|
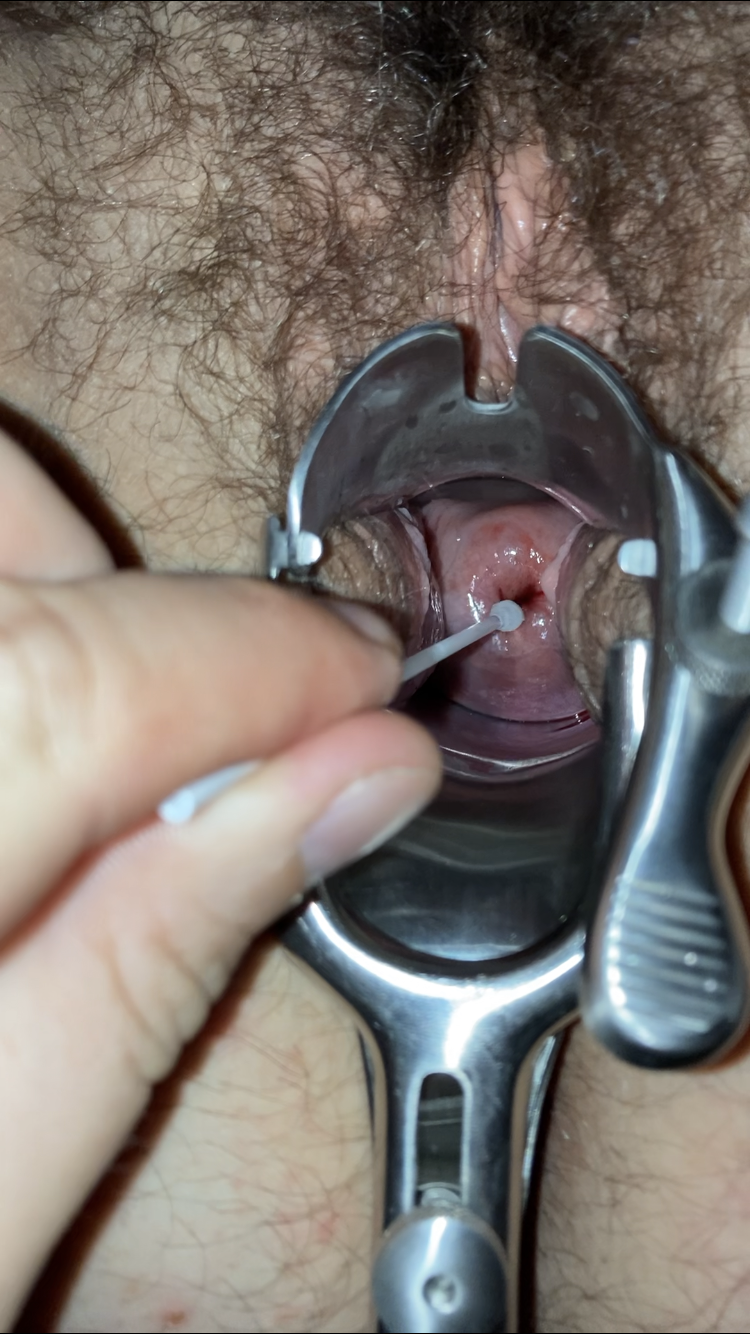
Ferning
The fern test is a medical laboratory test used in obstetrics and gynecology. The name refers to the detection of a characteristic "fern like" pattern of vaginal secretions when a specimen is allowed to dry on a glass slide and is viewed under a low-power microscope. The fern test is most commonly used to provide evidence of the presence of amniotic fluid and is used in obstetrics to detect preterm premature rupture of membranes and/or the onset of labor. It also may provide indirect evidence of ovulation and fertility, although it does not predict the time of ovulation.Patrick Duff, MD (2016). "Preterm premature (prelabor) rupture of membranes". In Vanessa A Barss, MD, FACOG (Ed.), ''uptodate'' Retrieved from http://www.uptodate.com/ Ferning was first described in the field of gynecology in 1945 by Georgios Papanikolaou, inventor of the pap smear, as a test for ovulation during a normal menstrual cycle. When high levels of estrogen are present, such as just before ovulation (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotic Fluid
The amniotic fluid is the protective liquid contained by the amniotic sac of a gravid amniote. This fluid serves as a cushion for the growing fetus, but also serves to facilitate the exchange of nutrients, water, and biochemical products between mother and fetus. Colloquially, the amniotic fluid is commonly called water or waters (Latin liquor amnii). Development Amniotic fluid is present from the formation of the gestational sac. Amniotic fluid is in the amniotic sac. It is generated from maternal plasma, and passes through the fetal membranes by osmotic and hydrostatic forces. When fetal kidneys begin to function around week 16, fetal urine also contributes to the fluid. In earlier times, it was believed that the amniotic fluid was composed entirely of excreted fetal urine. The fluid is absorbed through the fetal tissue and skin. After 22 to 25 week of pregnancy, keratinization of an embryo's skin occurs. When this process completes around the 25th week, the fluid is pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Fern Test
Positive is a property of Positivity (other), positivity and may refer to: Mathematics and science * Positive formula, a logical formula not containing negation * Positive number, a number that is greater than 0 * Plus sign, the sign "+" used to indicate a positive number * Positive operator, a type of linear operator in mathematics * Positive result, a result that has been found significant in Statistical hypothesis test, statistical hypothesis testing * Positive test, a diagnostic test result that indicates some parameter being evaluated was present * Positive charge, one of the two types of electrical charge * Positive (electrical polarity), in electrical circuits * Positive lens, in optics * Positive (photography), a positive image, in which the color and luminance correlates directly with that in the depicted scene * Positive sense, said of an RNA sequence that codes for a protein Philosophy and humanities * Affirmative (policy debate), the team which affirms the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field. Main areas Prenatal care Prenatal care is important in screening for various complications of pregnancy. This includes routine office visits with physical exams and routine lab tests along with telehealth care for women with low-risk pregnancies: Image:Ultrasound_image_of_a_fetus.jpg, 3D ultrasound of fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) Image:Sucking his thumb and waving.jpg, Fetus at 17 weeks Image:3dultrasound 20 weeks.jpg, Fetus at 20 weeks First trimester Routine tests in the first trimester of pregnancy generally include: * Complete blood count * Blood type ** Rh-negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGAM at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease. * Indirect Coombs test (AGT) to assess risk of hem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecology
Gynaecology or gynecology (see American and British English spelling differences) is the area of medicine concerned with conditions affecting the Female reproductive system, female reproductive system. It is often paired with the field of obstetrics, which focuses on pregnancy and childbirth, thereby forming the combined area of obstetrics and gynaecology (OB-GYN). Gynaecology encompasses both Primary care, primary and Preventive healthcare, preventative care of issues related to female reproduction and sexual health, such as the uterus, vagina, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and breasts; subspecialties include family planning; minimally invasive surgery; pediatric and adolescent gynecology; and pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery. While gynaecology has traditionally centered on Cisgender, cisgender women, it increasingly encompasses anyone with female organs, including transgender, intersex, and Non-binary gender, nonbinary individuals; however, many non-cis women face acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients, and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaf, leaves called megaphylls that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled Fiddlehead fern, fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate (Polypodiidae (plant), Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, Psilotaceae, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid ferns. The fern crown group, consisting of the leptosporangiates and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Secretion
Vaginal discharge is a mixture of liquid, cells, and bacteria that lubricate and protect the vagina. This mixture is constantly produced by the cells of the vagina and cervix, and it exits the body through the vaginal opening. The composition, quality, and amount of discharge varies between individuals, and can vary throughout the menstrual cycle and throughout the stages of sexual and reproductive development. Normal vaginal discharge may have a thin, watery consistency or a thick, sticky consistency, and it may be clear or white in color. Normal vaginal discharge may be large in volume but typically does not have a strong odor, nor is it typically associated with itching or pain. While most discharge is considered physiologic (represents normal functioning of the body), some changes in discharge can reflect infection or other pathological processes. Infections that may cause changes in vaginal discharge include vaginal yeast infections, bacterial vaginosis, and sexually transm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premature Rupture Of Membranes
Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), previously known as premature rupture of membranes, is breakage of the amniotic sac before the onset of labour. Women usually experience a painless gush or a steady leakage of fluid from the vagina. Complications in the baby may include premature birth, cord compression, and infection. Complications in the mother may include placental abruption and postpartum endometritis. Risk factors include infection of the amniotic fluid, prior PROM, bleeding in the later parts of pregnancy, smoking, and a mother who is underweight. Diagnosis is suspected based on symptoms and speculum exam and may be supported by testing the vaginal fluid or by ultrasound. If it occurs before 37 weeks it is known as PPROM (preterm prelabor rupture of membranes) otherwise it is known as term PROM. Treatment is based on how far along a woman is in pregnancy and whether complications are present. In those at or near term without any complications, induction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovulation
Ovulation is an important part of the menstrual cycle in female vertebrates where the egg cells are released from the ovaries as part of the ovarian cycle. In female humans ovulation typically occurs near the midpoint in the menstrual cycle and after the follicular phase. Ovulation is stimulated by an increase in luteinizing hormone (LH). The ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm. If it is not, it will break down in less than a day. Meanwhile, the uterine lining ( endometrium) continues to thicken to be able to receive a fertilized egg. If no conception occurs, the uterine lining will eventually break down and be shed from the body via the vagina during menstruation. Some people choose to track ovulation in order to improve or aid becoming pregnant by timing intercourse with their ovulation. The signs of ovulation may include cervical muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgios Papanikolaou
Georgios Nikolaou Papanikolaou (or George Papanicolaou ; ; 13 May 1883 – 19 February 1962) was a Greek physician, zoologist and microscopist who was a pioneer in cytopathology and early cancer detection, and inventor of the pap smear for detection of cervical cancer. After studying medicine in Greece and Germany, in 1913 he emigrated to the United States and was on the faculty at Cornell Medical College. He first reported that uterine cancer cells could be detected in vaginal smears in 1928, but his work was not widely recognized until the 1940s. An extensive trial of his techniques was carried out in the early 1950s. In 1961 he was invited to the University of Miami to lead and develop there the Papanicolaou Cancer Research Institute. Early life and education Papanikolaou was born in Kymi, Greece, on 13 May 1883. He attended the University of Athens, where he studied literature, philosophy, languages and music. Urged by his physician father, he pursued a medical degree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pap Smear
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb) or, more rarely, anus (in both men and women). Abnormal findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was independently invented in the 1920s by the Greek physician Georgios Papanikolaou and named after him. A simplified version of the test was introduced by the Canadian obstetrician Anna Marion Hilliard in 1957. A Pap smear is performed by opening the vagina with a speculum and collecting cells at the outer opening of the cervix at the transformation zone (where the outer squamous cervical cells meet the inner glandular endocervical cells), using an Ayre spatula or a cyto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs and the cyclic release of estrogen and progesterone. The uterine cycle governs the preparation and maintenance of the lining of the uterus (womb) to receive an embryo. These cycles are concurrent and coordinated, normally last between 21 and 35 days, with a median length of 28 days. Menarche (the onset of the first period) usually occurs around the age of 12 years; menstrual cycles continue for about 30–45 years. Naturally occurring hormones drive the cycles; the cyclical rise and fall of the follicle stimulating hormone prompts the production and growth of oocytes (immature egg cells). The hormone estrogen stimulates the uterus lining ( endometrium) to thicken to accommodate an embryo should fertilization occur. The blood suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal activity: estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3). Estradiol, an estrane, is the most potent and prevalent. Another estrogen called estetrol (E4) is produced only during pregnancy. Estrogens are synthesized in all vertebrates and some insects. Quantitatively, estrogens circulate at lower levels than androgens in both men and women. While estrogen levels are significantly lower in males than in females, estrogens nevertheless have important physiological roles in males. Like all steroid hormones, estrogens readily diffuse across the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, they bind to and activate estrogen receptors (ERs) which in turn modulate the expression of many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |