|
Flus
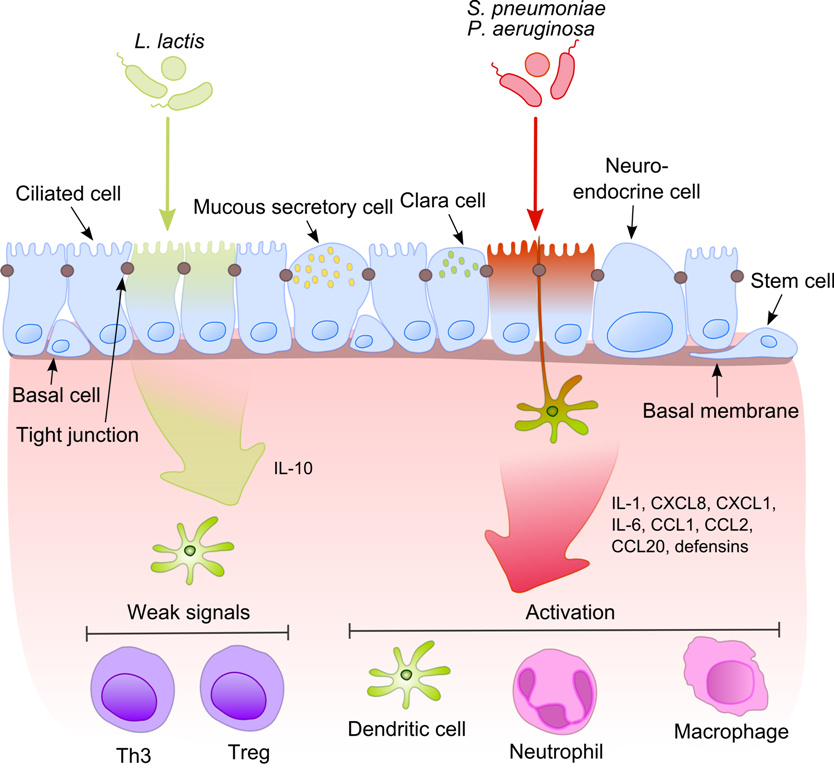
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin one to four (typically two) days after exposure to the virus and last for about two to eight days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia from the virus or a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease. There are four types of influenza virus: types A, B, C, and D. Aquatic birds are the primary source of influenza A virus (IAV), which is also widespread in various mammals, including humans and pigs. Influenza B virus (IBV) and influenza C virus (ICV) primarily infect humans, and influenza D virus (IDV) is found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flu Vaccine
Influenza vaccines, colloquially known as flu shots or the flu jab, are vaccines that protect against infection by influenza viruses. New versions of the vaccines are developed twice a year, as the influenza virus rapidly changes. While their effectiveness varies from year to year, most provide modest to high protection against influenza. Vaccination against influenza began in the 1930s, with large-scale availability in the United States beginning in 1945. Both the World Health Organization and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend yearly vaccination for nearly all people over the age of six months, especially those at high risk, and the influenza vaccine is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) also recommends yearly vaccination of high-risk groups, particularly pregnant women, the elderly, children between six months and five years, and those with certain he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point in the hypothalamus. There is no single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature: sources use values ranging between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle tone, muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes Flushing (physiology), flushed, and may begin to Perspiration, sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral infection, viral, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Infection
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and many are beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are considered part of the gut flora, with a few hundred species present in each individual human's digestive tract. The body is continually exposed to many species of bacteria, including beneficial commensals, which grow on the skin and mucous membranes, and saprophytes, which grow mainly in the soil and in decaying matter. The blood and tissue fluids contain nutrients sufficient to sustain the growth of many bacteria. The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immunity or innate resistance against many microorganisms. Pathogenic bacteria are speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
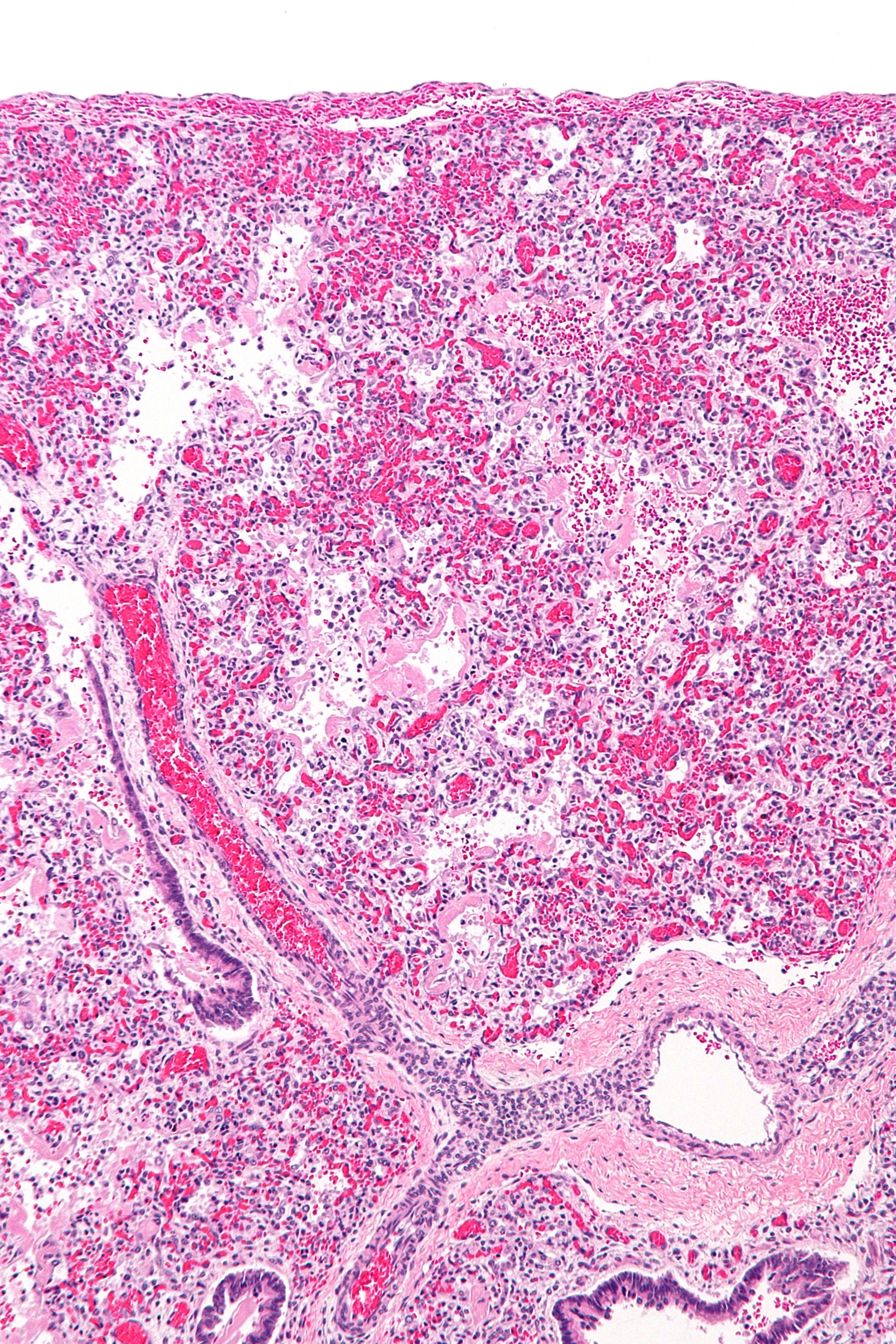
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin coloration (cyanosis). For those who survive, a decreased quality of life is common. Causes may include sepsis, pancreatitis, trauma, pneumonia, and aspiration. The underlying mechanism involves diffuse injury to cells which form the barrier of the microscopic air sacs of the lungs, surfactant dysfunction, activation of the immune system, and dysfunction of the body's regulation of blood clotting. In effect, ARDS impairs the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Adult diagnosis is based on a PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen) of less than 300 mm Hg despite a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of more than 5 cm H2O. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasionally photophobia. Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness, nausea, and an inability to tolerate loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, fungi or parasites. Non-infectious causes include malignancy (cancer), subarachnoid hemorrhage, chronic inflammatory disease ( sarcoidosis) and certain drugs. Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation's proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore, the condition is classified as a medical emergency. A lumba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is inflammation of the Human brain, brain. The severity can be variable with symptoms including reduction or alteration in consciousness, aphasia, headache, fever, confusion, a stiff neck, and vomiting. Complications may include seizures, hallucinations, trouble speaking, memory problems, and problems with hearing. Causes of encephalitis include viruses such as herpes simplex virus and rabies virus as well as bacteria, fungi, or parasites. Other causes include autoimmune diseases and certain medications. In many cases the cause remains unknown. Risk factors include a immunosuppression, weak immune system. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and supported by blood tests, medical imaging, and analysis of cerebrospinal fluid. Certain types are preventable with vaccines. Treatment may include antiviral medications (such as acyclovir), anticonvulsants, and corticosteroids. Treatment generally takes place in hospital. Some people require artificial respiration. Once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. A sudden worsening of asthma symptoms sometimes called an 'asthma attack' or an 'asthma exacerbation' can occur when allergens, pollen, dust, or other particles, are inhaled into the lungs, causing the bronchioles to constrict and produce mucus, which then restricts oxygen flow to the alveoli. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease (medical Specialty)
Infectious diseases (ID), also known as infectiology, is a medical specialty dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of infections. An infectious diseases specialist's practice consists of managing nosocomial (Hospital-acquired infection, healthcare-acquired) infections or community-acquired infections. An ID specialist investigates and determines the cause of a disease (bacteria, virus, parasite, fungus or prions). Once the cause is known, an ID specialist can then run various tests to determine the best drug to treat the disease. While infectious diseases have always been around, the infectious disease specialty did not exist until the late 1900s after scientists and physicians in the 19th century paved the way with research on the sources of infectious disease and the development of vaccines. Scope Infectious diseases specialists typically serve as consultants to other physicians in cases of complex infections, and often manage patients with HIV/AIDS and other forms of immuno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganisms. Identifying the responsible pathogen can be difficult. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and physical examination. Chest X-rays, blood tests, and Microbiological culture, culture of the sputum may help confirm the diagnosis. The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia. Risk factors for pneumonia include cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sickle cell disease, asthma, diabetes, heart failure, a history of smoking, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Bird
A water bird, alternatively waterbird or aquatic bird, is a bird that lives on or around water. In some definitions, the term ''water bird'' is especially applied to birds in freshwater ecosystems, although others make no distinction from seabirds that inhabit marine environments. Some water birds (e.g. wading birds) are more terrestrial while others (e.g. waterfowls) are more aquatic, and their adaptations will vary depending on their environment. These adaptations include webbed feet, beaks, and legs adapted to feed in the water, and the ability to dive from the surface or the air to catch prey in water. The term ''aquatic bird'' is sometimes also used in this context. A related term that has a narrower meaning is waterfowl. Some piscivorous birds of prey, such as ospreys, sea eagles, fish eagles, fish owls, and fishing owls, hunt aquatic prey but do not stay in water for long and live predominantly over dry land, and are not considered water birds. The term waterb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza A Virus
''Influenza A virus'' (''Alphainfluenzavirus influenzae'') or IAV is the only species of the genus ''Alphainfluenzavirus'' of the virus family '' Orthomyxoviridae''. It is a pathogen with strains that infect birds and some mammals, as well as causing seasonal flu in humans. Mammals in which different strains of IAV circulate with sustained transmission are bats, pigs, horses and dogs; other mammals can occasionally become infected. IAV is an enveloped negative-sense RNA virus, with a segmented genome. Through a combination of mutation and genetic reassortment the virus can evolve to acquire new characteristics, enabling it to evade host immunity and occasionally to jump from one species of host to another. Subtypes of IAV are defined by the combination of the antigenic H and N proteins in the viral envelope; for example, "H1N1" designates an IAV subtype that has a type-1 hemagglutinin (H) protein and a type-1 neuraminidase (N) protein. Almost all possible combinations of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |