|
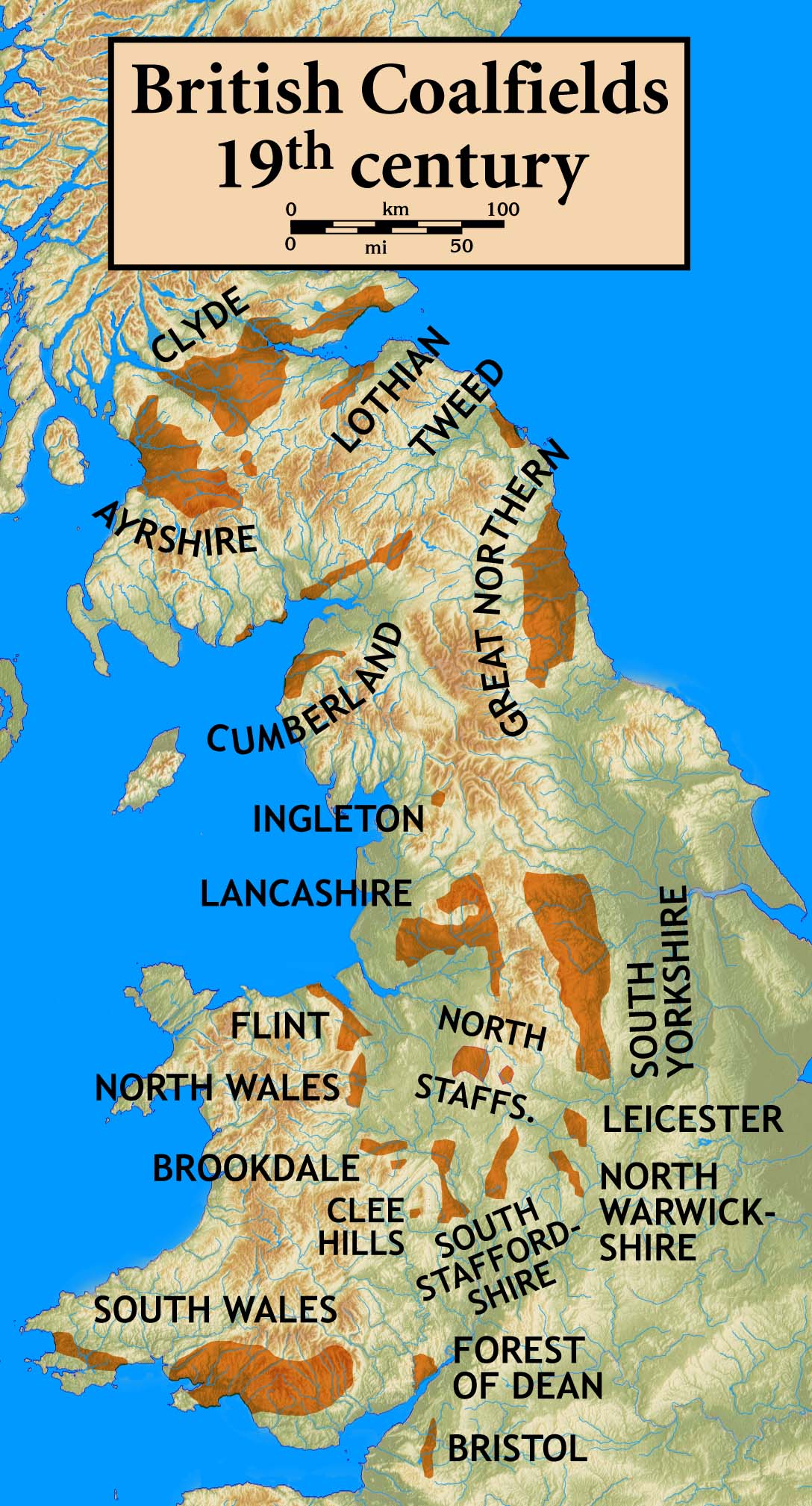
Fife Coalfield
The Fife Coalfield was one of the principal coalfields in Scotland. Over fifty collieries were in operation at various times between the middle of the nineteenth century and the closure of the last pit in 1988. The coalfield extended across the southern part of Fife where rocks of the Coal Measures Group occur and was one of a series of coalfields throughout the Midland Valley from which coal was won by both deep workings and opencasting methods. It is traditionally divided into the West Fife, Central Fife and East Fife coalfields with Kirkcaldy having been a particularly important area. Some of the mines extended beyond Fife under the Firth of Forth following the seams which occupy the Leven Syncline which extends to the south shore of the firth at Musselburgh and beyond.ch17, Trewin, N.H. (ed) 2002 ''The Geology of Scotland'', The Geological Society, London The Longannet power station near Kincardine used to source much of its coal from nearby pits but the Longannet coal mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musselburgh
Musselburgh (; ; ) is the largest settlement in East Lothian, Scotland, on the coast of the Firth of Forth, east of Edinburgh city centre. It had a population of as of . History The name Musselburgh is Old English language, Old English in origin, with ''mussel'' referring to Mussel, the shellfish.Musselburgh was famous for the mussel beds which grew in the Firth of Forth; after many years of claims that the mussels were unsafe for consumption, a movement has been started to reestablish the mussel beds as a commercial venture. The ''burgh'' element appears to derive from burh, in the same way as Edinburgh, before the introduction of formal burghs by David I of Scotland, David I. Its earliest Anglic name was ''Eskmuthe'' (Eskmouth) for its location at the mouth of the River Esk, Lothian, River Esk. Musselburgh was first settled by the Roman Britain, Romans in the years following their invasion of Scotland in 80 AD. They built a Inveresk Roman Fort, fort a little inland f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Fife
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines." Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic theory." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fife Coal Company
The Fife Coal Company was formed in 1872 to acquire the small Beath and Blairadam Colliery with its pits in Kelty. Its head office was in Leven. In addition to coal, the company worked some ironstone. For the whole of its operating life, the company was run by Charles Carlow and then his son C. Augustus Carlow. Output was expanded from an initial 70,000 tons a year to 4.3m. in 1911. Although it became the largest coal company in Scotland, Fife Coal never regained that level of output in the inter-war period. History Expansion The first meeting of the directors was held in Edinburgh in September 1872, under the chairmanship of William Lindsay, a shipowner and Lord Provost of Leith. It was resolved to form a new company and for £22,000 to buy the Beath and Blairadam Colliery which held a number of small pits in Kelty, in Fife. Shares were allotted in January 1873 and the task of modernising the Kelty pits and the construction of new collieries began. Given their ambitions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fife And Kinross Miners' Association
The Fife and Kinross Miners' Association was a coal miners' trade union based in Fife and Kinross-shire in Scotland. History The union was founded in 1869 or 1870, and proved immediately successful by achieving the eight-hour day for miners in the counties, and was the first union to be recognised by Scottish mine owners. In 1877, employers organised a lockout, targeting the union, but alone out of Scottish coal miners' unions, it survived. The union was a strong supporter of the 1892 UK miners' strike, even publishing a list of strikebreakers in the county. In 1894, the association became a founding member of the Scottish Miners Federation The National Union of Scottish Mineworkers (NUSW) is a trade union in Scotland, founded in 1894 as the Scottish Miners Federation. It joined the Miners' Federation of Great Britain, and in 1914 changed its name to National Union of Scottish Mine ..., which in turn affiliated to the Miners' Federation of Great Britain (MFGB). By 1907, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longannet Coal Mine
Longannet coal mine was a deep mine complex in Fife, Scotland. History Longannet was the remnant of three mines, established in the 1960s. Built on the north side of the Firth of Forth, east of Kincardine, it connected with the Bogside, Castlehill and Solsgirth Collieries, forming a single, tunnel. They provided fuel for the nearby, 2,400 MW Longannet power station. The Bogside Colliery closed in the 1980s, and by the early 1990s, the Castlehill and Solsgirth coal reserves were exhausted. Production continued from the Castlebridge area. On privatisation of the coal industry, the complex passed into the ownership of Mining Scotland and later Scottish Coal (Deep Mine) Ltd. In the late 1990s, new "roadway" tunnels were driven to access a coal seam beneath the Forth, downstream of the Kincardine Bridge. When production from Castlebridge ceased, in 2000, the northern side of the complex was sealed off and flooded. Dams were constructed, isolating the old workings from the active Kinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kincardine-on-Forth
Kincardine ( ; ) or Kincardine-on-Forth is a town on the north shore of the Firth of Forth, in Fife, Scotland. The town was given the status of a burgh of barony in 1663. It was at one time a reasonably prosperous minor port. The townscape retains many good examples of Scottish vernacular buildings from the 17th, 18th and early 19th centuries, although it was greatly altered during the construction of Kincardine Bridge in 1932–1936. It is in the civil parish of Tulliallan. Etymology The name ''Kincardine'', recorded in 1540 as ''Kincarne'', may be of either Pictish or Gaelic origin (It is also recorded as ''Kincarnyne''). The second element is Pictish ''*carden'', conceivably loaned into Gaelic, meaning "woodland" or perhaps "enclosure, encampment" (Middle Welsh ''cardden''). The first element is the Gaelic ''ceann'', "head end", but in view of the second element's "Pictish" distribution, it is most appropriately seen as an adaptation or translation of the cognate Pictis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firth Of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is a firth in Scotland, an inlet of the North Sea that separates Fife to its north and Lothian to its south. Further inland, it becomes the estuary of the River Forth and several other rivers. Name ''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meaning a narrow inlet. ''Forth'' stems from the name of the river; this is ('slow running') in Proto-Celtic, yielding in Old Gaelic and in Welsh. It was known as ' in Roman Empire, Roman times and was referred to as ' in Ptolemy's ''Geography_(Ptolemy), Geography''. In the Norse mythology, Norse sagas it was known as the . An early Welsh language, Welsh name is , or the 'sea of '. Geography and geology Geologically, the Firth of Forth is a fjord, formed by the Forth Glacier in the last glacial period. The drainage basin for the Firth of Forth covers a wide geographic area including places as far from the shore as Ben Lomond, Cumbernauld, Harthill, Scotland, Harthill, Penicuik and the edges of Gleneagles H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coalfield
A coalfield is an area of certain uniform characteristics where coal is mined. The criteria for determining the approximate boundary of a coalfield are geographical and cultural, in addition to geological. A coalfield often groups the seams of coal, railroad companies, cultural groups, and watersheds and other geographical considerations. At one time the coalfield designation was an important category in business and industrial discussions. The terminology declined into unimportance as the 20th century progressed, and was probably only referred to by a few small railroads and history buffs by the 1980s. Renewed interest in industrial heritage and coal mining history has brought the old names of the coalfields before a larger audience. Australia New South Wales *Gunnedah Basin coalfields *Hunter Valley coalfields * South Maitland coalfields *Sydney Basin coalfields Queensland *Bowen Basin coalfields *Galilee Basin coalfields *Surat Basin coalfields *Walloon coalfields Vict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkcaldy
Kirkcaldy ( ; ; ) is a town and former royal burgh in Fife, on the east coast of Scotland. It is about north of Edinburgh and south-southwest of Dundee. The town had a recorded population of 49,460 in 2011, making it Fife's second-largest settlement and the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, 11th most populous settlement in Scotland. Kirkcaldy has long been nicknamed the Lang Toun (; Scots language, Scots for "long town") in reference to the early town's main street, as indicated on maps from the 16th and 17th centuries. The street would finally reach a length of nearly , connecting the burgh to the neighbouring settlements of Linktown, Pathhead, Sinclairtown and Gallatown, which became part of the town in 1876. The formerly separate burgh of Dysart, Fife, Dysart was also later absorbed into Kirkcaldy in 1930 under an act of Parliament of the United Kingdom, Parliament. The area around Kirkcaldy has been inhabited since the Bronze Age. The first document t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
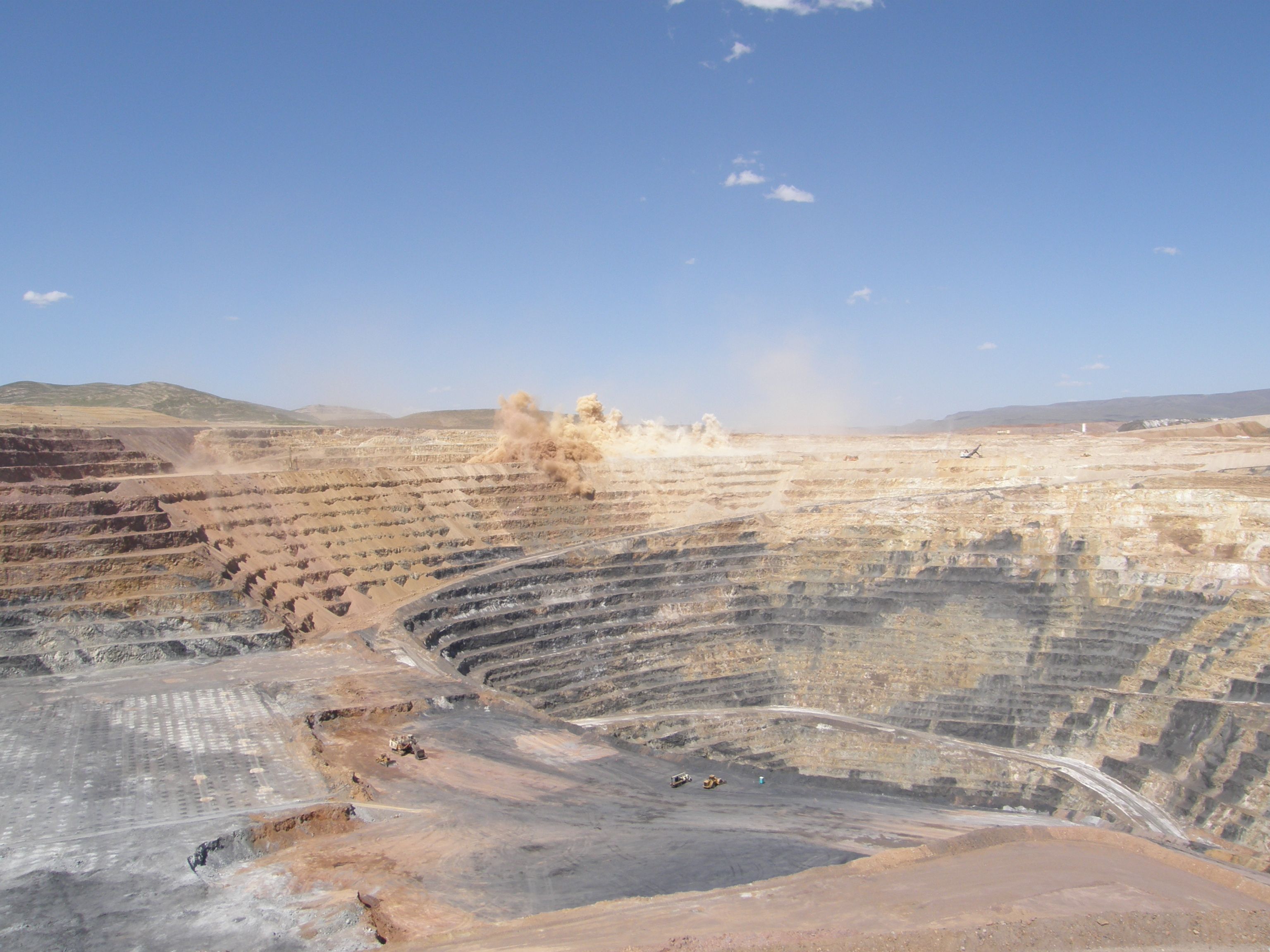
Opencast
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique that extracts rock or minerals from the earth. Open-pit mines are used when deposits of commercially useful ore or rocks are found near the surface where the overburden is relatively thin. In contrast, deeper mineral deposits can be reached using underground mining. Open-pit mining is considered one of the most dangerous sectors in the industrial world. It causes significant effects to miners' health, as well as damage to the ecological land and water. Open-pit mining causes changes to vegetation, soil, and bedrock, which ultimately contributes to changes in surface hydrology, groundwater levels, and flow paths. Additionally, open-pit produces harmful pollutants depending on the type of mineral being mined, and the type of mining process being used. Extraction Miners typically drill a series of test holes to locate an underground ore body. From the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |