|
Fiore Dei Liberi
Fiore Furlano de Cividale d'Austria, delli Liberi da Premariacco (Fiore dei Liberi, Fiore Furlano, Fiore de Cividale d'Austria; born ca. 1350; died after 1409) was a late 14th century knight, diplomat, and itinerant fencing master. He is the earliest Italian master from whom an martial arts manual has survived. His ''Flower of Battle'' (''Fior di Battaglia'', ''Flos Duellatorum'') is among the oldest surviving fencing manuals. Life Fiore dei Liberi was born in Cividale del Friuli, a town in the Patriarchal State of Aquileia in the Friuli region of modern-day Italy, the son of Benedetto and scion of a Liberi house of Premariacco.Liberi, Fiore dei (ca.1400s). ''Fior di Battaglia'' anuscript Ms. M.383. New York City: Morgan Library & Museum. ff 1r–2r.Liberi, Fiore dei (ca.1400). ''Fior di Battaglia'' anuscript Ms. Ludwig XV 13 (ACNO 83.MR.183). Los Angeles: J. Paul Getty Museum. ff 1r–2r.Liberi, Fiore dei (1409). ''Flos Duellatorum'' anuscript Pisani Dossi Ms. Italy: P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cividale Del Friuli
Cividale del Friuli (, locally ; ; ) is a town and (municipality) in the Regional decentralization entity of Udine, part of the North-Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia. The town lies above sea-level in the foothills of the eastern Alps, by rail from the city of Udine and close to the Slovenian border. It is situated on the river Natisone, which forms a picturesque ravine here. Formerly an important regional power, it is today a quiet, small town that attracts tourists thanks to its medieval center. History Archaeological findings reveal that the area was already inhabited in Paleolithic and Neolithic times. During the Iron Age the region was settled by Veneti and Celts. Due to the location's strategic position on the northeastern frontier of Roman Italy, in 50 BC, the Romans founded there a ''castrum'', which afterwards was transformed by Julius Caesar into a '' forum'' and its name changed into ''Forum Iulii'' ("Julius' marketplace"; Fréjus had the same Roman name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
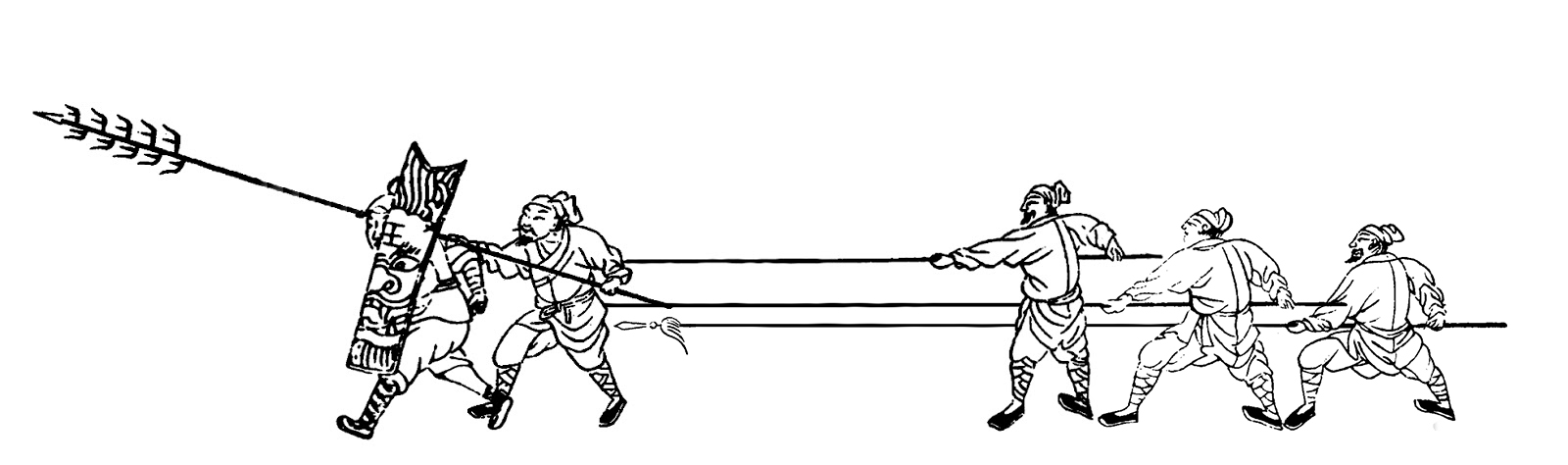
Jixiao Xinshu
The ''Jixiao Xinshu'' () or ''New Treatise on Military Efficiency'' is a military manual written during the 1560s and 1580s by the Ming dynasty general Qi Jiguang. Its primary significance is in advocating for a combined arms approach to warfare using five types of infantry and two type of support. Qi Jiguang separated infantry into five separate categories: firearms, swordsmen, archers with fire arrows, ordinary archers, and spearmen. He split support crews into horse archers and artillery units. The ''Jixiao Xinshu'' is also one of the earliest-existing East Asian texts to address the relevance of Chinese martial arts with respect to military training and warfare. Several contemporary martial arts styles of Qi's era are mentioned in the book, including the staff method of the Shaolin temple. Background In the late 16th century the military of the Ming dynasty was in poor condition. As the Mongol forces of Altan Khan raided the northern frontier, China's coastline fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars. For most of its history the Empire comprised the entirety of the modern countries of Germany, Czechia, Austria, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Slovenia, and Luxembourg, most of north-central Italy, and large parts of modern-day east France and west Poland. On 25 December 800, Pope Leo III crowned the Frankish king Charlemagne Roman emperor, reviving the title more than three centuries after the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The title lapsed in 924, but was revived in 962 when Otto I, OttoI was crowned emperor by Pope John XII, as Charlemagne's and the Carolingian Empire's successor. From 962 until the 12th century, the empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry V (; probably 11 August 1081 or 1086 – 23 May 1125) was King of Germany (from 1099 to 1125) and Holy Roman Emperor (from 1111 to 1125), as the fourth and last ruler of the Salian dynasty. He was made co-ruler by his father, Henry IV, in 1098. In Emperor Henry IV's conflicts with the imperial princes and the struggle against the reform papacy during the Investiture Controversy, young Henry V allied himself with the opponents of his father. He forced Henry IV to abdicate on 31 December 1105 and ruled for five years in compliance with the imperial princes. He tried, unsuccessfully, to withdraw the regalia from the bishops. Then in order to at least preserve the previous right to invest, he captured Pope Paschal II and forced him to perform his imperial coronation in 1111. Once crowned emperor, Henry departed from joint rule with the princes and resorted to earlier Salian autocratic rule. After he had failed to increase control over the church, the princes in Saxony and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cristallo Dei Liberi
Cristallo is a glass that is totally clear (like rock crystal), without the slight yellow or greenish color originating from iron oxide impurities. This effect is achieved through small additions of manganese oxide.R. W. Douglas: ''A history of glassmaking'', G T Foulis & Co Ltd, Henley-on-Thames, 1972, . Cristallo often has a low lime content, which makes it prone to glass corrosion (otherwise known as glass disease). The invention of Cristallo glass is attributed to Angelo Barovier around 1450. Materials In addition to common glass making materials, manganese, quartz pebbles, and alume catino, a particularly suitable form of soda ash, are used in the making of cristallo glass. Rather than using common sand, crushed quartz pebbles were used instead. The quartz pebbles were typically from the Ticino and the Adige rivers. The quartz pebbles went through a rigorous screening process before being selected for use in cristallo production. The quartz pebbles had to be free of yellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Knight
The Free Imperial Knights (, ) were free nobles of the Holy Roman Empire, whose direct overlord was the Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor. They were the remnants of the medieval free nobility (''edelfrei'') and the ministerialis, ministeriales. What distinguished them from other knights, who were vassals of a higher lord, was that they had been granted Imperial immediacy, and as such were the equals in most respects to the other individuals or entities, such as the secular and ecclesiastical territorial rulers of the Empire (margraves, dukes, princes, counts, archbishops, bishops, abbots, etc.) and the Free imperial city, free imperial cities, that also enjoyed Imperial immediacy. However, unlike all of those, the Imperial knights did not possess the status of Imperial State, Estates (''Stände'') of the Empire, and therefore were not represented, individually or collectively, in the Imperial Diet (Holy Roman Empire), Imperial Diet. They tended to define their responsibilities to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically hereditary and patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, but nobility also existed in such regimes as the Dutch Republic (1581–1795), the Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity. The concept of a knighthood may have been inspired by the ancient Greek '' hippeis'' (ἱππεῖς) and Roman ''equites''. In the Early Middle Ages in Western Christian Europe, knighthoods were conferred upon mounted warriors. During the High Middle Ages, a knighthood was considered a class of petty nobility. By the Late Middle Ages, the rank had become associated with the ideals of chivalry, a code of conduct for the perfect courtly Christian warrior. Often, a knight was a vassal who served as an elite fighter or a bodyguard for a lord, with payment in the form of land holdings. The lords trusted the knights, who were skilled in battle on horseback. In the Middle Ages, a knighthood was closely linked with horsemanship (and especially the joust) from its orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, implemented in 1949 following the end of World War II, defines a German as a German nationality law, German citizen. During the 19th and much of the 20th century, discussions on German identity were dominated by concepts of a common language, culture, descent, and history.. "German identity developed through a long historical process that led, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, to the definition of the German nation as both a community of descent (Volksgemeinschaft) and shared culture and experience. Today, the German language is the primary though not exclusive criterion of German identity." Today, the German language is widely seen as the primary, though not exclusive, criterion of German identity. Estimates on the total number of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edelfrei
The term ''edelfrei'' or ''hochfrei'' ("free noble" or "free knight") was originally used to designate and distinguish those Germanic noblemen from the Second Estate (see Estates of the realm social hierarchy), who were legally entitled to atonement reparation of three times their "Weregild" (Wergeld) value from a guilty person or party. Such knights were known as ''Edelfreie'' or ''Edelinge''. This distinguished them from those other free men or free knights who came from the Third Estate social hierarchy, and whose atonement reparation value was the standard "Weregild" (Wergeld) amount set according to regional laws. In the Holy Roman Empire, the "high nobility" (') emerged from the ''Edelfreie'' during the course of the 12th century, in contrast to the so-called '' ministeriales'', most of whom were originally unfree knights or '.Karl Bosl: ''Die Gesellschaft in der Geschichte des Mittelalters.'' 4. Auflage. Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, Göttingen 1987, {{ISBN, 3-525-33389-7, p. 56 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Immediacy
In the Holy Roman Empire, imperial immediacy ( or ) was the status of an individual or a territory which was defined as 'immediate' () to Emperor and Empire () and not to any other intermediate authorities, while one that did not possess that status was defined as 'mediate' (). The possession of this imperial immediacy granted a constitutionally unique form of territorial authority known as "territorial superiority" () which had nearly all the attributes of sovereignty, but fell short of true sovereignty since the rulers of the Empire remained answerable to the Empire's institutions and basic laws. In the early modern period, the Empire consisted of over 1,800 immediate territories, ranging in size from quite large such as Austria, Bavaria, Saxony, and Brandenburg, down to the several hundred tiny immediate estates of the Imperial knights of only a few square kilometers or less, which were by far the most numerous. Acquisition The criteria of immediacy varied and classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morgan Library & Museum
The Morgan Library & Museum (originally known as the Pierpont Morgan Library and colloquially known the Morgan) is a museum and research library in New York City, New York, U.S. Completed in 1906 as the private library of the banker J. P. Morgan, the institution is housed at 225 Madison Avenue in the Murray Hill neighborhood of Manhattan. , the museum is directed by Colin B. Bailey and governed by a board of trustees. The site was formerly occupied by several Phelps family residences, one of which was sold to J. P. Morgan in 1880. After collecting thousands of objects in the late 19th century, Morgan erected the main library building between 1902 and 1906, with Belle da Costa Greene serving as its first librarian for more than four decades. The library was made a public institution in 1924 by J. P. Morgan's son John Pierpont Morgan Jr., in accordance with his father's will, and further expansions were completed in 1928, 1962, and 1991. The Morgan Library was renamed the Mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |