|
Ferdinand Ellerman
Ferdinand Ellerman (May 13, 1869 to March 20, 1940) was an American astronomer and photographer. He spent a good part of his career as an associate of the solar astronomer George E. Hale, and is known for his study of a phenomenon in the solar chromosphere later dubbed Ellerman bombs. Biography He was born in Centralia, Illinois on May 13, 1869, the son of Mathias Ellerman and Rosa A. née Fleischbein. Ferdinand attended High School in Belleville, Illinois, then moved to Chicago and was employed at the James S. Kirk Company, a soap manufacturing business. During his work, he acquired skill in the use of machine tools and photography. Ellerman was hired as an assistant by astronomer George E. Hale in 1892 to observe at his private Kenwood Observatory in Chicago, beginning a working relationship that would last until Hale's death in 1938. The two likely first met during the initial meeting for the Chicago Section of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, in November 1890, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centralia, Illinois
Centralia is a city in Clinton, Jefferson, Marion, and Washington counties in the U.S. state of Illinois with the largest portion in Marion County. The city is the largest in three of the counties; Clinton, Marion, and Washington, but is not a county seat of any of them. The population was 12,182 as of the 2020 census, down from 13,032 in 2010. History Centralia is named for the Illinois Central Railroad, built in 1853. The city was founded at the location where the two original branches of the railroad converged. Centralia was first chartered as a city in 1859. Now Canadian National owns the line. In the southern city limits is the intersection of the Third Principal Meridian and its baseline. This initial point was established in 1815, and it governs land surveys for about 60% of the state of Illinois, including Chicago. The original monument is at the junction of Highway 51 and the Marion-Jefferson County Line Road; today there is a small easement situated in the northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Astronomical Society
The American Astronomical Society (AAS, sometimes spoken as "double-A-S") is an American society of professional astronomers and other interested individuals, headquartered in Washington, DC. The primary objective of the AAS is to promote the advancement of astronomy and closely related branches of science, while the secondary purpose includes enhancing astronomy education and providing a political voice for its members through lobbying and grassroots activities. Its current mission is to enhance and share humanity's scientific understanding of the universe as a diverse and inclusive astronomical community. History The society was founded in 1899 through the efforts of George Ellery Hale. The constitution of the group was written by Hale, George Comstock, Edward Morley, Simon Newcomb and Edward Charles Pickering. These men, plus four others, were the first Executive Council of the society; Newcomb was the first president. The initial membership was 114. The AAS name of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halley's Comet
Halley's Comet or Comet Halley, officially designated 1P/Halley, is a List of periodic comets, short-period comet visible from Earth every 75–79 years. Halley is the only known short-period comet that is regularly visible to the naked eye from Earth, and thus the only naked-eye comet that can appear twice in a human lifetime. Halley last appeared in the inner parts of the Solar System in 1986 and will next appear in mid-2061. Halley's periodic returns to the inner Solar System have been observed and recorded by astronomers around the world since at least 240 BC. But it was not until 1705 that the English astronomer Edmond Halley understood that these appearances were reappearances of the same comet. As a result of this discovery, the comet is named after Halley. During its 1986 visit to the inner Solar System, Halley's Comet became the first comet to be observed in detail by spacecraft, providing the first observational data on the structure of a comet nucleus and the mecha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
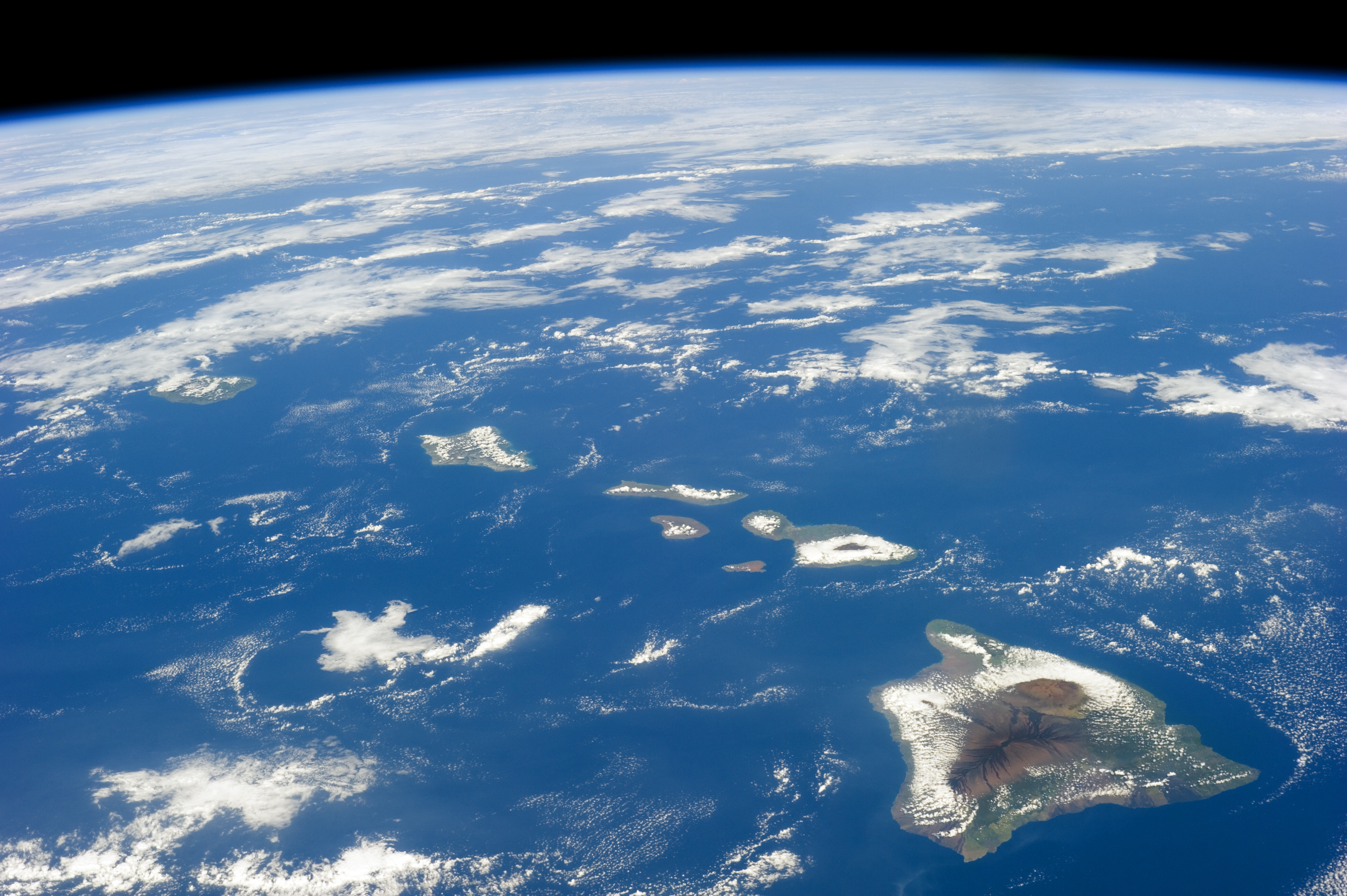
Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll. Formerly the group was known to Europeans and Americans as the Sandwich Islands, a name that James Cook chose in honor of the 4th Earl of Sandwich, the then First Lord of the Admiralty. Cook came across the islands by chance when crossing the Pacific Ocean on his Third Voyage in 1778, on board HMS ''Resolution''; he was later killed on the islands on a return visit. The contemporary name of the islands, dating from the 1840s, is derived from the name of the largest island, Hawaii Island. Hawaii sits on the Pacific Plate and is the only U.S. state that is not geographically connected to North America. It is part of the Polynesia subregion of Oceania. The state of Hawaii occupies the archipelago almost in its entirety (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Polarity
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, etc. and attracts or repels other magnets. A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called Ferromagnetism, ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include the elements iron, nickel and cobalt and their alloys, some alloys of rare-earth element, rare-earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
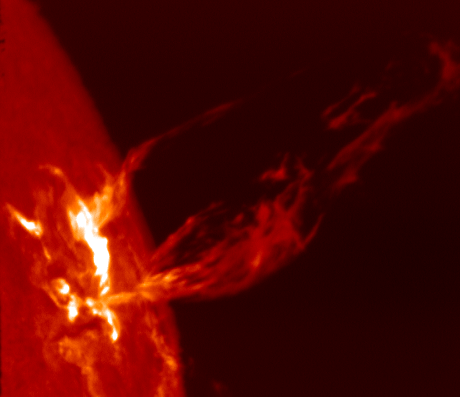
Sun Spot
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots appear within active regions, usually in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle. Individual sunspots or groups of sunspots may last anywhere from a few days to a few months, but eventually decay. Sunspots expand and contract as they move across the surface of the Sun, with diameters ranging from to . Larger sunspots can be visible from Earth without the aid of a telescope. They may travel at relative speeds, or proper motions, of a few hundred meters per second when they first emerge. Indicating intense magnetic activity, sunspots accompany other active region phenomena such as coronal loops, prominences, and reconnection events. Most solar flares and coronal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Magnetic Field
A stellar magnetic field is a magnetic field generated by the motion of conductive plasma inside a star. This motion is created through convection, which is a form of energy transport involving the physical movement of material. A localized magnetic field exerts a force on the plasma, effectively increasing the pressure without a comparable gain in density. As a result, the magnetized region rises relative to the remainder of the plasma, until it reaches the star's photosphere. This creates starspots on the surface, and the related phenomenon of coronal loops. Measurement The magnetic field of a star can be measured by means of the Zeeman effect. Normally the atoms in a star's atmosphere will absorb certain frequencies of energy in the electromagnetic spectrum, producing characteristic dark absorption lines in the spectrum. When the atoms are within a magnetic field, however, these lines become split into multiple, closely spaced lines. The energy also becomes polarized with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Wilson Observatory
The Mount Wilson Observatory (MWO) is an astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson, a peak in the San Gabriel Mountains near Pasadena, northeast of Los Angeles. The observatory contains two historically important telescopes: the Hooker telescope, which was the largest aperture telescope in the world from its completion in 1917 to 1949, and the 60-inch telescope which was the largest operational telescope in the world when it was completed in 1908. It also contains the Snow solar telescope completed in 1905, the 60 foot (18 m) solar tower completed in 1908, the 150 foot (46 m) solar tower completed in 1912, and the CHARA array, built by Georgia State University, which became fully operational in 2004 and was the largest optical interferometer in the world at its completion. Due to the inversion layer that traps warm air and smog over Los Angeles, Mount Wilson has steadier air than any other location in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
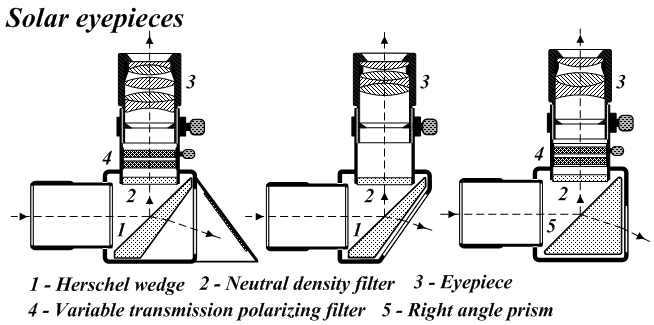
Solar Telescope
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Horizontal Telescope
The Snow Solar Telescope is a solar telescope at the Mount Wilson Observatory in California. It was originally named the Snow Horizontal Telescope as it uses a coelostat to deflect light from the Sun into a fixed horizontal shed where it can be studied. The telescope was funded by a donation from Helen E. Snow of Chicago in 1903. It was assembled at Yerkes Observatory then transferred to Mt. Wilson in 1905. This telescope is notable for the discovery that sunspots have a lower temperature than the photosphere, and for finding evidence they are associated with a magnetic field. History During his time at Yerkes Observatory, American solar astronomer George Ellery Hale developed a horizontal telescope for observation of the Sun. This instrument used a diameter coelostat to track the Sun and reflect the illumination onto a second mirror, which directed the light horizontally onto a concave objective mirror. The optical train produced an image of the Sun that could be examined wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Institution For Science
The Carnegie Institution of Washington (the organization's legal name), known also for public purposes as the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS), is an organization in the United States established to fund and perform scientific research. The institution is headquartered in Washington, D.C. , the Institution's endowment was valued at $926.9 million. In 2018 the expenses for scientific programs and administration were $96.6 million.Eric Isaacs is president of the institution. Name More than 20 independent organizations were established through the philanthropy of Andrew Carnegie and now feature his surname. They perform work involving topics as diverse as art, education, international affairs, world peace, and scientific research. In 2007, the Carnegie Institution of Washington adopted the public name "Carnegie Institution for Science" to distinguish itself from other organizations established by and named for Andrew Carnegie. The Institution remains officially and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Wilson (California)
Mount Wilson is a peak in the San Gabriel Mountains, located within the San Gabriel Mountains National Monument and Angeles National Forest in Los Angeles County, California. With only minor topographical prominence the peak is not naturally noticeable from a distance, although it is easily identifiable due to the large number of antennas near its summit. It is a subsidiary peak of nearby San Gabriel Peak. It is the location of the Mount Wilson Observatory, which is an important astronomical facility in Southern California with historic and telescopes, and and solar towers. The newer CHARA Array, run by Georgia State University, is also sited there and does important interferometric stellar research. The summit is at . While not the tallest peak in its vicinity, it is high enough in elevation that snow can sometimes interrupt astronomical activities on the mountain. All of the mountains south of the summit are far shorter leading to unobstructed views across the Los ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_2007-04-30_T001456.gif)