|
Fillingham
Fillingham is a village and civil parish in the West Lindsey district of Lincolnshire, England. It is situated north from the city and county town of Lincoln, and just over west from the A15 road. Fillingham Grade II* listed Anglican church is dedicated to St Andrew. Originally a building in Early English and Decorated style, it was largely rebuilt in 1777 with a new chancel and tower. It was further restored in 1866.Cox, J. Charles (1916) ''Lincolnshire'' p. 125; Methuen & Co. Ltd The earliest element is a c.1200 round-headed doorway in the west transept.''Kelly's Directory of Lincolnshire with the port of Hull'' 1885, p. 392 In the churchyard is a cross, high, dedicated to Major Thomas N. Dalton, killed in the Battle of Inkerman in 1854. John Wycliffe was rector of the village from 1361 to 1368. There is evidence of a Roman camp in the village and Anglo Saxon pottery has also been found. Archaeological excavations have also found evidence of an Anglo Saxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Cecil Wray, 13th Baronet
Sir Cecil Wray, 13th Baronet (3 September 1734 – 10 January 1805) was an English landowner and politician, and one of the Wray baronets. Life Wray was born into an old Lincolnshire family as the eldest and only surviving son of Sir John Wray, 12th Baronet (died 1752), who had married Frances (died 1770), the daughter and sole heiress of Fairfax Norcliffe of Langton, Yorkshire. Cecil was educated at Westminster School (1745) and Trinity College, Cambridge (1749). On the death of his father in 1752 Cecil succeeded to the baronetcy and to large estates in Lincolnshire, Norfolk, and Yorkshire. He lived in a large house on the north-east side of Eastgate, Lincoln, but, through annoyance from ‘the clanging of anvils in a blacksmith's shop opposite, got disgusted’ with it. He also procured the demolition of the four gatehouses across Eastgate. From 26 December 1755 to 20 December 1757, he was a cornet in the 1st dragoons, and on 17 June 1778 he was appointed captain in the So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
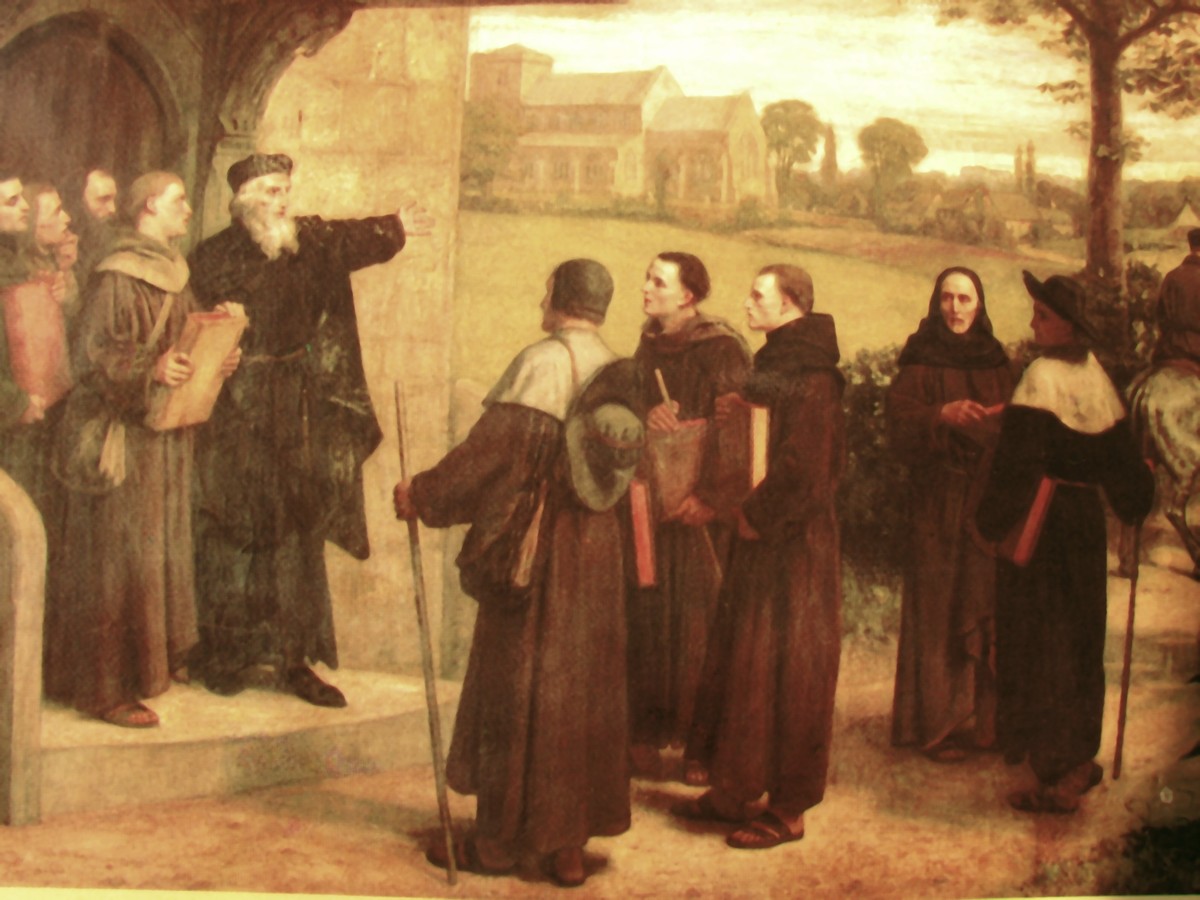
John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe (; also spelled Wyclif, Wickliffe, and other variants; 1328 – 31 December 1384) was an English scholastic philosopher, theologian, biblical translator, reformer, Catholic priest, and a seminary professor at the University of Oxford. He became an influential dissident within the Catholic priesthood during the 14th century and is considered an important predecessor to Protestantism. Wycliffe questioned the privileged status of the clergy, who had bolstered their powerful role in England, and the luxury and pomp of local parishes and their ceremonies. Wycliffe advocated translation of the Bible into the common vernacular. According to tradition, Wycliffe is said to have completed a translation direct from the Vulgate into Middle English – a version now known as Wycliffe's Bible. While it is probable that he personally translated the Gospels of Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John, it is possible he translated the entire New Testament. At any rate, it is ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Till, Lincolnshire
The River Till is a river in the county of Lincolnshire in England and is ultimately a tributary of the River Witham. Its upper reaches drain the land east of Gainsborough. The middle section is embanked, as the water level is higher than that of the surrounding land, and pumping stations pump water from low level drainage ditches into the river. Its lower reaches from the hamlet of Odder near Saxilby into the city of Lincoln were canalised, possibly as early as Roman times, as part of the Foss Dyke. Much of the channel is managed by the Environment Agency as it is classified as a main river, while the upper river and the land drainage ditches which border the river are managed by the Upper Witham internal drainage board. In order the help protect the city of Lincoln from flooding, a sluice has been built across the channel at the Till Washlands site. When flooding is a possibility, the sluice is closed, and other sluices allow the surrounding farmland to be inundated until wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for National Statistics (ONS) is responsible for the census in England and Wales, the General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) is responsible for the census in Scotland, and the Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency (NISRA) is responsible for the census in Northern Ireland. The Office for National Statistics is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department formed in 2008 and which reports directly to Parliament. ONS is the UK Government's single largest statistical producer of independent statistics on the UK's economy and society, used to assist the planning and allocation of resources, policy-making and decision-making. ONS designs, manages and runs the census in England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
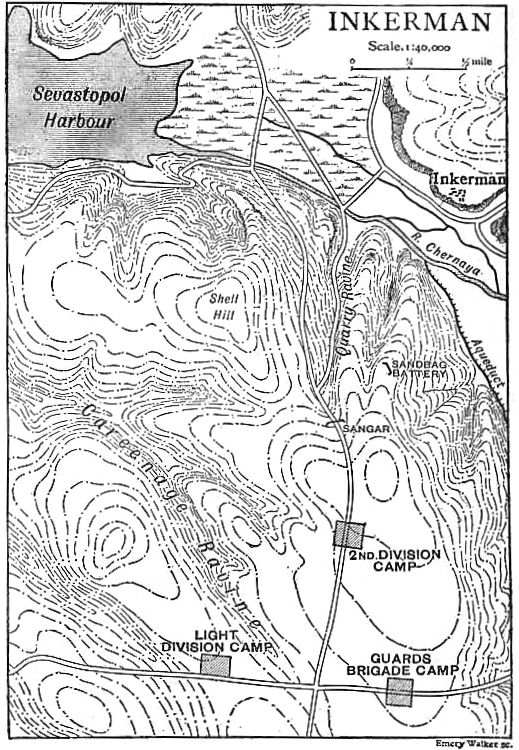
Battle Of Inkerman
The Battle of Inkerman was fought during the Crimean War on 5 November 1854 between the allied armies of Britain and France against the Imperial Russian Army. The battle broke the will of the Russian Army to defeat the allies in the field, and was followed by the siege of Sevastopol. The role of troops fighting mostly on their own initiative due to the foggy conditions during the battle has earned the engagement the name "The Soldier's Battle." Prelude to the battle The allied armies of Britain, France, Sardinia, and the Ottoman Empire had landed on the west coast of Crimea on 14 September 1854, intending to capture the Russian naval base at Sevastopol. The allied armies fought off and defeated the Russian Army at the Battle of Alma, forcing them to retreat in some confusion toward the River Kacha. While the allies could have taken this opportunity to attack Sevastopol before Sevastopol could be put into a proper state of defence, the allied commanders, British general FitzR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages In Lincolnshire
A village is a clustered human settlement or Residential community, community, larger than a hamlet (place), hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a Church (building), church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genuki
GENUKI is a genealogy web portal, run as a charitable trust. It "provides a virtual reference library of genealogical information of particular relevance to the UK and Ireland". It gives access to a large collection of information, with the emphasis on primary sources, or means to access them, rather than on existing genealogical research. Name The name derives from "GENealogy of the UK and Ireland", although its coverage is wider than this. From the GENUKI website: Structure The website has a well defined structure at four levels. * The first level is information that is common to all "the United Kingdom and Ireland". * The next level has information for each of England (see example) Ireland, Scotland, Wales, the Channel Islands and the Isle of Man. * The third level has information on each pre-1974 county of England and Wales, each of the pre-1975 counties of Scotland, each of the 32 counties of Ireland and each island of the Channel Islands (e.g. Cheshire, County Kerry an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossdyke Navigation
The Foss Dyke, or Fossdyke, connects the River Trent at Torksey to Lincoln, the county town of Lincolnshire, and may be the oldest canal in England that is still in use. It is usually thought to have been built around AD 120 by the Roman Britain, Romans, but there is no consensus among authors. It was refurbished in 1121, during the reign of King Henry I of England, Henry I, and responsibility for its maintenance was transferred to the city of Lincoln by King James I of England, James I. Improvements made in 1671 included a navigable sluice or lock at Torksey, and warehousing and wharves were built at Brayford Pool in the centre of Lincoln. Connection to the River Witham at Brayford was hampered by the small bore and depth of High Bridge, a medieval structure just below the pool. The channel through it was made deeper in 1795, but John Rennie the Elder, John Rennie's plans to demolish it in 1803 were not adopted. The canal was leased to several generations of the Ellison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manor House
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals with manorial tenants and great banquets. The term is today loosely applied to various country houses, frequently dating from the Late Middle Ages, which formerly housed the landed gentry. Manor houses were sometimes fortified, albeit not as fortified as castles, and were intended more for show than for defencibility. They existed in most European countries where feudalism was present. Function The lord of the manor may have held several properties within a county or, for example in the case of a feudal baron, spread across a kingdom, which he occupied only on occasional visits. Even so, the business of the manor was directed and controlled by regular manorial courts, which appointed manorial officials such as the bailiff, granted copyhol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mansion
A mansion is a large dwelling house. The word itself derives through Old French from the Latin word ''mansio'' "dwelling", an abstract noun derived from the verb ''manere'' "to dwell". The English word '' manse'' originally defined a property large enough for the parish priest to maintain himself, but a mansion is no longer self-sustaining in this way (compare a Roman or medieval villa). ''Manor'' comes from the same root—territorial holdings granted to a lord who would "remain" there. Following the fall of Rome, the practice of building unfortified villas ceased. Today, the oldest inhabited mansions around the world usually began their existence as fortified houses in the Middle Ages. As social conditions slowly changed and stabilised fortifications were able to be reduced, and over the centuries gave way to comfort. It became fashionable and possible for homes to be beautiful rather than grim and forbidding allowing for the development of the modern mansion. In British Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battlement
A battlement in defensive architecture, such as that of city walls or castles, comprises a parapet (i.e., a defensive low wall between chest-height and head-height), in which gaps or indentations, which are often rectangular, occur at intervals to allow for the launch of arrows or other projectiles from within the defences. These gaps are termed " crenels" (also known as ''carnels'', or '' embrasures''), and a wall or building with them is called crenellated; alternative (older) terms are castellated and embattled. The act of adding crenels to a previously unbroken parapet is termed crenellation. The function of battlements in war is to protect the defenders by giving them something to hide behind, from which they can pop out to launch their own missiles. A defensive building might be designed and built with battlements, or a manor house might be fortified by adding battlements, where no parapet previously existed, or cutting crenellations into its existing parapet wall. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cemetery
A cemetery, burial ground, gravesite or graveyard is a place where the remains of dead people are buried or otherwise interred. The word ''cemetery'' (from Greek , "sleeping place") implies that the land is specifically designated as a burial ground and originally applied to the Roman catacombs. The term ''graveyard'' is often used interchangeably with cemetery, but a graveyard primarily refers to a burial ground within a churchyard. The intact or cremated remains of people may be interred in a grave, commonly referred to as burial, or in a tomb, an "above-ground grave" (resembling a sarcophagus), a mausoleum, columbarium, niche, or other edifice. In Western cultures, funeral ceremonies are often observed in cemeteries. These ceremonies or rites of passage differ according to cultural practices and religious beliefs. Modern cemeteries often include crematoria, and some grounds previously used for both, continue as crematoria as a principal use long after the intermen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |