|
Fishing Reel
A fishing reel is a hand-crank (mechanism), cranked reel used in angling to wind and stow fishing line, typically mounted onto a fishing rod, but may also be used on compound bows or crossbows to retrieve tethered arrows when bowfishing. Modern recreational fishing reels usually have fittings aiding in casting (fishing), casting for distance and accuracy, as well as controlling the speed and tension of line retrieval to avoid line snap and fishing hook, hook dislodgement. Fishing reels are traditionally used for bass fishing in angling and fly casting, competitive casting. They are typically attached near the handle of a fishing rod, though some specialized reels with pressure sensors for immediate retrieval are equipped on downrigger systems which are mounted directly to an ocean-going sport boat's gunwales or transom (nautical), transoms and are used for "deep drop" and trolling (fishing), trolling. The earliest fishing reel was invented in China at least since the Song dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period#Ten Kingdoms, Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song frequently came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao dynasty, Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China following attacks by the Jin dynasty, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The History of the Song dynasty, dynasty's history is divided into two periods: during the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now East China. The #Southern Song, 1127–1279, Southern Song (; 1127–1279) comprise the period following ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biking
Cycling, also known as bicycling or biking, is the activity of riding a bicycle or other types of pedal-driven human-powered vehicles such as balance bikes, unicycles, tricycles, and quadricycles. Cycling is practised around the world for purposes including transport, recreation, exercise, and competitive sport. History Cycling became popularized in Europe and North America in the latter part and especially the last decade of the 19th century. Today, over 50 percent of the human population knows how to ride a bike. War The bicycle has been used as a method of reconnaissance as well as transporting soldiers and supplies to combat zones. In this it has taken over many of the functions of horses in warfare. In the Second Boer War, both sides used bicycles for scouting. In World War I, France, Germany, Australia and New Zealand used bicycles to move troops. In its 1937 invasion of China, Japan employed some 50,000 bicycle troops, and similar forces were instrumental in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
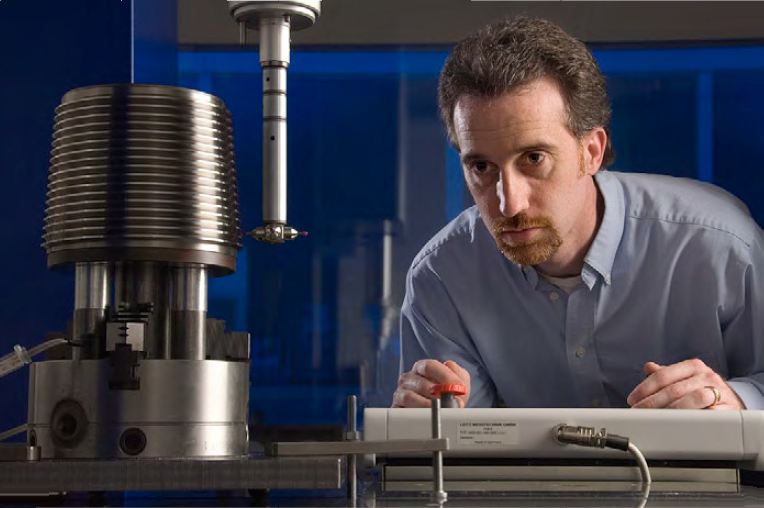
Precision Engineering
Precision engineering is a subdiscipline of electrical engineering, software engineering, electronics engineering, mechanical engineering, and optical engineering concerned with designing machines, fixtures, and other structures that have exceptionally low tolerances, are repeatable, and are stable over time. These approaches have applications in machine tools, MEMS, NEMS, optoelectronics design, and many other fields. Precision engineering is a branch of engineering that focus on the design, development and manufacture of product with high levels of accuracy and repeatability. It involves the use of advanced technologies and techniques to achieve tight tolerance and dimensional control in the manufacturing process. Overview Professors Hiromu Nakazawa and Pat McKeown provide the following list of goals for precision engineering: # Create a highly precise movement. # Reduce the dispersion of the product's or part's function. # Eliminate fitting and promote assembly, espec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABU Garcia
ABU Garcia, originally AB Urfabriken ( Swedish: "Watch Factory Ltd."), then ABU Svängsta, is a fishing reel and equipment manufacturing company founded in Svängsta, Sweden, and is now owned by Pure Fishing conglomerate of the United States. Early history AB Urfabriken began at a factory located near the Mörrum River in Svängsta, Blekinge, Sweden. The company, founded in 1921, originally manufactured watches, telephone timers and taximeters. However, the founder's son, Göte Borgström, a fishing enthusiast, soon redirected its focus towards fishing reels during World War II, when demand for those traditional products diminished. The leading American outdoor sports participant distributing and manufacturing firm Garcia Corporation (1947–1978) was the largest fishing tackle company of its time, formerly known under the earlier name Charles Garcia & Company, New York City. The Garcia Corporation started importing and marketing ABU Svängsta's many reels in the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globeride
, formerly until 2009, is a Japanese manufacturing company that produces fishing equipment in addition to tennis, golf and biking gears. Globeride's fishing products, sold under the Daiwa brand, account for the majority of its sales, including rods, reels, lines and fishing-related apparels (such as polarized sunglasses). The company also offers licensed Prince brand tennis gear, G-III brand golf gear, Bottecchia bicycles and other outdoor products. Founded by engineer Yoshio Matsui (, 1906-1983) in 1955 as and then formally established in 1958 as , the company renamed itself Globeride on October 1, 2009. The company operates from offices throughout Japan and internationally from subsidiaries in Australia, France, Germany, Mainland China and Taiwan, Thailand, the United Kingdom and the United States. The British subsidiary, Daiwa Sports Ltd., was established in 1977 and production commenced the following year with the production of fishing rods and golf clubs. Brands G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimano
, originally and later , is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational manufacturing company for cycling components, fishing tackle and rowing (sport), rowing equipment, which also produced golf supplies until 2005 and snowboarding gear until 2008. Named after founder Shozaburo Shimano (, 1894–1958) and headquartered in Sakai, Osaka, Sakai, Osaka Prefecture, the company has 32 consolidated and 11 unconsolidated subsidiaries, with the primary manufacturing plants based in Kunshan (China), Malaysia and Singapore. In 2017, Shimano had net sales of US dollar, US $3.2 billion, 38% in Europe, 35% in Asia, and 11% in North America. Bicycle components represented 80%, fishing tackle 19%, and other products 0.1%. The company is publicly traded, with 93 million shares of common stock outstanding. They are also the official neutral support for most of the UCI World Tour. Cycling Shimano sales constitute an estimated 85% of the global bicycle component market by value. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishing Tackle
Fishing tackle is the equipment used by fishermen, anglers when fishing. Almost any equipment or gear used in fishing can be called fishing tackle, examples being fishing hook, hooks, fishing line, lines, fishing bait, baits/fishing lure, lures, fishing rod, rods, fishing reel, reels, fishing float, floats, fishing sinker, sinkers/groundbait#Method feeder, feeders, fishing net, nets, spearfishing, spears, fishing gaff, gaffs and fishing trap, traps, as well as wires, snaps, beads, spoons, blades, spinners, clevises and tools that make it easy to tie knots. Tackle attached to the end of a fishing line that gets casting (fishing), cast out along with the bait are referred to as terminal tackle. Terminal tackle can include hooks, leaders, floats, sinkers/feeders, fishing swivel, swivels and attached shackle, snaps and/or circle cotter, split rings. Sometimes the term "rig (fishing), rig" is used for a specific assemblage of terminal tackle. Fishing tackle can be contrasted with fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Barker (fishing Guide)
Thomas Barker ('' fl''.1591–1651) was an English fishing guide and author of ''The Art of Angling'' (1651). Life For more than sixty years, he practised the art of angling, and "spent many pounds in the gaining of it". In the dedicatory address to Lord Montague, the author tells us that he was born at " Bracemeol in the liberty of Salop (ie Meole Brace in the vicinity of Shrewsbury, Shropshire), "being a freeman and burgess of the same city(''sic'')". Barker is described by Hugh Chisholm, in his ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' (1911) article on Izaak Walton, as being "a retired cook, and humorist".''Encyclopaedia Britannica'' (1911), Volume 28, p. 301;article on Izaak Walton by Hugh Chisholm, who misdate's Barker's "own treatise" to 1659. Treatise At the time of writing his treatise he was living in Westminster, and seems to have gained a livelihood by accompanying gentlemen on fishing expeditions, or giving instruction at home in the use of baits and tackle. The following inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the 180th meridian.- The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Geopolitically, the term Western Hemisphere is often used as a metonym for the Americas or the "New World", even though geographically the hemisphere also includes parts of other continents. Geography The Western Hemisphere consists of the Americas, excluding some of the Aleutian Islands to the southwest of the Alaskan mainland; the westernmost portions of Europe and Africa, both mainland and islands; the extreme eastern tip of the Russian mainland and islands ( North Asia); numerous territories in Oceania; and a large portion of Antarctica. The center of the Western Hemisphere is located in the Pacific Ocean at the intersection of the 90th meridian west and the Equator, among the Galápagos Islands. The nearest land is Genovesa Island at . The hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
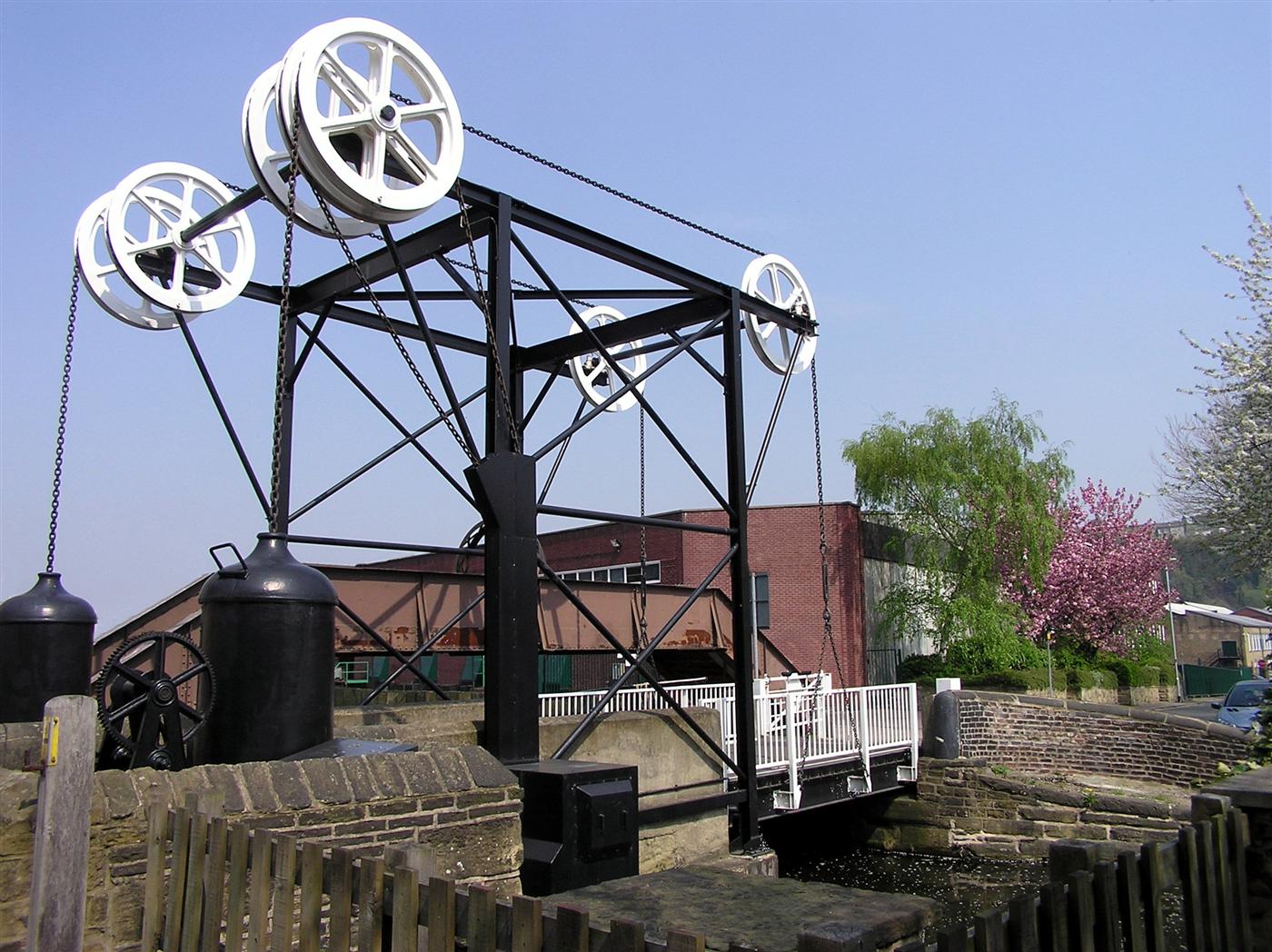
Windlass
The windlass is an apparatus for moving heavy weights. Typically, a windlass consists of a horizontal cylinder (barrel), which is rotated by the turn of a crank or belt. A winch is affixed to one or both ends, and a cable or rope is wound around the winch, pulling a weight attached to the opposite end. The Greek scientist Archimedes was the inventor of the windlass. A surviving medieval windlass, dated to –1400, is in the Church of St Mary and All Saints, Chesterfield. The oldest depiction of a windlass for raising water can be found in the Book of Agriculture published in 1313 by the Chinese official Wang Zhen (inventor), Wang Zhen of the Yuan Dynasty ( 1290–1333). Uses * Vitruvius, a military engineer writing about 28 BC, defined a machine as "a combination of timber fastened together, chiefly efficacious in moving great weights". About a century later, Hero of Alexandria summarized the practice of his day by naming the "five simple machines" for "moving a given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |