|
Fields Medalists
The Fields Medal is a prize awarded to two, three, or four mathematicians under 40 years of age at the International Congress of Mathematicians, International Congress of the International Mathematical Union (IMU), a meeting that takes place every four years. The name of the award honours the Canadian mathematician John Charles Fields. The Fields Medal is regarded as one of the highest honors a mathematician can receive, and has been list of prizes known as the Nobel or the highest honors of a field, described as the Nobel Prize of Mathematics, although there are several major differences, including frequency of award, number of awards, age limits, monetary value, and award criteria. According to the annual Academic Excellence Survey by Academic Ranking of World Universities, ARWU, the Fields Medal is consistently regarded as the top award in the field of mathematics worldwide, and in another reputation survey conducted by IREG Observatory on Academic Ranking and Excellence, IR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Mathematical Union
The International Mathematical Union (IMU) is an international organization devoted to international cooperation in the field of mathematics across the world. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC) and supports the International Congress of Mathematicians (ICM). Its members are national mathematics organizations from more than 80 countries. The objectives of the International Mathematical Union are: promoting international cooperation in mathematics, supporting and assisting the International Congress of Mathematicians and other international scientific meetings/conferences, acknowledging outstanding research contributions to mathematics through the awarding of scientific prizes, and encouraging and supporting other international mathematical activities, considered likely to contribute to the development of mathematical science in any of its aspects, whether pure, applied, or educational. History The IMU was established in 1920, but dissolved in September 1932 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prizes Known As The Nobel Of A Field
Several fields of human cultural and scientific development are not included in the list of Nobel Prizes, because they are neither among the prizes established as part of Alfred Nobel's will nor, in the case of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, sponsored afterwards by the Nobel Foundation. While the foundation has discouraged (and occasionally taken legal action against) individuals and organizations that have used the Nobel name to refer to prizes not meeting the aforementioned criteria, several prominent individuals and organizations have nonetheless used the label "Nobel Prize of X" to refer to highly prestigious awards in fields of activity not covered by the official Nobel Prizes. These awards are listed below. Prizes sponsored by the Nobel Foundation Alfred Nobel's last will of 1895 only included five prizes, covering outstanding achievements who confer the "greatest benefit on mankind" in the fields of chemistry, physics, literature, peace, and physiology or m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
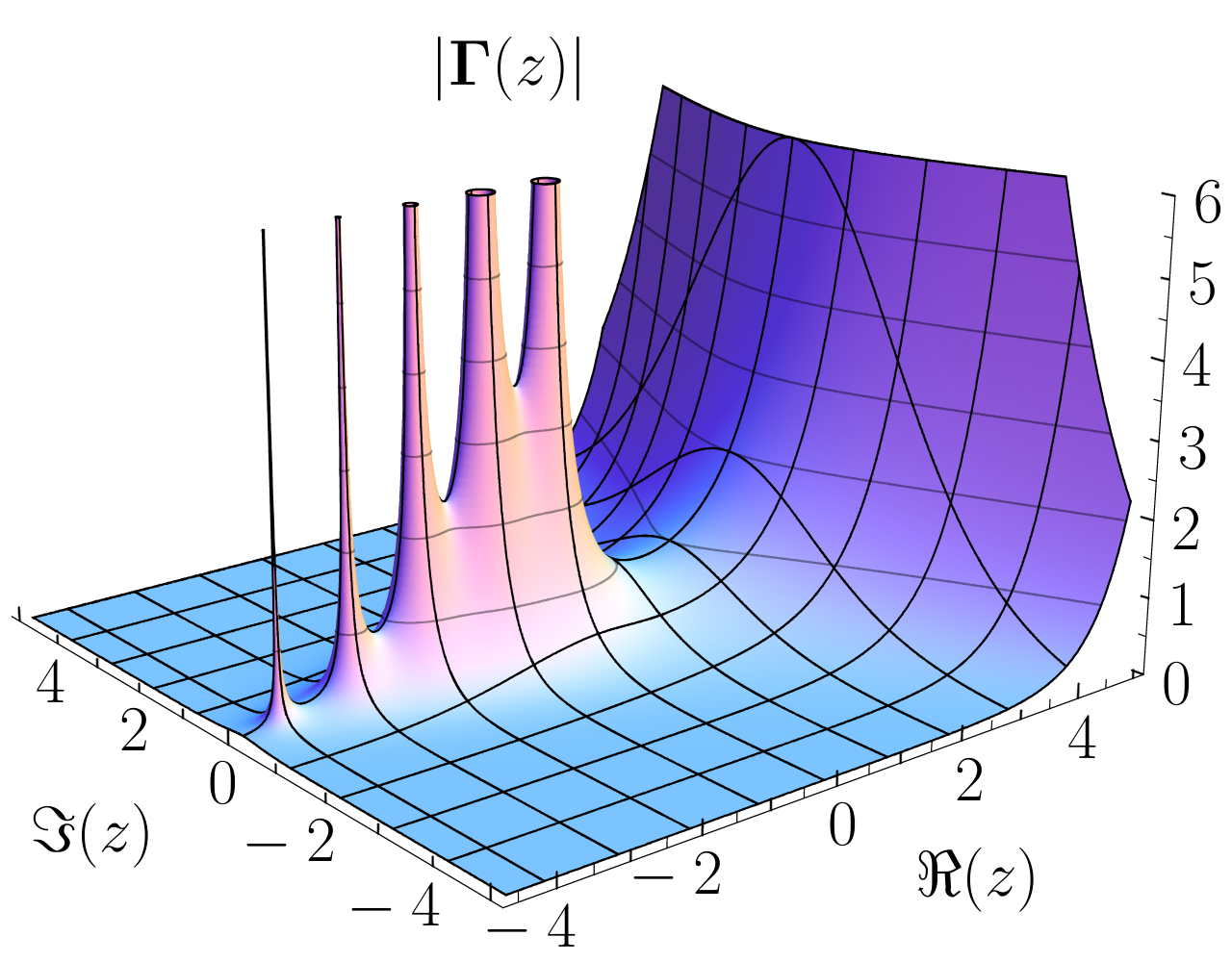
Meromorphic Function
In the mathematical field of complex analysis, a meromorphic function on an open subset ''D'' of the complex plane is a function that is holomorphic on all of ''D'' ''except'' for a set of isolated points, which are ''poles'' of the function. The term comes from the Greek ''meros'' ( μέρος), meaning "part". Every meromorphic function on ''D'' can be expressed as the ratio between two holomorphic functions (with the denominator not constant 0) defined on ''D'': any pole must coincide with a zero of the denominator. Heuristic description Intuitively, a meromorphic function is a ratio of two well-behaved (holomorphic) functions. Such a function will still be well-behaved, except possibly at the points where the denominator of the fraction is zero. If the denominator has a zero at ''z'' and the numerator does not, then the value of the function will approach infinity; if both parts have a zero at ''z'', then one must compare the multiplicity of these zeros. From an algeb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Function
In mathematics, the inverse function of a function (also called the inverse of ) is a function that undoes the operation of . The inverse of exists if and only if is bijective, and if it exists, is denoted by f^ . For a function f\colon X\to Y, its inverse f^\colon Y\to X admits an explicit description: it sends each element y\in Y to the unique element x\in X such that . As an example, consider the real-valued function of a real variable given by . One can think of as the function which multiplies its input by 5 then subtracts 7 from the result. To undo this, one adds 7 to the input, then divides the result by 5. Therefore, the inverse of is the function f^\colon \R\to\R defined by f^(y) = \frac . Definitions Let be a function whose domain is the set , and whose codomain is the set . Then is ''invertible'' if there exists a function from to such that g(f(x))=x for all x\in X and f(g(y))=y for all y\in Y. If is invertible, then there is exactly one functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riemann Surface
In mathematics, particularly in complex analysis, a Riemann surface is a connected one-dimensional complex manifold. These surfaces were first studied by and are named after Bernhard Riemann. Riemann surfaces can be thought of as deformed versions of the complex plane: locally near every point they look like patches of the complex plane, but the global topology can be quite different. For example, they can look like a sphere or a torus or several sheets glued together. Examples of Riemann surfaces include Graph of a function, graphs of Multivalued function, multivalued functions such as √''z'' or log(''z''), e.g. the subset of pairs with . Every Riemann surface is a Surface (topology), surface: a two-dimensional real manifold, but it contains more structure (specifically a Complex Manifold, complex structure). Conversely, a two-dimensional real manifold can be turned into a Riemann surface (usually in several inequivalent ways) if and only if it is orientable and Metrizabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyman John Harvard (clergyman), John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States. Its influence, wealth, and rankings have made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world. Harvard was founded and authorized by the Massachusetts General Court, the governing legislature of Colonial history of the United States, colonial-era Massachusetts Bay Colony. While never formally affiliated with any Religious denomination, denomination, Harvard trained Congregationalism in the United States, Congregational clergy until its curriculum and student body were gradually secularized in the 18th century. By the 19th century, Harvard emerged as the most prominent academic and cultural institution among the Boston B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Helsinki
The University of Helsinki (, ; UH) is a public university in Helsinki, Finland. The university was founded in Turku in 1640 as the Royal Academy of Åbo under the Swedish Empire, and moved to Helsinki in 1828 under the sponsorship of Alexander I of Russia, Tsar Alexander I. The University of Helsinki is the oldest and largest university in Finland with a range of disciplines available. In 2022, around 31,000 students were enrolled in the degree programs of the university spread across 11 faculties and 11 research institutes. As of 1 August 2005, the university complies with the harmonized structure of the Europe-wide Bologna Process and offers bachelor, master, licenciate, and Doctorate, doctoral degrees. Admission to degree programmes is usually determined by entrance examinations, in the case of bachelor's degrees, and by prior degree results, in the case of master and postgraduate degrees. The university is bilingual, with teaching by law provided both in Finnish and Swedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lars Ahlfors - MFO
Lars is a common male name in Scandinavian countries. Origin ''Lars'' means "from the city of Laurentum". Lars is derived from the Latin name Laurentius, which means "from Laurentum" or "crowned with laurel", and is therefore related to the name Laurence and Lauren. A homonymous Etruscan name was borne by several Etruscan kings, and later used as a last name by the Roman Lartia family. The etymology of the Etruscan name is unknown. Notable people *, bishop of Linköping (1236–1258) *, bishop of Linköping (1292–1307) *Lars (archbishop of Uppsala) (1255–1267) *Lars Kristian Abrahamsen (1855–1921), Norwegian politician * Lars Ahlfors (1907–1996), Finnish Fields Medal recipient * Lars Amble (1939–2015), Swedish actor and director *Lars Herminius Aquilinus, ancient Roman consul *Lars Bak (born 1980), Danish road bicycle racer *Lars Bak (computer programmer) (born 1965), Danish computer programmer *Lars Beckman (born 1967), Swedish politician *Lars Bender (born 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oslo
Oslo ( or ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of 1,064,235 in 2022, and the metropolitan area had an estimated population of in 2021. During the Viking Age, the area was part of Viken. Oslo was founded as a city at the end of the Viking Age in 1040 under the name Ánslo, and established as a ''kaupstad'' or trading place in 1048 by Harald Hardrada. The city was elevated to a bishopric in 1070 and a capital under Haakon V of Norway around the year 1300. Personal unions with Denmark from 1397 to 1523 and again from 1536 to 1814 reduced its influence. After being destroyed by a fire in 1624, during the reign of King Christian IV, a new city was built closer to Akershus Fortress and named Christiania in honour of the king. It became a municipality ('' formannskapsdistrikt'') on 1 January 1838. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 1,603,797 in the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The city is the urban core of the Philadelphia metropolitan area (sometimes called the Delaware Valley), the nation's Metropolitan statistical area, seventh-largest metropolitan area and ninth-largest combined statistical area with 6.245 million residents and 7.379 million residents, respectively. Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by William Penn, an English Americans, English Quakers, Quaker and advocate of Freedom of religion, religious freedom, and served as the capital of the Colonial history of the United States, colonial era Province of Pennsylvania. It then played a historic and vital role during the American Revolution and American Revolutionary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constance Reid
Constance Bowman Reid (January 3, 1918 – October 14, 2010) was the author of several biographies of mathematicians and popular books about mathematics. She received several awards for mathematical exposition. She was not a mathematician but came from a mathematical family—one of her sisters was Julia Robinson, and her brother-in-law was Raphael M. Robinson. Background and education Reid was born in St. Louis, Missouri, the daughter of Ralph Bowers Bowman and Helen (Hall) Bowman. One of her younger sisters was the mathematician Julia Robinson. The family moved to Arizona and then to San Diego when the girls were a few years old. In 1950 she married a law student, Neil D. Reid, with whom she had two children, Julia and Stewart. Reid received a Bachelor of Arts degree from San Diego State University in 1938 and a Master of Education degree from University of California, Berkeley in 1949. She worked as a teacher of English and journalism at San Diego High School from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald L
Gerald is a masculine given name derived from the Germanic languages prefix ''ger-'' ("spear") and suffix ''-wald'' ("rule"). Gerald is a Norman French variant of the Germanic name. An Old English equivalent name was Garweald, the likely original name of Gerald of Mayo, a British Roman Catholic monk who established a monastery in Mayo, Ireland in 670. Nearly two centuries later, Gerald of Aurillac, a French count, took a vow of celibacy and later became known as the Roman Catholic patron saint of bachelors. The name was in regular use during the Middle Ages but declined after 1300 in England. It remained a common name in Ireland, where it was a common name among the powerful FitzGerald dynasty. The name was revived in the Anglosphere in the 19th century by writers of historical novels along with other names that had been popular in the medieval era. British novelist Ann Hatton published a novel called ''Gerald Fitzgerald'' in 1831. Author Dorothea Grubb published her novel '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |