Värmland, whereas Dalälven runs from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Language
Swedish ( ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, spoken predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland. It has at least 10 million native speakers, making it the Germanic_languages#Statistics, fourth most spoken Germanic language, and the first among its type in the Nordic countries overall. Swedish, like the other North Germanic languages, Nordic languages, is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian language, Norwegian and Danish language, Danish, although the degree of mutual intelligibility is dependent on the dialect and accent of the speaker. Standard Swedish, spoken by most Swedes, is the national language that evolved from the Central Swedish dialects in the 19th century, and was well established by the beginning of the 20th century. While distinct regional Variety ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petty Kingdom
A petty kingdom is a kingdom described as minor or "petty" (from the French 'petit' meaning small) by contrast to an empire or unified kingdom that either preceded or succeeded it (e.g. the numerous kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England unified into the Kingdom of England in the 10th century, or the numerous Gaelic kingdoms of Ireland as the Kingdom of Ireland in the 16th century). Alternatively, a petty kingdom would be a minor kingdom in the immediate vicinity of larger kingdoms, such as the medieval Kingdom of Mann and the Isles relative to the kingdoms of Scotland or England or the Viking kingdoms of Scandinavia. In the parallel mainland Southeast Asian political model, petty kingdoms were known as ''mueang''. By the European High Middle Ages, many post-Roman Early Middle Ages petty kingdoms had evolved into principalities, grand duchies, or duchies. By the European Early Modern era, many of these principalities had been mediatized into larger monarchies, but the ruling fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folke The Fat
Folke the Fat (), according to ''Gesta Danorum'' by the 12th century Danish chronicler Saxo Grammaticus, was the most powerful man in Sweden around 1100. He married Ingegerd Knutsdotter of Denmark, daughter of the Danish king Canute IVThe article Folkunga-ätten' in ''Nordisk familjebok'' (1908).] who was murdered in 1086. Folke and Ingrid had the sons Knut and Bengt Snivil, Benedict according to Saxo. The chronicler furthermore reports that Folke was the paternal grandfather of Birger Brosa, who was still alive at the time of writing. See also * House of Bjälbo * Folkung In modern Swedish, Folkung has two meanings, which appear to be opposites: # The medieval " House of Bjälbo" in Sweden Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in ... Notes References American pictures - Genealogy of Folke(contains disputed claims) Swedish politicians 11th-century Swedish people House of Bj� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |