|
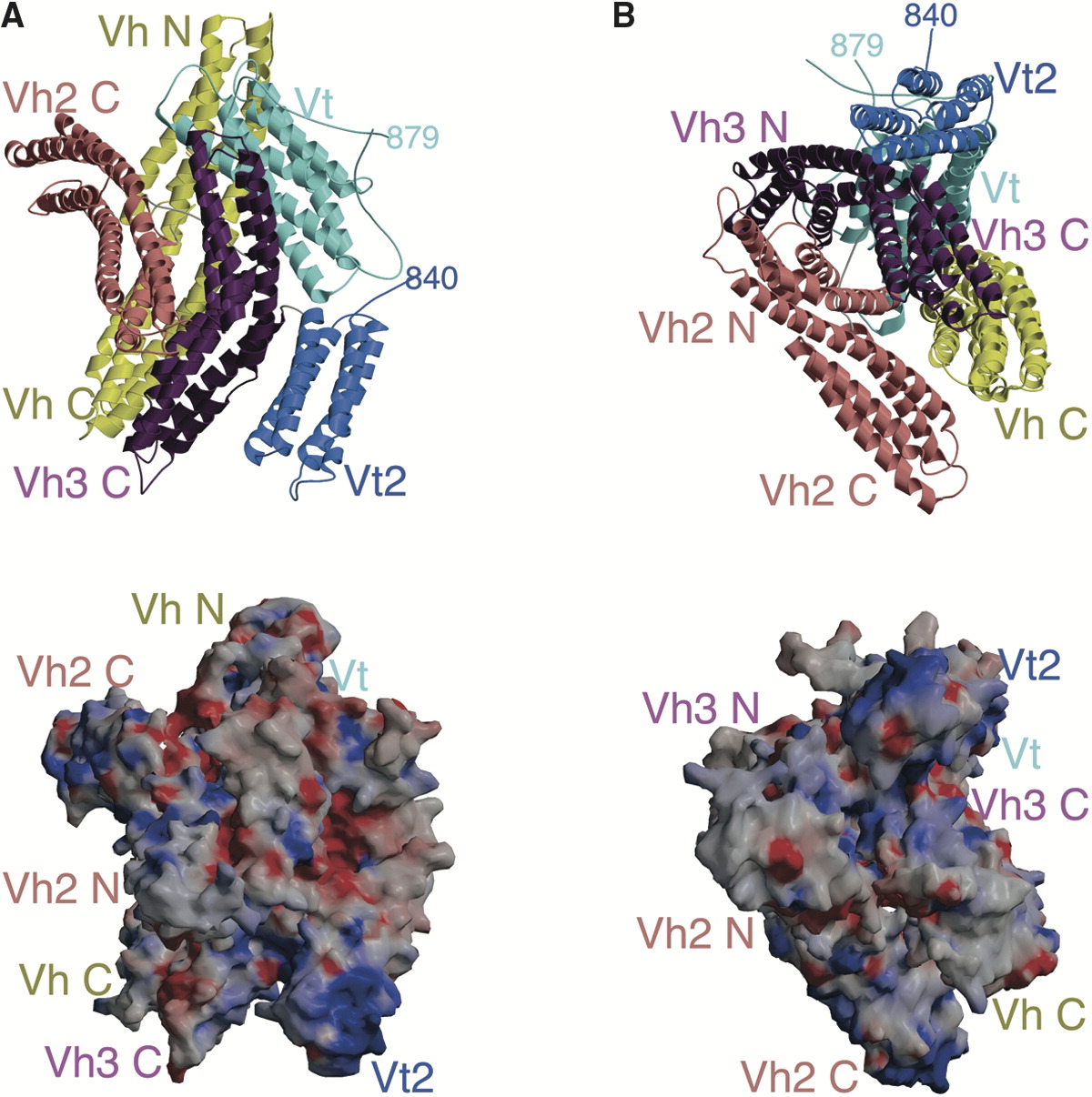
Focal Adhesion Targeting Region
In structural and cell biology, the focal adhesion targeting domain is a conserved protein domain that was first identified in focal adhesion kinase (FAK), also known as PTK2 protein tyrosine kinase 2 (PTK2). Focal adhesions are multi-protein intracellular signalling complexes that link the cellular actin microfilament cytoskeleton, through the cell membrane via transmembrane integrin proteins, to the extracellular matrix. Focal adhesions form and dissipate as cells attach and detach from matrix during cell adhesion and cell migration. The FAK focal adhesion targeting (FAT) domain is a C-terminal region necessary and sufficient for localizing FAK to focal adhesions, allowing FAK to regulate cell adhesion and migration by localizing its protein kinase activity at the junction of internal cytoskeleton and external cell attachment points. The crystal structure of FAT shows it to form a four- helix bundle that binds specifically to Leucine-Aspartate (LD)-repeat motif peptides in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Migration
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryonic development, wound healing and immune responses all require the orchestrated movement of cells in particular directions to specific locations. Cells often migrate in response to specific external signals, including chemical signals and mechanical signals. Errors during this process have serious consequences, including intellectual disability, vascular disease, tumor formation and metastasis. An understanding of the mechanism by which cells migrate may lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies for controlling, for example, invasive tumour cells. Due to the highly viscous environment (low Reynolds number), cells need to continuously produce forces in order to move. Cells achieve active movement by very different mechanisms. Many less complex prokaryotic organisms (and sperm cells) use flagella or cilia to propel themselves. Eukaryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GIT1
ARF GTPase-activating protein GIT1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''GIT1'' gene. GIT1 contains an ARFGAP domain, Anykrin repeats, and a GRK-interacting domain. The Arf-GAP domain, which enables it to act as a GTPase activating protein (GAP) for the Arf family of GTPases, has been shown to be involved in phosphorylation and inhibition of the ADRB2. If synaptic localization of GIT1 is disturbed, then this is known to affect dendritic spine morphology and formation---this is thought to occur through the Rac1/PAK1/LIMK/CFL1 pathway. Interactions GIT1 has been shown to interact with: * ARHGEF7, * Beta adrenergic receptor kinase, * GIT2, * PCLO, * PLCG1, * PPFIA4 * PTK2, and * liprin-alpha-1 Liprin-alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PPFIA1'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the LAR protein tyrosine phosphatase-interacting protein (liprin) family. Liprins interact with members of LA .... References Further ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDCD10
Programmed cell death protein 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PDCD10'' gene. Function This gene encodes a protein, originally identified in a premyeloid cell line, with similarity to proteins that participate in apoptosis. Three alternative transcripts encoding the same protein, differing only in their 5' UTRs, have been identified for this gene. Gene Loss of function mutations in ''PDCD10'' result in the onset of Cerebral Cavernous Malformations (CCM) illness. Therefore, this gene is also called ''CCM3''. Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs) are vascular malformations in the brain and spinal cord made of dilated capillary vessels. Interactions CCM3 encodes a protein called Programmed Cell Death 10 (PDCD10). The function of this protein has only recently begun to be understood. PDCD10 has roles in vascular development and VEGF signaling1, apoptosis and functions as part of a larger signaling complex that includes germinal center kinase III. Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinculin
In mammalian cells, vinculin is a membrane-cytoskeletal protein in focal adhesion plaques that is involved in linkage of integrin adhesion molecules to the actin cytoskeleton. Vinculin is a cytoskeletal protein associated with cell-cell and cell-matrix junctions, where it is thought to function as one of several interacting proteins involved in anchoring F-actin to the membrane. Discovered independently by Benny Geiger and Keith Burridge, its sequence is 20%–30% similar to α-catenin, which serves a similar function. Binding alternately to talin or α-actinin, vinculin's shape and, as a consequence, its binding properties are changed. The vinculin gene occurs as a single copy and what appears to be no close relative to take over functions in its absence. Its splice variant metavinculin (see below) also needs vinculin to heterodimerize and work in a dependent fashion. Structure Vinculin is a 117-kDa cytoskeletal protein with 1066 amino acids. The protein contains an ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-catenin
Alpha-catenin functions as the primary protein link between cadherins and the actin cytoskeleton. It has been reported that the actin binding proteins vinculin and alpha-actinin can bind to alpha-catenin. It has been suggested that alpha-catenin does not bind with high affinity to both actin filaments and the E-cadherin-beta-catenin complex at the same time. It has been observed that when alpha-catenin is not in a molecular complex with beta-catenin, it dimerizes and functions to regulate actin filament assembly, possibly by competing with Arp2/3 protein. Alpha catenin exhibits significant protein dynamics. However, a protein complex including a cadherin, actin, beta-catenin and alpha-catenin has not been isolated. The amino acid sequence of alpha-catenin has sequence similarity to that of vinculin. Types Three alpha-catenin genes are expressed in humans: * CTNNA1, alpha-1-catenin (also called alpha-E-catenin) * CTNNA2, alpha-2-catenin (also called alpha-N-catenin) * CTNNA3, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTK2B
Protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTK2B'' gene. Function This gene encodes a cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase that is involved in calcium-induced regulation of ion channels and activation of the MAP kinase signaling pathway. The encoded protein may represent an important signaling intermediate between neuropeptide-activated receptors or neurotransmitters that increase calcium flux and the downstream signals that regulate neuronal activity. The encoded protein undergoes rapid tyrosine phosphorylation and activation in response to increases in the intracellular calcium concentration , nicotinic acetylcholine receptor activation, membrane depolarization, or protein kinase C activation. In addition, SOCE-induced Pyk2 activation mediates disassembly of endothelial adherens junctions, via tyrosine (Y1981-residue) phosphorylation of VE-PTP. This protein has been shown to bind a CRK-associated substrate, a nephrocystin, a GTPase reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TGFB1I1
Transforming growth factor beta-1-induced transcript 1 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TGFB1I1'' gene. Often put together with and studied alongside TGFB1I1 is the mouse homologue HIC-5 ( Hydrogen Peroxide-Inducible Clone-5). As the name suggests, TGFB1I1 is an induced form of the larger family of TGFB1. Studies suggest TGFB1I1 plays a role in processes of cell growth, proliferation, migration, differentiation and senescence. TGFB1I1 is most localized at focal adhesion complexes of cells, although it may be found active in the cytosol, nucleus and cell membrane as well. Functions Transforming growth factor beta-1-induced transcript 1 plays a role in a number of cell functions. Originally, TGFB1I1 was isolated as a senescence-inducing gene from mouse osteoblastic cells through treatment with transforming growth factor beta-1 and hydrogen peroxide. During this, TGFB1I1 was also being independently discovered by numerous other groups and was characterized a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LPXN
Leupaxin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LPXN'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... The product encoded by this gene is preferentially expressed in hematopoietic cells and is most homologous to the focal adhesion protein, paxillin. It may function in cell type-specific signaling by associating with PYK2, a member of focal adhesion kinase family. As a substrate for a tyrosine kinase in lymphoid cells, this protein may also function in, and be regulated by tyrosine kinase activity. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-11-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paxillin
Paxillin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PXN'' gene. Paxillin is expressed at focal adhesions of non-striated cells and at costameres of striated muscle cells, and it functions to adhere cells to the extracellular matrix. Mutations in ''PXN'' as well as abnormal expression of paxillin protein has been implicated in the progression of various cancers. Structure Human paxillin is 64.5 kDa in molecular weight and 591 amino acids in length. The C-terminal region of paxillin is composed of four tandem double zinc finger LIM domains that are cysteine/histidine-rich with conserved repeats; these serve as binding sites for the protein tyrosine phosphatase-PEST, tubulin and serves as the targeting motif for focal adhesions. The N-terminal region of paxillin has five highly conserved leucine-rich sequences termed LD motifs, which mediate several interactions, including that with pp125FAK and vinculin. The LD motifs are predicted to form amphipathic alpha helices, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Helix
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues earlier along the protein sequence. The alpha helix is also called a classic Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix. The name 3.613-helix is also used for this type of helix, denoting the average number of residues per helical turn, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond. Among types of local structure in proteins, the α-helix is the most extreme and the most predictable from sequence, as well as the most prevalent. Discovery In the early 1930s, William Astbury showed that there were drastic changes in the X-ray fiber diffraction of moist wool or hair fibers upon significant stretching. The data suggested that the unstretched fibers had a coiled molecular structure with a characteristic repeat of ≈. Astbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in the material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of the principal axes, or edges, of the unit cell and the angles between them are the lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |