|
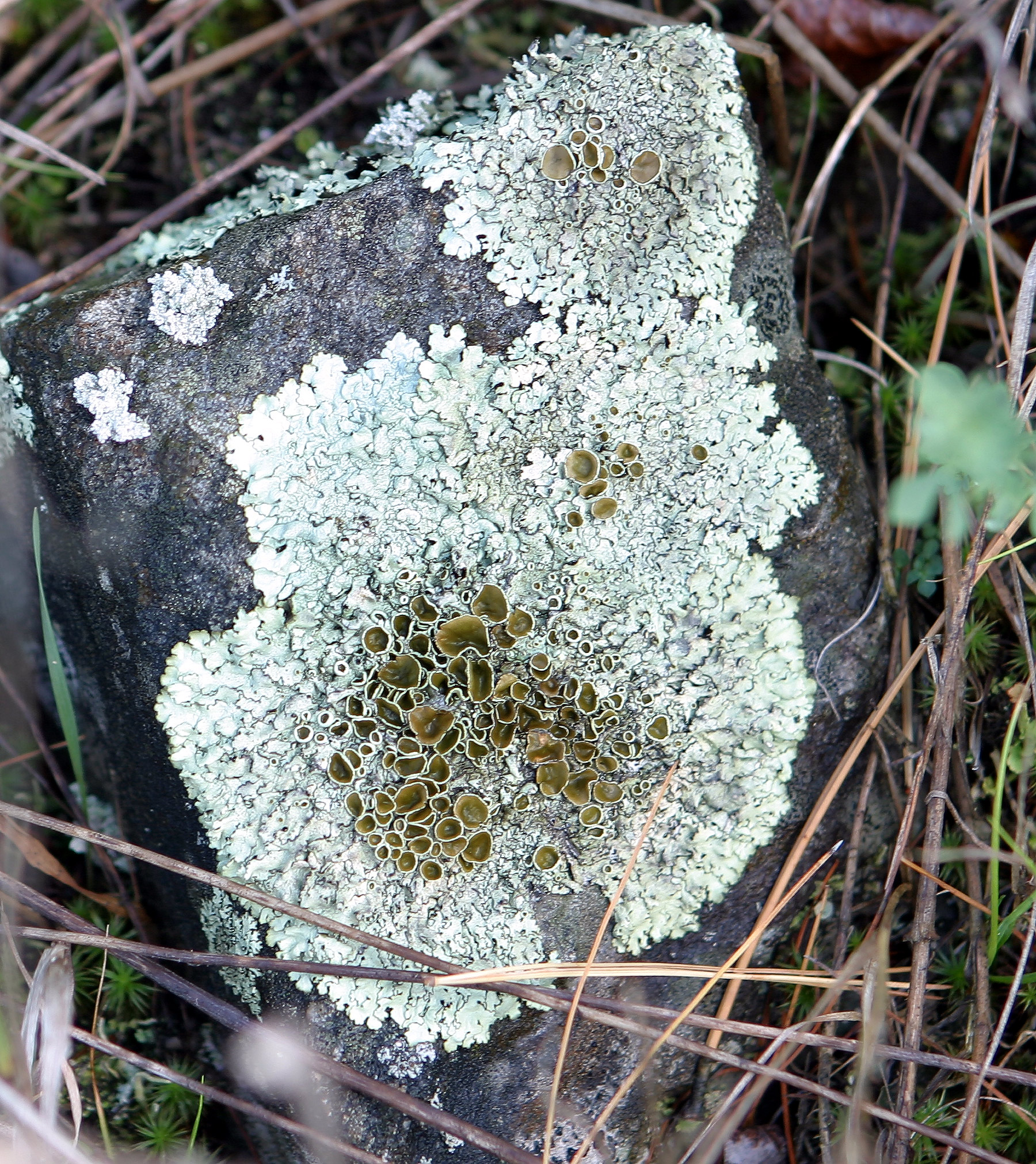
Foliose
A foliose lichen is a lichen with flat, leaf-like , which are generally not firmly bonded to the substrate on which it grows. It is one of the three most common lichen growth forms, growth forms of lichens. It typically has distinct upper and lower surfaces, each of which is usually covered with a cortex (botany), cortex; some, however, lack a lower cortex. The photobiont layer lies just below the upper cortex. Where present, the lower cortex is usually dark (sometimes even black), but occasionally white. Foliose lichens are attached to their substrate either by hyphae extending from the cortex or , or by root-like structures called . The latter, which are found only in foliose lichens, come in a variety of shapes, the specifics of which can aid in species identification. Some foliose lichens attach only at a single stout peg called a , typically located near the lichen's centre. Lichens with this structure are called "umbilicate". In general, medium to large epiphytic foliose lic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen Cross Section Diagram
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. . Lichens are the lifeform that first brought the term symbiosis (as ''Symbiotismus'') into biological context. Lichens have since been recognized as important actors in nutrient cycling and producers which many higher trophic feeders feed on, such as reindeer, gastropods, nematodes, mites, and springtails. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
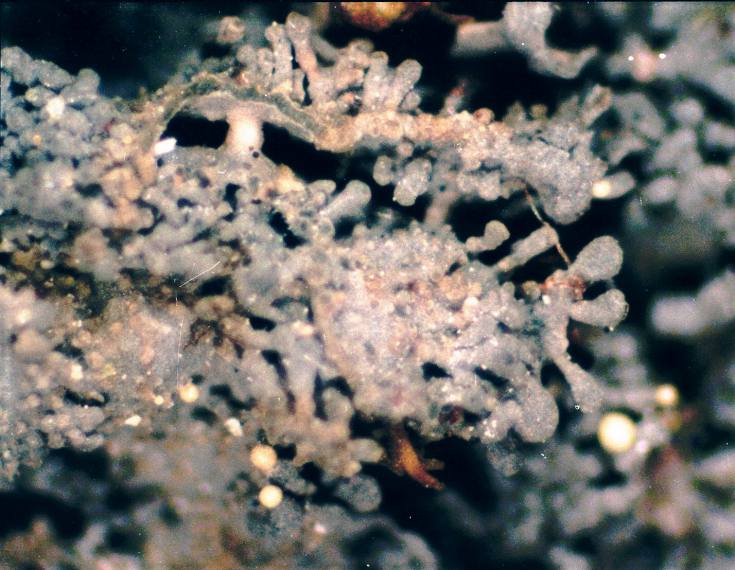
Lichen Growth Forms
Lichens are symbiotic organisms made up of multiple species: a fungus, one or more photobionts (an alga and/or a cyanobacteria) and sometimes a yeast. They are regularly grouped by their external appearance – a characteristic known as their growth form. This form, which is based on the appearance of vegetative part of the lichen (its thallus), varies depending on the species and the environmental conditions it faces. Those who study lichens ( lichenologists) have described a dozen of these forms: areolate, byssoid, calicioid, cladoniform, crustose, filamentous, foliose, fruticose, gelatinous, leprose, placodioid and squamulose. Traditionally, crustose (flat), foliose (leafy) and fruticose (shrubby) are considered to be the three main forms. In addition to these more formalised, traditional growth types, there are a handful of informal types named for their resemblance to the lichens of specific genera. These include alectorioid, catapyrenioid, cetrarioid, hypogymnioid, parm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isidium
An isidium (plural: isidia) is a tiny, wart- or finger-like outgrowth on the thallus surface of certain lichen species. It is one of two principal types of vegetative reproductive structures in lichens, the other being soredia. Each isidium contains both fungal and algal partners and is wrapped in a thin protective layer (the ), distinguishing it from soredia, which lack this covering. While both function in vegetative reproduction, the heavier, corticate structure of isidia means they tend to establish in microhabitats close to the parent thallus, often favouring stable, humid niches where mechanical protection improves survival. Unlike spores, which are microscopic and easily carried over long distances by wind, isidia are larger, multicellular fragments that rely on external forces such as wind, rain, or animal contact, but typically disperse over much shorter ranges. Isidia are morphologically diverse, ranging from spherical and cylindrical to club-shaped or scale-like, typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavoparmelia Caperata - Lichen - Caperatflechte
''Flavoparmelia'' is a genus of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. Because of their appearance, they are commonly known as greenshield lichens. The widely distributed genus contains about 40 species. Taxonomy The genus was circumscribed by the American lichenologist Mason Hale in 1986 to contain 17 former '' Pseudoparmelia'' species with broad , usnic acid in the cortex, and isolichenan in the cell walls. Description ''Flavoparmelia'' lichens are medium-sized foliose lichens that are yellow-green in colour, with a thallus comprising rounded lobed that measure 2–8 mm wide, which form flat and loosely attached patches that are wide. Older parts of the upper thallus surface are wrinkled, while the newer parts are smooth. There is a black lower surface with simple, unbranched rhizines, and a distinct bare zone around the margin. The photobiont partner is green algae from genus ''Trebouxia''. ''Flavoparmelia'' has larger spores than other segregate genera of ''Pseu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asphalt Shingle
An asphalt shingle is a type of wall or roof shingle that uses asphalt for waterproofing. It is one of the most widely used roofing covers in North America because it has a relatively inexpensive up-front cost and is fairly simple to install. History Asphalt shingles are an American invention by Henry Reynolds of Grand Rapids, Michigan. They were first used in 1903, in general use in parts of the United States by 1911 and by 1939 11 million squares () of shingles were being produced. A U.S. National Board of Fire Underwriters campaign to eliminate the use of wood shingles on roofs was a contributing factor in the growth in popularity of asphalt shingles during the 1920s. The forerunner of these shingles was first developed in 1893 and called ''asphalt prepared roofing'', which was similar to asphalt roll roofing without the surface granules.Craig R Dixon, et al.. "An Historical Perspective on the Wind Resistance of Asphalt Shingles" accessed 12/20/2013 In 1897 slate granule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizoids
Rhizoids are protuberances that extend from the lower epidermal cells of bryophytes and algae. They are similar in structure and function to the root hairs of vascular land plants. Similar structures are formed by some fungi. Rhizoids may be unicellular or multicellular. Evolutionary development Plants originated in aquatic environments and gradually migrated to land during their long course of evolution. In water or near it, plants could absorb water from their surroundings, with no need for any special absorbing organ or tissue. Additionally, in the primitive states of plant development, tissue differentiation and division of labor were minimal, thus specialized water-absorbing tissue was not required. The development of specialized tissues to absorb water efficiently and anchor the plant body to the ground enabled the spread of plants onto land. Description Rhizoids absorb water mainly by capillary action in which water moves up between threads of rhizoids; this is in con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetative Reproduction
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is a form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or specialized reproductive structures, which are sometimes called vegetative propagules. Many plants naturally reproduce this way, but it can also be induced artificially. Horticulturists have developed asexual propagation techniques that use vegetative propagules to replicate plants. Success rates and difficulty of propagation vary greatly. Monocotyledons typically lack a vascular cambium, making them more challenging to propagate. Plant propagation Plant propagation is the process of plant reproduction of a species or cultivar, and it can be sexual or asexual. It can happen through the use of vegetative parts of the plants, such as leaves, stems, and roots to produce new plants or through growth from specialized vegetative plant parts. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascocarp
An ascocarp, or ascoma (: ascomata), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the size of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism. The sexual fusion of haploid cells is called karyogamy, the result of which is the formation of a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, diploid cell called the zygote or zygospore. History German zoologists Oscar Hertwig, Oscar and Richard Hertwig made some of the first discoveries on animal zygote formation in the late 19th century. In multicellular organisms The zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In humans and most other Anisogamy, anisogamous organisms, a zygote is formed when an egg cell and sperm, sperm cell come together to create a new unique organism. The formation of a cell potency, totipotent zygote with the potential to produce a whole organism depends on epigenetics, epigenetic reprogramming. DNA demethyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalic Acid
Oxalic acid is an organic acid with the systematic name ethanedioic acid and chemical formula , also written as or or . It is the simplest dicarboxylic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that forms a colorless solution in water. Its name is derived from early investigators who isolated oxalic acid from flowering plants of the genus '' Oxalis'', commonly known as wood-sorrels. It occurs naturally in many foods. Excessive ingestion of oxalic acid or prolonged skin contact can be dangerous. Oxalic acid is a much stronger acid than acetic acid. It is a reducing agent and its conjugate bases hydrogen oxalate () and oxalate () are chelating agents for metal cations. It is used as a cleaning agent, especially for the removal of rust, because it forms a water-soluble ferric iron complex, the ferrioxalate ion. Oxalic acid typically occurs as the dihydrate with the formula . History The preparation of salts of oxalic acid from plants had been known since at least 1745, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |