|
Flaviviruses
''Flavivirus'', renamed ''Orthoflavivirus'' in 2023, is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Flaviviridae''. The genus includes the West Nile virus, dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, yellow fever virus, Zika virus and several other viruses which may cause encephalitis, as well as insect-specific flaviviruses (ISFs) such as cell fusing agent virus (CFAV), Palm Creek virus (PCV), and Parramatta River virus (PaRV). While dual-host flaviviruses can infect vertebrates as well as arthropods, insect-specific flaviviruses are restricted to their competent arthropods. The means by which flaviviruses establish persistent infection in their competent vectors and cause disease in humans depends upon several virus-host interactions, including the intricate interplay between flavivirus-encoded immune antagonists and the host antiviral innate immune effector molecules. Flaviviruses are named for the yellow fever virus; the word ''flavus'' means 'yellow' in Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parramatta River Virus
Parramatta River virus (PaRV) is an insect virus belonging to ''Flaviviridae'' and endemic to Australia. It was discovered in 2015. The virus was identified from the mosquito '' Aedes vigilax'' collected from Sydney under the joint research project by scientists at the University of Queensland and the University of Sydney. In experimental infections, the virus is unable to grow in vertebrate cells, but only in ''Aedes''-derived mosquito cell lines. This suggests that the virus does not infect vertebrates. The name is given because it was discovered from Silverwater, a suburb of Sydney on the southern bank of the Parramatta River. The mosquitoes from which the virus was isolated were actually collected in 2007, and had been preserved since then. The study commenced only after the development of the technique of viral detection in mosquitoes in the University of Queensland. The virus was identified as a result of investigation on the outbreak of '' Ross River virus'' in 2015. Both t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
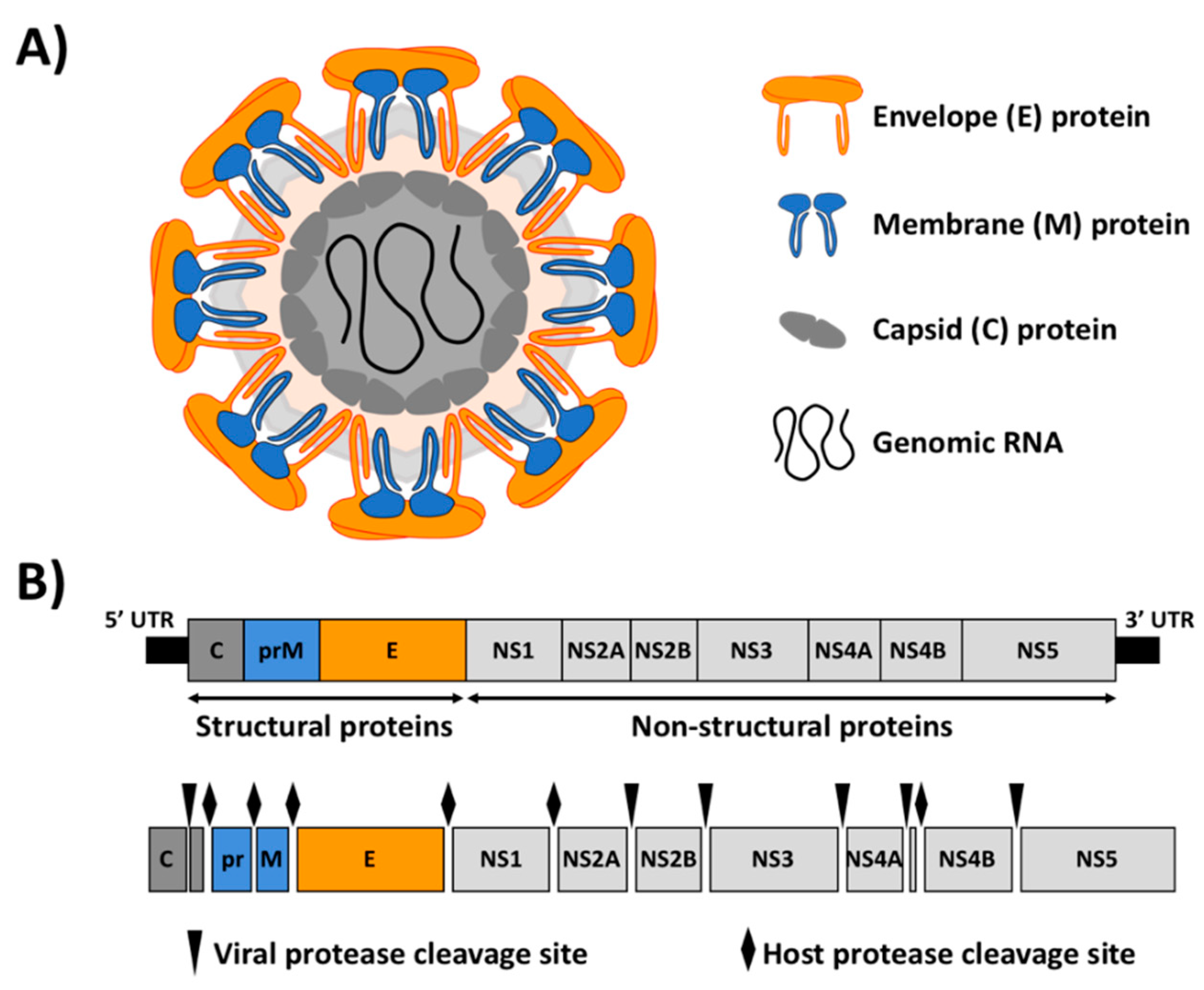
Flaviviridae
''Flaviviridae'' is a family of Viral envelope, enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds. They are primarily spread through arthropod vector (epidemiology), vectors (mainly ticks and mosquitoes). The family gets its name from the yellow fever virus; ''flavus'' is Latin for "yellow", and yellow fever in turn was named because of its propensity to cause jaundice in victims. There are 89 species in the family divided among four genera. Diseases associated with the group include: hepatitis (hepaciviruses), Bleeding, hemorrhagic syndromes, Bovine viral diarrhea, fatal mucosal disease (pestiviruses), Viral hemorrhagic fever, hemorrhagic fever, encephalitis, and the birth defect microcephaly (flaviviruses). Structure Virus particles are enveloped and spherical with icosahedral-like geometries that have pseudo T=3 symmetry. They are about 40–60 nanometer, nm in diameter. Genome Members of the family ''Flaviviridae'' have monopartite, linear, single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zika Virus
Zika virus (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family ''Flaviviridae''. It is spread by daytime-active ''Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as '' A. aegypti'' and '' A. albopictus''. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, where the virus was first isolated in 1947. Zika virus shares a genus with the dengue, yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, and West Nile viruses. Since the 1950s, it has been known to occur within a narrow equatorial belt from Africa to Asia. From 2007 to , the virus spread eastward, across the Pacific Ocean to the Americas, leading to the 2015–2016 Zika virus epidemic. The infection, known as Zika fever or Zika virus disease, often causes no or only mild symptoms, similar to a very mild form of dengue fever. While there is no specific treatment, paracetamol (acetaminophen) and rest may help with the symptoms. Zika can spread from a pregnant woman to her baby. This can result in microcephaly, severe brain malformations, and other b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dengue Virus
Dengue virus (DENV) is the cause of dengue fever. It is a mosquito-borne, single positive-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''; genus '' Flavivirus''. Four serotypes of the virus have been found, and a reported fifth has yet to be confirmed,Dwivedi, V. D., Tripathi, I. P., Tripathi, R. C., Bharadwaj, S., & Mishra, S. K. (2017). Genomics, proteomics and evolution of ''Dengue virus''. Briefings in functional genomics.16(4): 217–227, https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/elw040 all of which can cause the full spectrum of disease. Nevertheless, the mainstream scientific community's understanding of dengue virus may be simplistic as, rather than distinct antigenic groups, a continuum appears to exist. This same study identified 47 strains of ''dengue virus''. Additionally, coinfection with and lack of rapid tests for Zika virus and chikungunya complicate matters in real-world infections. ''Dengue virus'' has increased dramatically within the last 20 years, becoming one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus
Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) is a positive-strand RNA virus associated with tick-borne encephalitis in the genus '' Flavivirus''. Classification Taxonomy TBEV is a member of the genus '' Flavivirus''. Other close relatives, members of the TBEV serocomplex, include Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus, Kyasanur Forest disease virus, Alkhurma virus, Louping ill virus and Langat virus. Subtypes TBEV has three subtypes: * Western European subtype (formerly Central European encephalitis virus, CEEV; principal tick vector: ''Ixodes ricinus''); * Siberian subtype (formerly West Siberian virus; principal tick vector: '' Ixodes persulcatus''); * Far Eastern subtype (formerly Russian Spring Summer encephalitis virus, RSSEV; principal tick vector: ''Ixodes persulcatus''). The reference strain is the Sofjin strain. Virology Structure TBEV is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus, contained in a 40-60 nm spherical, enveloped capsid. The TBEV genome is approximately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Nile Virus
West Nile virus (WNV) is a single-stranded RNA virus that causes West Nile fever. It is a member of the family ''Flaviviridae'', from the genus ''Flavivirus'', which also contains the Zika virus, dengue virus, and yellow fever virus. The virus is primarily transmitted by mosquitoes, mostly species of ''Culex''. The primary host (biology), hosts of WNV are birds, so that the virus remains within a "bird–mosquito–bird" Transmission (medicine), transmission cycle. The virus is genetically related to the Japanese encephalitis family of viruses. Humans and horses both exhibit disease symptoms from the virus, and symptoms rarely occur in other animals. West Nile virus was not named directly after the Nile River, but rather, after the West_Nile_sub-region, West Nile district of Uganda where the virus was first isolated in 1937. Structure Like most other flaviviruses, WNV is an Viral envelope, enveloped virus with icosahedral symmetry. Electron microscope studies reveal a 45–5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palm Creek Virus
Palm Creek virus (PCV) is an insect virus belonging to the genus ''Flavivirus'', of the family ''Flaviviridae''. It was discovered in 2013 from the mosquito '' Coquillettidia xanthogaster''. The female mosquitoes were originally collected in 2010 from Darwin, Katherine, Alice Springs, Alyangula, Groote Eylandt, Jabiru and the McArthur River Mine, and had since been preserved. The discovery was made by biologists at the University of Queensland. The virus is named after Palm Creek, near Darwin, from where it was originally isolated. PCV is the first insect-specific virus discovered in Australia. Genetically it most closely related to Nakiwogo virus, isolated from '' Mansonia'' mosquito in Uganda, and clustered more broadly with ''Culex''-associated viruses, such as ''Culex flavivirus'' (CxFV).In one experiment in 2016, when cultivated mosquito West Nile and Murray Valley encephalitis virus">Murray Valley encephalitis viruses were found to be unable to develop in the infected cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules that are crucial in all cells and viruses. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomer components: a pentose, 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is RNA; if the sugar is deoxyribose, a variant of ribose, the polymer is DNA. Nucleic acids are chemical compounds that are found in nature. They carry information in cells and make up genetic material. These acids are very common in all living things, where they create, encode, and store information in every living cell of every outline of life forms, life-form on Earth. In turn, they send and express that information inside and outside the cell nucleus. From the inner workings of the cell to the young of a living thing, they contain and provide information via the nucleic acid sequence. This gives the RNA and DNA their unmistakable 'la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The virus genomic component inside the capsid, along with occasionally present virus core protein, is called the virus core. The capsid and core together are referred to as a nucleocapsid (cf. also virion). Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icosahedral
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons". There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrical than others. The best known is the (convex, non- stellated) regular icosahedron—one of the Platonic solids—whose faces are 20 equilateral triangles. Regular icosahedra There are two objects, one convex and one nonconvex, that can both be called regular icosahedra. Each has 30 edges and 20 equilateral triangle faces with five meeting at each of its twelve vertices. Both have icosahedral symmetry. The term "regular icosahedron" generally refers to the convex variety, while the nonconvex form is called a ''great icosahedron''. Convex regular icosahedron The convex regular icosahedron is usually referred to simply as the ''regular icosahedron'', one of the five regular Platonic solids, and is represented by its Schläfli symbol , containi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive-sense
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. For example, the negative-sense strand of DNA is equivalent to the template strand, whereas the positive-sense strand is the non-template strand whose nucleotide sequence is equivalent to the sequence of the mRNA transcript. DNA sense Because of the complementary nature of base-pairing between nucleic acid polymers, a double-stranded DNA molecule will be composed of two strands with sequences that are reverse complements of each other. To help molecular biologists specifically identify each strand individually, the two strands are usually differentiated as the "sense" strand and the "antisense" strand. An individual strand of DNA is referred to as positive-sense (also positive (+) or simply sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or, less frequently, greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme metabolism, liver dysfunction, or biliary-tract obstruction. The prevalence of jaundice in adults is rare, while jaundice in babies is common, with an estimated 80% affected during their first week of life. The most commonly associated symptoms of jaundice are itchiness, pale feces, and dark urine. Normal levels of bilirubin in blood are below 1.0 mg/ dl (17 μmol/ L), while levels over 2–3 mg/dl (34–51 μmol/L) typically result in jaundice. High blood bilirubin is divided into two types: unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin. Causes of jaundice vary from relatively benign to potentially fatal. High unconjugated bilirubin may be due to excess red blood cell breakdown, large bruises, gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |