|
Fnord
"Fnord" () is a word coined in 1965 by Kerry Thornley and Greg Hill in the Discordian religious text ''Principia Discordia''. It entered into popular culture after appearing in '' The Illuminatus! Trilogy'' (1975) of novels written by Robert Shea and Robert Anton Wilson. Here, the interjection "fnord" is given hypnotic power over the unenlightened, and children in grade school are taught to be unable to see the word consciously. For the rest of their lives, every appearance of the word subconsciously generates a feeling of unease and confusion which prevents rational consideration of the text in which it appears. Other uses The word has been used in newsgroup and hacker culture to indicate irony, humor, or Surrealism.Raymond, Eric S. (1996''The New Hacker's Dictionary.''MIT Press, p. 196. Placement at the end of a statement in brackets (''fnord'') explicitly tags the intent, and may be so applied to any random or surreal sentence, coercive subtext, or anything jarringly out o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fnord Logo
"Fnord" () is a word coined in 1965 by Kerry Thornley and Gregory Hill (writer), Greg Hill in the Discordianism, Discordian religious text ''Principia Discordia''. It entered into popular culture after appearing in ''The Illuminatus! Trilogy'' (1975) of novels written by Robert Shea and Robert Anton Wilson. Here, the interjection "fnord" is given hypnotism, hypnotic power over the unenlightened, and children in grade school are taught to be unable to see the word consciously. For the rest of their lives, every appearance of the word subconsciously generates a feeling of unease and confusion which prevents rational consideration of the text in which it appears. Other uses The word has been used in newsgroup and hacker culture to indicate irony, humor, or Surrealism.Raymond, Eric S. (1996''The New Hacker's Dictionary.''MIT Press, p. 196. Placement at the end of a statement in brackets (''fnord'') explicitly tags the intent, and may be so applied to any random or surreal sentence, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Illuminatus! Trilogy
''The Illuminatus! Trilogy'' is a series of three novels by American writers Robert Shea and Robert Anton Wilson, first published in 1975.''Illuminatus!'' was written between 1969 and 1971, but not published until 1975 according to Robert Anton Wilson, '' Cosmic Trigger I: The Final Secret of the Illuminati'' (1977), p. 145. The trilogy is a satirical, postmodern, science fiction–influenced adventure story; a drug-, sex-, and magic-laden trek through a number of conspiracy theories, both historical and imaginary, related to the authors' version of the Illuminati. The narrative often switches between third- and first-person perspectives in a nonlinear narrative. It is thematically dense, covering topics like counterculture, numerology, and Discordianism. The trilogy comprises three parts which contain five books and appendices: ''The Eye in the Pyramid'' (first two books), ''The Golden Apple'' (third and part of fourth book), ''Leviathan'' (part of fourth and all of fifth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metasyntactic Variable
A metasyntactic variable is a specific word or set of words identified as a placeholder in computer science and specifically computer programming. These words are commonly found in source code and are intended to be modified or substituted before real-world usage. For example, ''foo'' and ''bar'' are used in over 330 Internet Engineering Task Force Requests for Comments, the documents which define foundational internet technologies like HTTP (web), TCP/IP, and email protocols. By mathematical analogy, a metasyntactic variable is a word that is a variable for other words, just as in algebra letters are used as variables for numbers. Metasyntactic variables are used to name entities such as variables, functions, and commands whose exact identity is unimportant and serve only to demonstrate a concept, which is useful for teaching programming. Common metasyntactic variables Since English is the foundation language or lingua franca of most computer programming languages, varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerry Thornley
Kerry Wendell Thornley (April 17, 1938 – November 28, 1998) was an American author. He is known as the co-founder (along with childhood friend Greg Hill) of Discordianism, in which context he is usually known as Omar Khayyam Ravenhurst or simply Lord Omar. He and Hill authored the religion's text ''Principia Discordia, Or, How I Found Goddess, and What I Did to Her When I Found Her.'' Thornley also was known for his 1962 manuscript ''The Idle Warriors'', which was inspired by the activities of his acquaintance Lee Harvey Oswald before the 1963 assassination of John F. Kennedy. Thornley was highly active in the countercultural publishing scene, writing for a number of underground magazines and newspapers, and self-publishing many one-page (or ''broadsheet'') newsletters of his own. One such newsletter called ''Zenarchy'' was published in the 1960s under the pen name Ho Chi Zen. Zenarchy is described in the introduction of the collected volume as "the social order which springs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satire
Satire is a genre of the visual, literary, and performing arts, usually in the form of fiction and less frequently non-fiction, in which vices, follies, abuses, and shortcomings are held up to ridicule, often with the intent of exposing or shaming the perceived flaws of individuals, corporations, government, or society itself into improvement. Although satire is usually meant to be humorous, its greater purpose is often constructive social criticism, using wit to draw attention to both particular and wider issues in society. Satire may also poke fun at popular themes in art and film. A prominent feature of satire is strong irony or sarcasm—"in satire, irony is militant", according to literary critic Northrop Frye— but parody, burlesque, exaggeration, juxtaposition, comparison, analogy, and double entendre are all frequently used in satirical speech and writing. This "militant" irony or sarcasm often professes to approve of (or at least accept as natural) th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
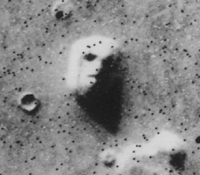
Pareidolia
Pareidolia (; ) is the tendency for perception to impose a meaningful interpretation on a nebulous stimulus (physiology), stimulus, usually visual, so that one detects an object, pattern, or meaning where there is none. Pareidolia is a specific but common type of apophenia (the tendency to perceive meaningful connections between unrelated things or ideas). Common examples include Cloud#In culture and religion, perceived images of animals, faces, or objects in cloud formations; seeing faces in inanimate objects; or lunar pareidolia like the Man in the Moon or the Moon rabbit. The concept of pareidolia may extend to include hidden messages in recorded music played in reverse or at higher- or lower-than-normal speeds, and hearing voices (mainly indistinct) or music in random noise, such as that produced by air conditioners or by fans. Face pareidolia has also been demonstrated in Rhesus macaque, rhesus macaques. Etymology The word derives from the Greek words ''wikt:para-, pará'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Fear
Culture of fear (or climate of fear) is the concept which describes the pervasive feeling of fear in a given group, often due to actions taken by leaders. The term was popularized by Frank Furedi and has been more recently popularized by the American sociologist Barry Glassner. In politics Nazi German politician Hermann Göring explained how people can be made fearful and to support a war they would otherwise oppose: In her book ''State and Opposition in Military Brazil'', Maria Helena Moreira Alves found a "culture of fear" was implemented as part of political repression since 1964. She used the term to describe methods implemented by the national security apparatus of Brazil in its effort to equate political participation with risk of arrest and torture. Cassação (English: cassation) is one such mechanism used to punish members of the military by legally declaring them dead. This enhanced the potential for political control through intensifying the culture of fear a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apophenia
Apophenia () is the tendency to perceive meaningful connections between unrelated things. The term ( from the ) was coined by psychiatrist Klaus Conrad in his 1958 publication on the beginning stages of schizophrenia. He defined it as "unmotivated seeing of connections ccompanied bya specific feeling of abnormal meaningfulness". He described the early stages of delusional thought as self-referential over-interpretations of actual sensory perceptions, as opposed to hallucinations. Apophenia has also come to describe a human propensity to unreasonably seek definite patterns in random information, such as can occur in gambling. Introduction Apophenia can be considered a commonplace effect of brain function. Taken to an extreme, however, it can be a symptom of psychiatric dysfunction, for example, as a symptom in schizophrenia, where a patient sees hostile patterns (for example, a conspiracy to persecute them) in ordinary actions. Apophenia is also typical of conspiracy theor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placeholder Name
Placeholder names are intentionally overly generic and ambiguous terms referring to things, places, or people, the names of which or of whom do not actually exist; are temporarily forgotten, or are unimportant; or in order to avoid stigmatization, or because they are unknowable or unpredictable given the context of their discussion; or to deliberately expunge direct use of the name. Placeholder names for people are often terms referring to an average person or a predicted persona of a typical user. Linguistic role These placeholders typically function grammatically as nouns and can be used for people (e.g. '' John Doe, Jane Doe''), objects (e.g. '' widget''), locations ("Main Street"), or places (e.g. ''Anytown, USA''). They share a property with pronouns because their referents must be supplied by context; but, unlike a pronoun, they may be used with no referent—the important part of the communication is not the thing nominally referred to by the placeholder, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Coe
Jonathan Coe (; born 19 August 1961) is an English novelist and writer. His work has an underlying preoccupation with political issues, although this serious engagement is often expressed comically in the form of satire. For example, '' What a Carve Up!'' (1994) reworks the plot of an old 1960s spoof horror film of the same name. It is set within the "carve up" of the UK's resources that was carried out by Margaret Thatcher's Conservative governments of the 1980s. Early life and education Coe was born in Bromsgrove, Worcestershire, on 19 August 1961 to Roger and Janet (née Kay) Coe. He studied at King Edward's School, Birmingham, and Trinity College, Cambridge. He taught at the University of Warwick, where he completed an MA and PhD in English Literature. Career Coe has long been interested in both music and literature. In the mid-1980s he played with a band (The Peer Group) and tried to get a recording of his music. He also wrote songs and played keyboards for a short-liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fighting Words
Fighting words are spoken words intended to provoke a retaliatory act of violence against the speaker. In United States constitutional law, the term describes words that inflict injury or would tend to incite an immediate breach of the peace. United States The fighting words doctrine, in United States constitutional law, is a limitation to freedom of speech as protected by the First Amendment to the United States Constitution. In 1942, the U.S. Supreme Court established the doctrine by a 9–0 decision in '' Chaplinsky v. New Hampshire''. It held that "insulting or 'fighting words', those that by their very utterance inflict injury or tend to incite an immediate breach of the peace" are among the "well-defined and narrowly limited classes of speech the prevention and punishment of hich... have never been thought to raise any constitutional problem." ''Chaplinsky'' decision Walter Chaplinsky, a Jehovah's Witness, had purportedly told a New Hampshire town marshal who wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumerism
Consumerism is a socio-cultural and economic phenomenon that is typical of industrialized societies. It is characterized by the continuous acquisition of goods and services in ever-increasing quantities. In contemporary consumer society, the purchase and the consumption of products have evolved beyond the mere satisfaction of basic human needs, Stearns, Peter (2006). ''Consumerism in World History''. 2nd ed. Routledge. p. vii–viii. transforming into an activity that is not only economic but also cultural, social, and even identity-forming. It emerged in Western Europe and the United States during the Industrial Revolution and became widespread around the 20th century. In economics, consumerism refers to policies that emphasize consumption. It is the consideration that the free choice of consumers should strongly inform the choice by manufacturers of what is produced and how, and therefore influence the economic organization of a society. Consumerism has been criticized b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |