|
File-sharing
File sharing is the practice of distributing or providing access to digital media, such as computer programs, multimedia (audio, images and video), documents or electronic books. Common methods of storage, transmission and dispersion include removable media, centralized servers on computer networks, Internet-based hyperlinked documents, and the use of distributed peer-to-peer networking. File sharing technologies, such as BitTorrent, are integral to modern media piracy, as well as the sharing of scientific data and other free content. History Files were first exchanged on removable media. Computers were able to access remote files using filesystem mounting, bulletin board systems (1978), Usenet (1979), and FTP servers (1970's). Internet Relay Chat (1988) and Hotline (1997) enabled users to communicate remotely through chat and to exchange files. The mp3 encoding, which was standardized in 1991 and substantially reduced the size of audio files, grew to widespread use in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnutella
Gnutella is a peer-to-peer network protocol. Founded in 2000, it was the first decentralized peer-to-peer network of its kind, leading to other, later networks adopting the model. In June 2005, Gnutella's population was 1.81 million computers increasing to over three million nodes by January 2006.On the Long-term Evolution of the Two-Tier Gnutella Overlay . Rasti, Stutzbach, Rejaie, 2006. See Figure 2a. In late 2007, it was the most popular file-sharing network on the Internet with an estimated market share of more than 40%. History The first client (also called Gnutella) from which the network got its name was developed by Justin Frankel and Tom Pepper of Nullsoft in early 2000, soon after the company's acquisition by AOL. On March 14, the program was ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BitTorrent
BitTorrent is a Protocol (computing), communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P), which enables users to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a Decentralised system, decentralized manner. The protocol is developed and maintained by Rainberry, Inc., and was first released in 2001. To send or receive files, users use a Comparison of BitTorrent clients, BitTorrent client on their Internet-connected computer, which are available for a variety of computing platforms and Comparison of BitTorrent clients#Operating system support, operating systems, including BitTorrent (software), an official client. BitTorrent trackers provide a list of files available for transfer and allow the client to find peer users, known as "seeds", who may transfer the files. BitTorrent downloading is considered to be faster than HTTP ("direct downloading") and File Transfer Protocol, FTP due to the lack of a central server that could limit bandwidth. BitTorrent is one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of Node (networking), nodes. In addition, a personal area network (PAN) is also in nature a type of Decentralized computing, decentralized peer-to-peer network typically between two devices. Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage, or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional client–server model in which the consumption and supply of resources are divided. While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the architecture was popularized by the Internet file sharing system Napster, originally released in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazaa
Kazaa Media Desktop ( ) (once stylized as "KaZaA", but later usually written "Kazaa") was a peer-to-peer file sharing application using the FastTrack protocol licensed by Joltid Ltd. and operated as Kazaa by Sharman Networks. Kazaa was subsequently under license as a legal music subscription service by Atrinsic, Inc., which lasted until August 2012. Kazaa Media Desktop was commonly used to exchange MP3 music files and other file types, such as videos, applications, and documents over the Internet. The Kazaa Media Desktop client could be downloaded free of charge; however, it was bundled with adware and for a period there were "No spyware" warnings found on Kazaa's website. During the years of Kazaa's operation, Sharman Networks and its business partners and associates were the target of copyright-related lawsuits, related to the content distributed via Kazaa Media Desktop on the FastTrack protocol. By August 2012, the Kazaa website was no longer active. History Kazaa and F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napster
Napster was an American proprietary peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing application primarily associated with digital audio file distribution. Founded by Shawn Fanning and Sean Parker, the platform originally launched on June 1, 1999. Audio shared on the service was typically encoded in the MP3 format. As the software became popular, the company encountered legal difficulties over copyright infringement. Napster ceased operations in 2001 after losing multiple lawsuits and filed for bankruptcy in June 2002. The P2P model employed by Napster involved a centralized database that indexed a complete list of all songs being shared from connected clients. While effective, the service could not function without the central database, which was hosted by Napster and eventually forced to shut down. Following Napster's demise, alternative decentralized methods of P2P file-sharing emerged, including LimeWire, Gnutella, Freenet, FastTrack, I2P, and BitTorrent. Napster's assets were event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audiogalaxy
Audiogalaxy was an Internet music service with three incarnations. From 1998 to 2002, it was a file sharing system that indexed MP3 files. From mid-2002 to mid-2010, it was a promotional website for the Rhapsody music subscription service. Finally, from mid-2010 through 2012, it was a personal audio place shifting service. Audiogalaxy ceased operations on January 31, 2013. History The original Audiogalaxy system was created in 1998 by Michael Merhej as an FTP site index called The Borg Search. It quickly evolved into a robust peer-to-peer system with client software (the Audiogalaxy "Satellite"), a web-based search engine, always-on searching for requested files, auto-resume and low system impact. It quickly gained ground among file sharers abandoning Napster in 2001. Some observing the previous downfall of Napster via lawsuit were shocked at the design of Audiogalaxy, which was in some ways more centralized than Napster. Audiogalaxy's stated mission was to facilitate sharing o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FastTrack
FastTrack is a peer-to-peer (P2P) protocol that was used by the Kazaa, Grokster, iMesh and Morpheus file sharing programs. FastTrack was the most popular file sharing network in 2003, and used mainly for the exchange of music MP3 files. The network had approximately 2.4 million concurrent users in 2003. It is estimated that the total number of users was greater than that of Napster at its peak. History The FastTrack protocol and Kazaa were created and developed by Estonian programmers of BlueMoon Interactive headed by Jaan Tallinn, the same team that later created Skype. After selling it to Niklas Zennström from Sweden and Janus Friis from Denmark, it was introduced in March 2001 by their Dutch company Consumer Empowerment. It appeared during the end of the first generation of P2P networks – Napster shut down in July of that year. There are three FastTrack-based networks, and they use mutually incompatible versions of the protocol. The most popular clients on e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EDonkey2000
eDonkey2000 (nicknamed "ed2k") was a peer-to-peer file sharing application developed by US company MetaMachine ( Jed McCaleb and Sam Yagan), using the Multisource File Transfer Protocol. It supported both the eDonkey2000 network and the Overnet network. On September 28, 2005, eDonkey was discontinued following a cease and desist letter from the RIAA. eDonkey2000 network Users on the eDonkey2000 network predominantly share large files of tens or hundreds of megabytes, such as CD images, videos, games, and software programs. To ease file searching, some websites list the checksums of sought-after files in the form of an ed2k link. Some of those websites also have lists of active servers for users to update. MetaMachines has also created another file-sharing network called Overnet, which interoperates with the eDonkey network, but without the use of servers. Most eDonkey clients also now use the Overnet network. In 2004, MetaMachines announced it would stop development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freenet
Hyphanet (until mid-2023: Freenet) is a peer-to-peer platform for censorship-resistant, Anonymity application, anonymous communication. It uses a decentralized distributed data store to keep and deliver information, and has a suite of free software for publishing and communicating on the Web without fear of censorship.What is Freenet? , ''Freenet: The Free network official website''.Taylor, Ian J. ''From P2P to Web Services and Grids: Peers in a Client/Server World''. London: Springer, 2005. Both Freenet and some of its associated tools were originally designed by Ian Clarke (computer scientist), Ian Clarke, who defined Freenet's goal as providing freedom of speech on the Internet with strong anonymity protection. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usenet
Usenet (), a portmanteau of User's Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP, Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis (computing), Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was established in 1980.''From Usenet to CoWebs: interacting with social information spaces'', Christopher Lueg, Danyel Fisher, Springer (2003), , Users read and post messages (called ''articles'' or ''posts'', and collectively termed ''news'') to one or more topic categories, known as Usenet newsgroup, newsgroups. Usenet resembles a bulletin board system (BBS) in many respects and is the precursor to the Internet forums that have become widely used. Discussions are Threaded discussion, threaded, as with web forums and BBSes, though posts are stored on the server sequentially. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audio File Format
An audio file format is a file format for storing digital audio data on a computer system. The bit layout of the audio data (excluding metadata) is called the audio coding format and can be uncompressed, or audio compression (data), compressed to reduce the file size, often using lossy compression. The data can be a raw bitstream in an audio coding format, but it is usually embedded in a container format or an audio data format with defined storage layer. Format types It is important to distinguish between the audio coding format, the Container format (digital), container containing the Raw audio format, raw audio data, and an audio codec. A codec performs the encoding and decoding of the raw audio data while this encoded data is (usually) stored in a container file. Although most audio file formats support only one type of audio coding data (created with an audio codec, audio coder), a multimedia container format (as Matroska or Audio Video Interleave, AVI) may support multiple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
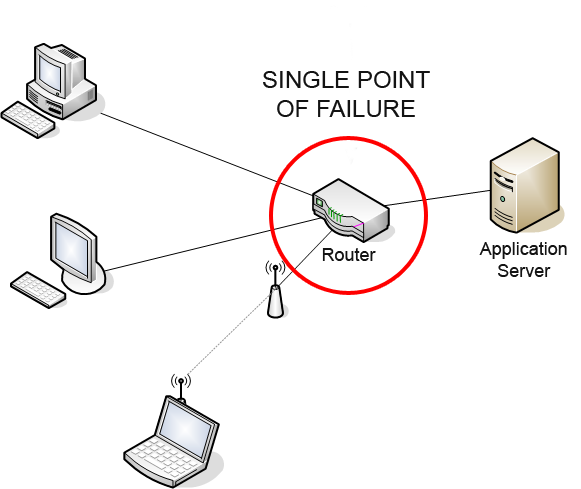
Single Point Of Failure
A single point of failure (SPOF) is a part of a system that would Cascading failure, stop the entire system from working if it were to fail. The term single point of failure implies that there is not a backup or redundant option that would enable the system to continue to function without it. SPOFs are undesirable in any system with a goal of high availability or Reliability engineering, reliability, be it a business practice, software application, or other industrial system. If there is a SPOF present in a system, it produces a potential interruption to the system that is substantially more disruptive than an error would elsewhere in the system. Overview Systems can be made robust by adding Redundancy (engineering), redundancy in all potential SPOFs. Redundancy can be achieved at various levels. The assessment of a potential SPOF involves identifying the critical components of a complex system that would provoke a total systems failure in case of wikt:malfunction, malfunction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |