|
Fiammetta Wilson
Fiammetta Wilson (born Helen Frances Worthington; 19 July 186421 July 1920) was a British astronomer elected a fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society in 1916. Early life and education Fiammetta Wilson was born Helen Frances Worthington on 19 July 1864 to Helen Felicite (Till) Worthington (1839–1922) and Francis Samuel Worthington (1837–1912) of Lowestoft, Suffolk. She had four younger siblings, two brothers and two sisters. Her father was a physician and a surgeon with a strong interest in the natural sciences. After he retired he spent time doing microscopical studies, and encouraged Fiammetta to study her natural surroundings. She was educated by governesses, went to schools in Germany and Switzerland, and was trained as a musician in Italy. Marriages and identity On 29 October 1889, Helen Frances Worthington married Herbert William Webster (1864–1922) at St Gabriel's Church, Pimlico, London. Webster was a singer and music teacher in a family of clergymen. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiammetta Wilson In Knowledge Vol 12 1915 Image By Lafayette
Maria d'Aquino (died in 1382) was a Neapolitan noblewoman who is traditionally identified with Giovanni Boccaccio's beloved and muse Fiammetta (Italian for "little flame"). Maria d'Aquino was a “royal bastard”, an illegitimate daughter of Robert the Wise, King of Naples and Count of Provence. She was an accomplice in the 1345 murder of King Andrew, the husband of her niece and Robert's successor, Queen Joanna I. For this Maria was sentenced to death and beheaded in 1382 on the orders of Queen Joanna I's successor, King Charles III. Boccaccio wrote about Maria d'Aquino and their relationship in several of his literary works. She is traditionally identified as Fiammetta. According to him, Maria's mother was a Provençal noblewoman, Sibila Sabran, wife of Count Thomas IV of Aquino. She was born after Countess Sibila and King Robert committed adultery at his coronation festivities in 1310, but was given the family name of her mother's husband. Her putative father placed h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zodiacal Light
The zodiacal light (also called false dawn when seen before sunrise) is a faint glow of diffuse sunlight scattered by interplanetary dust. Brighter around the Sun, it appears in a particularly dark night sky to extend from the Sun's direction in a roughly triangular shape along the zodiac, and appears with less intensity and visibility along the whole ecliptic as the zodiacal band. Zodiacal light spans the entire sky and contributes to the natural light of a clear and moonless night sky. A related phenomenon is '' gegenschein'' (or ''counterglow''), sunlight backscattered from the interplanetary dust, appearing directly opposite to the Sun as a faint but slightly brighter oval glow. Zodiacal light is very faint, often outshined and rendered invisible by moonlight or light pollution. The interplanetary dust in the Solar System forms a thick, pancake-shaped cloud called the zodiacal cloud which straddles the ecliptic plane. The particle sizes range from 10 to 300 microm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women Astronomers
The following is a list of astronomers, astrophysicists and other notable women who have made contributions to the field of astronomy. __NOTOC__ A * Madge Adam (1912–2001), English solar astronomer * Maggie Aderin-Pocock (born 1968), English space scientist * Conny Aerts (born 1966), Belgian astrophysicist specializing in asteroseismology * Aglaonike (c. 1st or 2nd Century BCE), ancient Greek astronomer and thaumaturge * María Luisa Aguilar Hurtado (1938–2015), Peruvian astronomer * Eva Ahnert-Rohlfs (1912–1954), German variable star astronomer * Elizabeth Alexander (1908–1958), English geologist and physicist * Leah Allen (1884–1973), American astronomer and educator * Adelaide Ames (1900 - 1932), American astronomer * Anja Cetti Andersen (born 1965), Danish astronomer focused on cosmic dust * Necia H. Apfel (born 1930), American astronomer and educator * Alice Archenhold (1874–1943), German astronomer * Anne Archibald, Canadian astronomer and educator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horsewoman
Equestrianism (from Latin , , , 'horseman', 'horse'), commonly known as horse riding (Commonwealth English) or horseback riding (American English), includes the disciplines of riding, driving, and vaulting. This broad description includes the use of horses for practical working purposes, transportation, recreational activities, artistic or cultural exercises, and competitive sport. Overview of equestrian activities Horses are trained and ridden for practical working purposes, such as in police work or for controlling herd animals on a ranch. They are also used in competitive sports including dressage, endurance riding, eventing, reining, show jumping, tent pegging, vaulting, polo, horse racing, driving, and rodeo (see additional equestrian sports listed later in this article for more examples). Some popular forms of competition are grouped together at horse shows where horses perform in a wide variety of disciplines. Horses (and other equids such as mules) are used for non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadcast news organisation and generates about 120 hours of radio and television output each day, as well as online news coverage. The service maintains 50 foreign news bureaus with more than 250 correspondents around the world. Deborah Turness has been the CEO of news and current affairs since September 2022. In 2019, it was reported in an Ofcom report that the BBC spent £136m on news during the period April 2018 to March 2019. BBC News' domestic, global and online news divisions are housed within the largest live newsroom in Europe, in Broadcasting House in central London. Parliamentary coverage is produced and broadcast from studios in London. Through BBC English Regions, the BBC also has regional centres across England and national new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
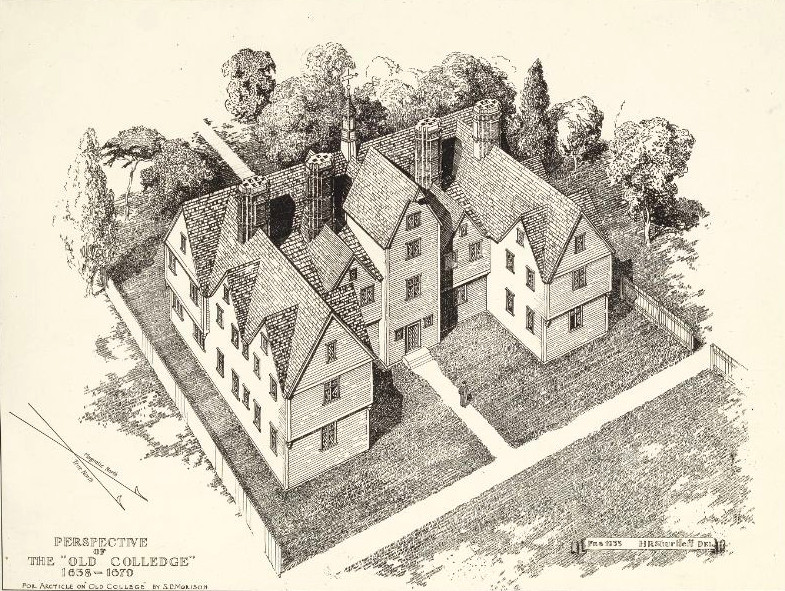
Harvard College
Harvard College is the undergraduate college of Harvard University, an Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636, Harvard College is the original school of Harvard University, the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and among the most prestigious in the world. Part of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Harvard College is Harvard University's traditional undergraduate program, offering AB and SB degrees. It is highly selective, with fewer than five percent of applicants being offered admission in recent years. Harvard College students participate in more than 450 extracurricular organizations and nearly all live on campus—first-year students in or near Harvard Yard, and upperclass students in community-oriented "houses". History The school came into existence in 1636 by vote of the Great and General Court of the Massachusetts Bay Colony—though without a single building, instructor, or student. In 1638, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Charles Pickering
Edward Charles Pickering (July 19, 1846 – February 3, 1919) was an American astronomer and physicist and the older brother of William Henry Pickering. Along with Carl Vogel, Pickering discovered the first spectroscopic binary stars. He wrote ''Elements of Physical Manipulations'' (2 vol., 1873–76). Personal life Pickering was born at 43 Bowdoin Street in Boston, Massachusetts, on July 19, 1846,Obituary, ''Boston Globe'', February 4, 1919 to a distinguished, cultivated family consisting of his brother, William Henry Pickering, father, Edward Pickering, and his mother, Charlotte Hammond. Edward's brother, William, was a graduate of MIT and professor of physics and astronomy. Edward was interested in the stars as a boy and constructed his own telescope by the age of 12. Pickering enjoyed his work at the observatory, but he was also enjoyed mountain climbing and bicycling in earlier days and later he was an interested spectator of football games. He was co-founder and first pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Société Astronomique De France
The Société astronomique de France (SAF; ), the French astronomical society, is a non-profit association in the public interest organized under French law ( Association loi de 1901). Founded by astronomer Camille Flammarion in 1887, its purpose is to promote the development and practice of astronomy. History SAF was established by Camille Flammarion and a group of 11 persons on 28 January 1887 in Flammarion's apartment at 16 rue Cassini, 75014 Paris, close to the Paris Observatory. Open to all, SAF includes both professional and amateur astronomers as members, from France and abroad.Ferlet R. (2003) "The Société Astronomique de France in the Astronomical Landscape: Evolution and Prospects." In: ''Organizations and Strategies in Astronomy''. Astrophysics and Space Science Library, vol 296. Springer, Dordrecht. Its objective was defined at the time of its establishment as: "A Society is founded with the aim to bring together people involved practically or theoretically in A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20D/Westphal
20D/Westphal was a periodic comet with an orbital period of 61 years. It fits the classical definition of a Halley-type comet with (20 years < period < 200 years). It was originally discovered by the German J. G. Westphal (, ) on July 24, 1852. It was independently discovered by the American astronomer [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp. 155–157. and developed in detail in 1893.Dooley 2004, p. A.187. They were patented in Germany in 1895 and in the United States in 1899. After the outstanding success of the Zeppelin design, the word ''zeppelin'' came to be commonly used to refer to all rigid airships. Zeppelins were first flown commercially in 1910 by Deutsche Luftschiffahrts-AG (DELAG), the world's first airline in revenue service. By mid-1914, DELAG had carried over 10,000 fare-paying passengers on over 1,500 flights. During World War I, the German military made extensive use of Zeppelins as bombers and as scouts, resulting in over 500 deaths in bombing raids in Britain. The defeat of Germany in 1918 temporarily slowed the airship business. Although DELAG establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
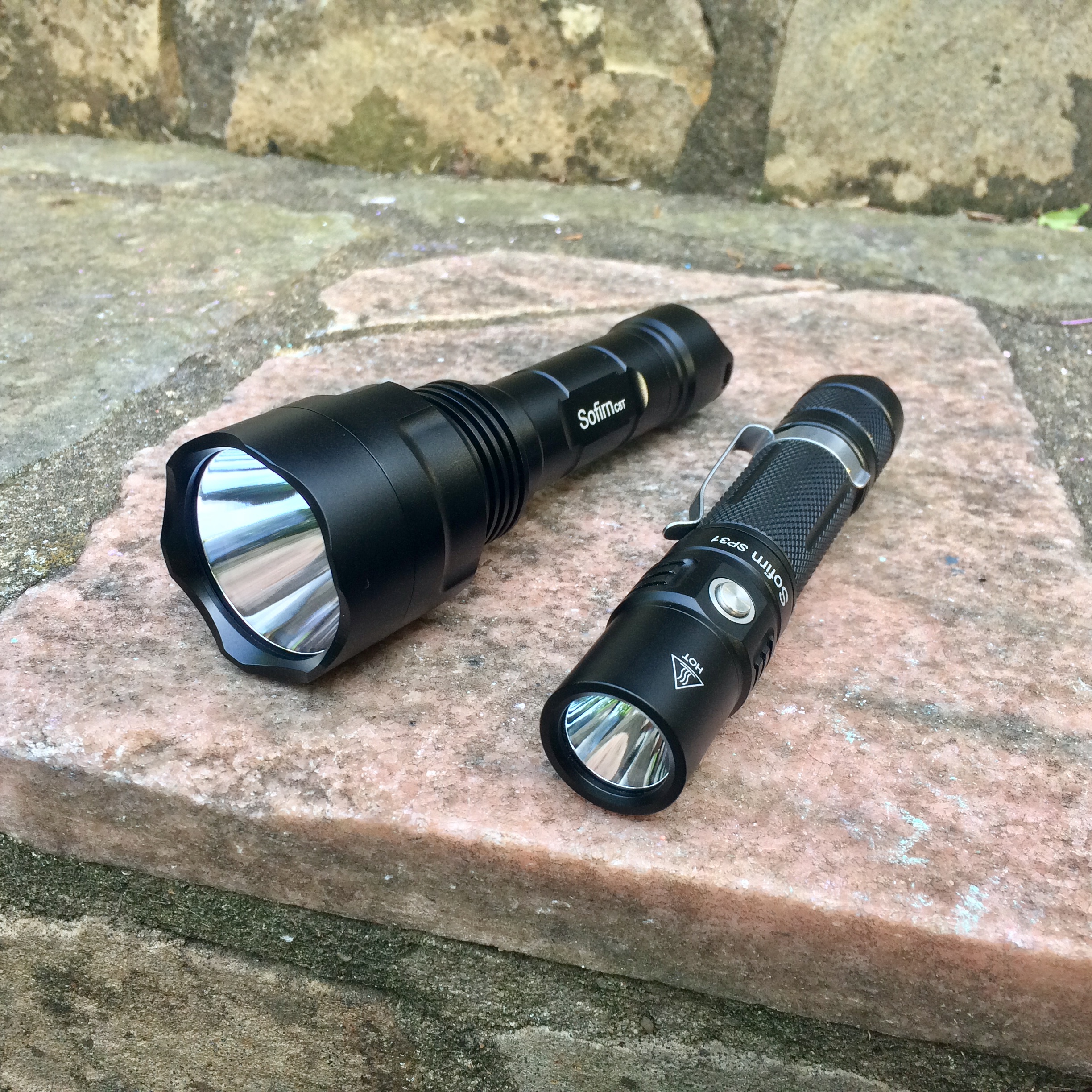
Flashlight
A flashlight ( US, Canada) or torch ( UK, Australia) is a portable hand-held electric lamp. Formerly, the light source typically was a miniature incandescent light bulb, but these have been displaced by light-emitting diodes (LEDs) since the mid-2000s. A typical flashlight consists of the light source mounted in a reflector, a transparent cover (sometimes combined with a lens) to protect the light source and reflector, a battery, and a switch, all enclosed in a case. The invention of the dry cell and miniature incandescent electric lamps made the first battery-powered flashlights possible around 1899. Today, flashlights use mostly light-emitting diodes and run on disposable or rechargeable batteries. Some are powered by the user turning a crank, shaking the lamp, or squeezing it. Some have solar panels to recharge the battery. Flashlights are used as a light source outdoors, in places without permanently installed lighting, during power outages, or when a portable ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific Ocean, Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in Genocides in history (World War I through World War II), genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the Spanish flu, 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising French Third Republic, France, Russia, and British Empire, Britain) and the Triple A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |