|
Fiscal Drag
Fiscal drag happens when the government's net fiscal position (spending minus taxation) fails to cover the net savings desires of the private economy, also called the private economy's spending gap (earnings minus spending and private investment). The resulting lack of aggregate demand leads to deflationary pressure, or drag, on the economy, essentially due to lack of state spending or to excess taxation. One cause of fiscal drag may be bracket creep, where progressive taxation increases automatically as taxpayers move into higher tax brackets due to inflation. This tends to moderate inflation, and can be characterized as an automatic stabilizer to the economy. Fiscal drag can also be a result of a hawkish stance towards government finances. Real fiscal drag Real fiscal drag takes place when tax thresholds are increased in line with price rises to avoid ''nominal fiscal drag'', but where a growing economy means that earnings rise faster still, so increasing taxes as proportion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budget Deficit
Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit, the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budget of a government, private company, or individual. A central point of controversy in economics, government deficit spending was first identified as a necessary economic tool by John Maynard Keynes in the wake of the Great Depression. Controversy Government deficit spending is a central point of controversy in economics, with prominent economists holding differing views. The mainstream economics position is that deficit spending is desirable and necessary as part of countercyclical fiscal policy, but that there should not be a structural deficit (i.e., permanent deficit): The government should run deficits during recessions to compensate for the shortfall in aggregate demand, but should run surpluses in boom times so that there is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggregate Demand
In economics, aggregate demand (AD) or domestic final demand (DFD) is the total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given time. It is often called effective demand, though at other times this term is distinguished. This is the demand for the gross domestic product of a country. It specifies the amount of goods and services that will be purchased at all possible price levels. Consumer spending, investment, corporate and government expenditure, and net exports make up the aggregate demand. The aggregate demand curve is plotted with real output on the horizontal axis and the price level on the vertical axis. While it is theorized to be downward sloping, the Sonnenschein–Mantel–Debreu results show that the slope of the curve cannot be mathematically derived from assumptions about individual rational behavior. Instead, the downward sloping aggregate demand curve is derived with the help of three macroeconomic assumptions about the functioning of markets: Pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
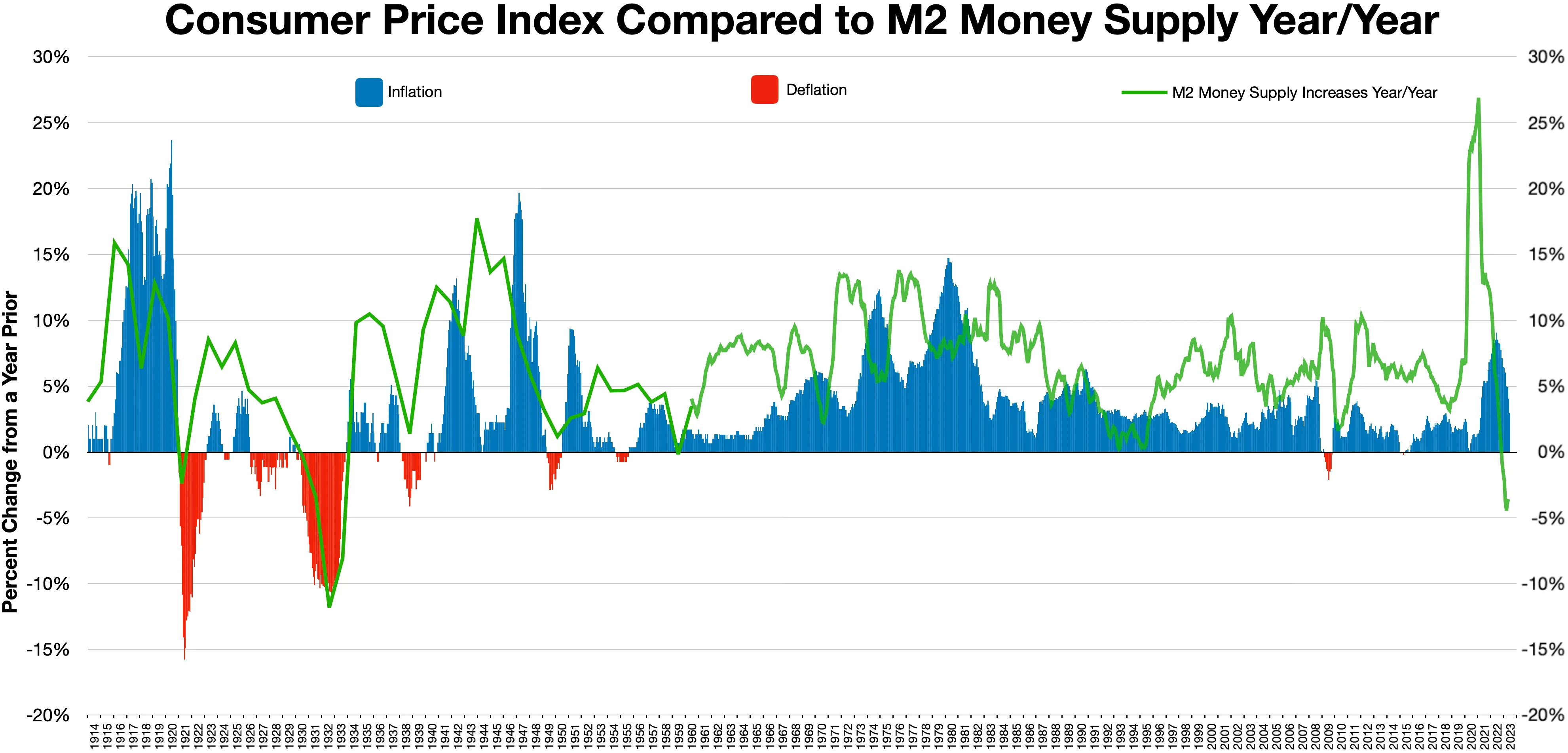
Deflationary
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% and becomes negative. While inflation reduces the value of currency over time, deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from '' disinflation'', a slowdown in the inflation rate; i.e., when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive. Economists generally believe that a sudden deflationary shock is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the real value of debt, especially if the deflation is unexpected. Deflation may also aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral . Some economists argue that prolonged deflationary periods are related to the underlying technological progress in an economy, because as productivity increases ( TFP), the cost of goods decreases. Deflation usually happens when supply is hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
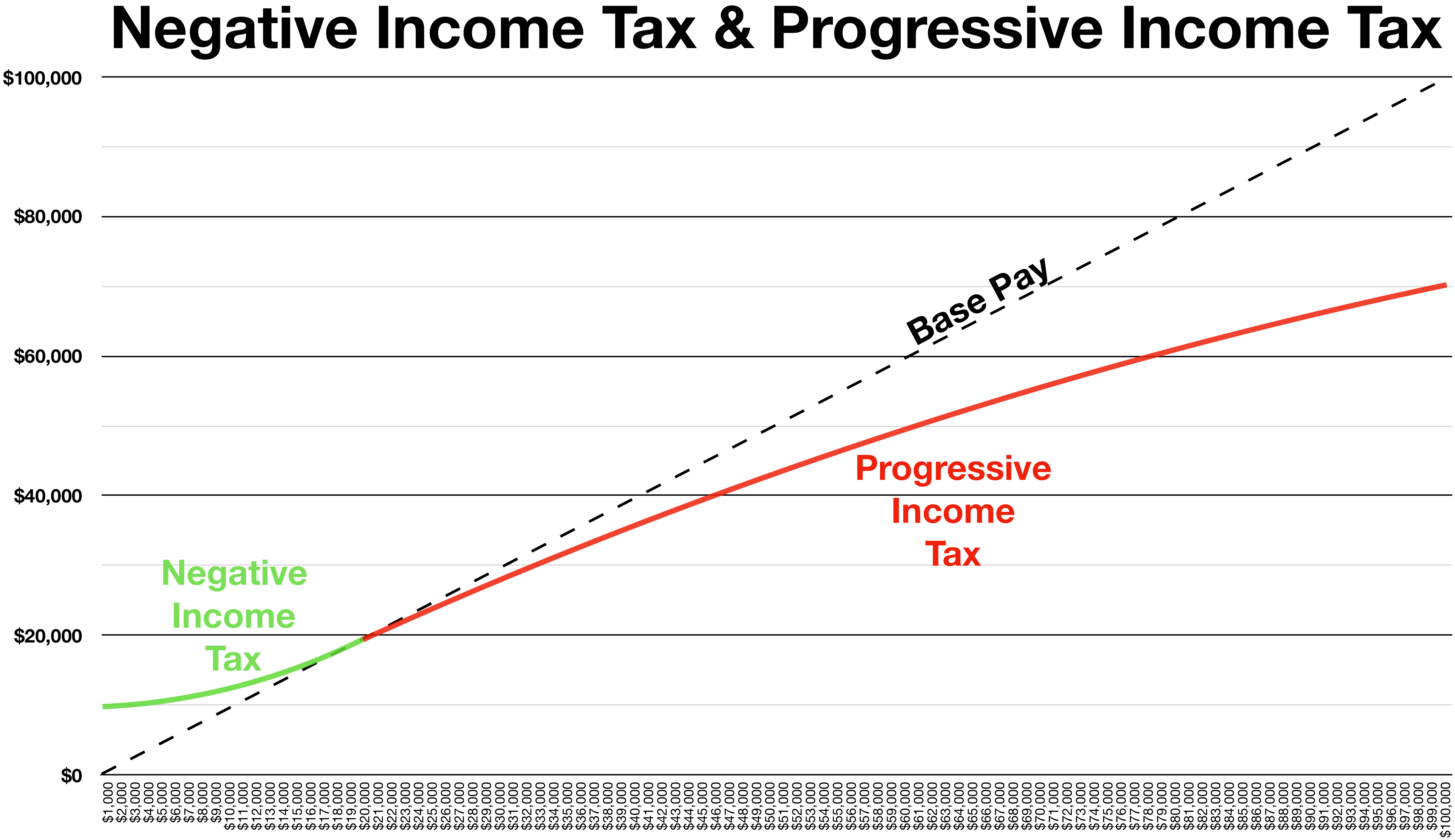
Bracket Creep
Bracket creep is usually defined as the process by which inflation pushes wages and salaries into higher tax brackets, leading to fiscal drag. However, even if there is only one tax bracket, or one remains within the same tax bracket, there will still be bracket creep resulting in a higher proportion of income being paid in tax. That is, although the marginal tax rate remains unchanged with inflation, the average tax rate will increase. Most progressive tax systems are not adjusted for inflation. As wages and salaries rise in nominal terms under the influence of inflation they become more highly taxed, even though in real terms the value of the wages and salaries has not increased at all. The net effect is that in real terms taxes rise unless the tax rates or brackets are adjusted to compensate. Examples Suppose a person earns $20,000 per year and is liable to 20% tax on earnings above a threshold of $5,000 per year. Then they pay ($20,000–$5,000)*0.2 = $3,000 in taxes, or 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Taxation
A progressive tax is a tax in which the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases. The term ''progressive'' refers to the way the tax rate progresses from low to high, with the result that a taxpayer's average tax rate is less than the person's marginal tax rate. The term can be applied to individual taxes or to a tax system as a whole. Progressive taxes are imposed in an attempt to reduce the tax incidence of people with a lower ability to pay, as such taxes shift the incidence increasingly to those with a higher ability-to-pay. The opposite of a progressive tax is a regressive tax, such as a sales tax, where the poor pay a larger proportion of their income compared to the rich (for example, spending on groceries and food staples varies little against income, so poor pay similar to rich even while latter has much higher income). The term is frequently applied in reference to personal income taxes, in which people with lower income pay a lower percentage of that inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of CPI inflation is deflation, a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index. Changes in inflation are widely attributed to fluctuations in Real versus nominal value (economics), real demand for goods and services (also known as demand shocks, including changes in fiscal policy, fiscal or monetary policy), changes in available supplies such as during energy crisis, energy crises (also known as supply shocks), or changes in inflation expectations, which may be self-fulfilling. Moderat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelanda sovereign state covering five-sixths of the island) and Northern Ireland (part of the United Kingdomcovering the remaining sixth). It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest in the world. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islands by population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Income Tax
A progressive tax is a tax in which the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases. The term ''progressive'' refers to the way the tax rate progresses from low to high, with the result that a taxpayer's average tax rate is less than the person's marginal tax rate. The term can be applied to individual taxes or to a tax system as a whole. Progressive taxes are imposed in an attempt to reduce the tax incidence of people with a lower ability to pay, as such taxes shift the incidence increasingly to those with a higher ability-to-pay. The opposite of a progressive tax is a regressive tax, such as a sales tax, where the poor pay a larger proportion of their income compared to the rich (for example, spending on groceries and food staples varies little against income, so poor pay similar to rich even while latter has much higher income). The term is frequently applied in reference to personal income taxes, in which people with lower income pay a lower percentage of that income ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Central Bank
The European Central Bank (ECB) is the central component of the Eurosystem and the European System of Central Banks (ESCB) as well as one of seven institutions of the European Union. It is one of the world's Big Four (banking)#International use, most important central banks with a balance sheet total of around 7 trillion. The Governing Council of the European Central Bank, ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy for the Eurozone and the European Union, administers the foreign exchange reserves of EU member states, engages in foreign exchange operations, and defines the intermediate monetary objectives and key interest rate of the EU. The Executive Board of the European Central Bank, ECB Executive Board enforces the policies and decisions of the Governing Council, and may direct the national central banks when doing so. The ECB has the exclusive right to authorise the issuance of euro banknotes. Member states can issue euro coins, but the volume must be approved by the EC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wage Inflation
Real wages are wages adjusted for inflation, or equivalently wages in terms of the amount of goods and services that can be bought. This term is used in contrast to nominal wages or unadjusted wages. Because it has been adjusted to account for changes in the prices of goods and services, real wages provide a clearer representation of an individual's wages in terms of what they can afford to buy with those wages – specifically, in terms of the amount of goods and services that can be bought; however, real wages suffer the disadvantage of not being well defined, since the amount of inflation (which can be calculated based on different combinations of goods and services) is itself not well defined. Hence real wage defined as the total amount of goods and services that can be bought with a wage, is also not defined. This is because of changes in the relative prices. Despite difficulty in defining one value for the real wage, in some cases a real wage can be said to have unequivoca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of CPI inflation is deflation, a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index. Changes in inflation are widely attributed to fluctuations in real demand for goods and services (also known as demand shocks, including changes in fiscal or monetary policy), changes in available supplies such as during energy crises (also known as supply shocks), or changes in inflation expectations, which may be self-fulfilling. Moderate inflation affects economies in both positive and negative ways. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purchasing Power Parity
Purchasing power parity (PPP) is a measure of the price of specific goods in different countries and is used to compare the absolute purchasing power of the countries' currency, currencies. PPP is effectively the ratio of the price of a market basket at one location divided by the price of the basket of goods at a different location. The PPP inflation and exchange rate may differ from the Exchange rate, market exchange rate because of tariffs, and other transaction costs. The purchasing power parity indicator can be used to compare economies regarding their gross domestic product (GDP), labour productivity and actual individual consumption, and in some cases to analyse price convergence and to compare the cost of living between places. The calculation of the PPP, according to the OECD, is made through a ''basket of goods'' that contains a "final product list [that] covers around 3,000 consumer goods and services, 30 occupations in government, 200 types of equipment goods and about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |