|
Ferchar Mac An TSacairt
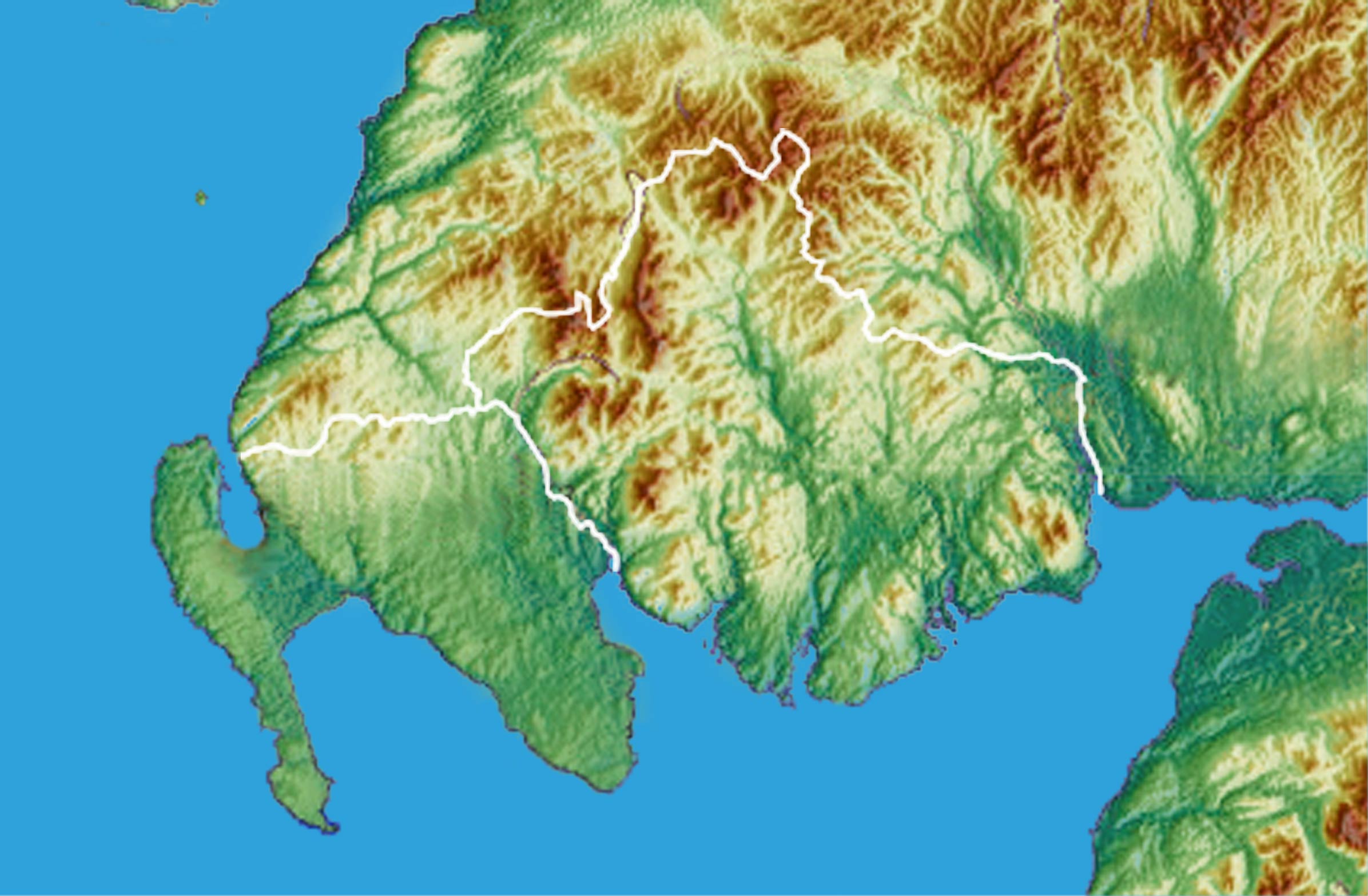
Fearchar of Ross or Ferchar mac in tSagairt (''Fearchar mac an t-sagairt'', often anglicization, anglicized as ''Farquhar MacTaggart''), was the first of the Scottish Ó Beólláin (O’Beolan, Beolan) family who received by Royal Grant the lands and Title of Mormaer or Earl of Mormaer of Ross, Ross (1223–1251) we know of from the thirteenth century, whose career brought Ross, Scotland, Ross into the fold of the Scottish kings for the first time, and who is remembered as the founder of the Earl of Ross, Earldom of Ross. Origins The traditional story is that Fearchar was part of the ancient family Ó Beólláin (O'Beolain, Boland, Bolan) of the Branches of the Cenél nEógain, Gaelic Cenél Eoghain that were co-arbs (hereditary abbots) of St. Maelrubha at Applecross in Ross-shire. This idea goes back to the work of the great William F. Skene, and indeed, even before him, with William Reeves (bishop), William Reeves, whom Skene cited. The historian Alexander Grant has recently ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arms Of The Earl Of Ross
Arms or ARMS may refer to: *Arm or arms, the upper limbs of the body Arm, Arms, or ARMS may also refer to: People * Ida A. T. Arms (1856–1931), American missionary-educator, temperance leader Coat of arms or weapons *Armaments or weapons **Firearm *Coat of arms **In this sense, "arms" is a common element in pub names Enterprises *Amherst Regional Middle School *Arms Corporation, originally named Dandelion, a defunct Japanese animation studio who operated from 1996 to 2020 * TRIN (finance) or Arms Index, a short-term stock trading index *Australian Relief & Mercy Services, a part of Youth With A Mission Arts and entertainment *ARMS (band), an American indie rock band formed in 2004 * ''Arms'' (album), a 2016 album by Bell X1 * "Arms" (song), a 2011 song by Christina Perri from the album ''lovestrong'' * ''Arms'' (video game), a 2017 fighting video game for the Nintendo Switch *ARMS Charity Concerts, a series of charitable rock concerts in support of Action into Research for M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander II Of Scotland
Alexander II ( Medieval Gaelic: '; Modern Gaelic: '; nicknamed "the Peaceful" by modern historians; 24 August 1198 – 6 July 1249) was King of Alba (Scotland) from 1214 until his death. He concluded the Treaty of York (1237) which defined the boundary between England and Scotland, largely unchanged today. Early life Alexander was born at Haddington, East Lothian, the only son of the Scottish king William the Lion and Ermengarde de Beaumont. He was forced to spend time in England under the terms of the Treaty of Falaise, and (John of England knighted him at Clerkenwell Priory in 1213) before he returned home. He succeeded to the kingdom on the death of his father on 4 December 1214, being crowned at Scone on 6 December the same year. At the time of his accession, his sisters Isabella and Margaret had been sent to England as hostages to King John. He appealed to John through the Magna Carta, which promised to deal with the rights of Alexander and his family. King of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galwegian Gaelic
Galwegian Gaelic (also known as Gallovidian Gaelic, Gallowegian Gaelic, or Galloway Gaelic) is an extinct dialect of Scottish Gaelic formerly spoken in southwest Scotland. It was spoken by the people of Galloway and Carrick until the early modern period. Little (except numerous placenames) and a song collected in North Uist have survived, so that its exact relationship with other Scottish Gaelic dialects is uncertain. History and extent Gaelicisation in Galloway and Carrick occurred at the expense of Northumbrian Old English and Cumbric, a Brittonic Celtic dialect related to Welsh. Use of Old Irish in Scotland can be traced in the Rhins of Galloway from at least the fifth century. How it developed and spread is largely unknown. The Gaelicisation of the land was complete probably by the eleventh century, although some have suggested a date as early as the beginning of the ninth century. The main problem is that this folk-movement is unrecorded in historical sources, so it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lords Of Galloway
The lords of Galloway consisted of a dynasty of heirs who were lords (or kings) and ladies who ruled over Galloway in southwest Scotland, mainly during the High Middle Ages. Many regions of Scotland, including Galloway and Mormaer of Moray, Moray, periodically had kings or subkings, similar to those in Ireland during the Middle Ages. The Scottish monarch was seen as being similar to a high king (''Ard-Righ'' in Goidelic, Gaelic). The lords of Galloway would have either paid tribute to the Scottish monarch, or at other times ignored him. The Lords of Galloway are fairly well recorded in the 12th and 13th centuries, but the records are incomplete or conflicting at other times. Later on, the kings were known as "lords" at the Scottish court, and "kings" at home, finally becoming "lords" in both arenas. The boundaries of the Kingdom of Galloway were ill-defined, and varied over time. During many periods Galloway was much larger than it is today, and took in parts of southern Ayrshir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gille Ruadh
Gille Ruadh was the Galwegian leader who led the revolt against King Alexander II of Scotland. His birth, death date and origins are all unknown. Upon the death of Alan, Lord of Galloway, in 1234, Galloway was left without a legitimate feudal heir. Alexander II had decided to partition the lordship between the Anglo-Norman husbands of Alan's three living daughters, Roger de Quincy (married to Ela), John de Balliol (married to Derborgaill) and William de Forz (married to Cairistiona). However, Alan had left an illegitimate son, Thomas. In Gaelic succession law, Thomas was a perfectly acceptable heir. Thus the native Galwegians and the Gaelic clergy of the province rose in revolt against the Scottish king. Leader of Galloway revolt The revolt of the Galwegians started in 1235, under Gille Ruadh's leadership. Matthew Paris says that Manx and Irish forces got involved too. Thomas received help from his father's father-in-law, Hugh de Lacy the Earl of Ulster, Hugh had his ow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galloway
Galloway ( ; ; ) is a region in southwestern Scotland comprising the counties of Scotland, historic counties of Wigtownshire and Kirkcudbrightshire. It is administered as part of the council areas of Scotland, council area of Dumfries and Galloway. Galloway is bounded by sea to the west and south, the Galloway Hills to the north, and the River Nith to the east; the border between Kirkcudbrightshire and Wigtownshire is marked by the River Cree. The definition has, however, fluctuated greatly in size over history. A native or inhabitant of Galloway is called a Gallovidian. The region takes its name from the ''Gall-Gàidheil'', or "stranger Gaels", Norse–Gaels, a people of mixed Gaelic and Norse descent who seem to have settled here in the 10th century. Galloway remained a Gàidhealtachd area for much longer than other regions of the Scottish Lowlands and a Galwegian Gaelic, distinct local dialect of the Scottish Gaelic language survived into at least the 18th century. A hardy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mormaer Of Carrick
Earl of Carrick (or Mormaer of Carrick) is the title applied to the ruler of Carrick (now South Ayrshire), subsequently part of the Peerage of Scotland. The position came to be strongly associated with the Scottish crown when Robert the Bruce, who had inherited it from his maternal kin, became King of Scots in the early 14th century. Since the 15th century, the title of Earl of Carrick has automatically been held by the heir apparent to the throne, thus the current holder of the title is Prince William, Duke of Rothesay. Early rulers The earldom emerged in 1186, out of the old Lordship of Galloway, which had previously encompassed all of what is now known as Galloway as well as the southern part of Ayrshire. Though the Lords of Galloway recognised the King of Scots as their overlord, their lordship was effectively a separate kingdom, and had its own laws. The first Lord recorded is Fergus, who died in 1161 leaving two sons: Uchtred and Gille Brigte (Gilbert). As was the cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mormaer Of Lennox
The Earl or Mormaer of Lennox was the ruler of the region of the Lennox in western Scotland. It was first created in the 12th century for David of Scotland, Earl of Huntingdon and later held by the Stewart dynasty. Ancient earls The first earl recorded is Ailin I, sometimes called 'Alwin'. He is traditionally said to have been created Earl of Lennox by King Malcolm IV in 1154, but this is likely too early a date. [Note: Other sources say Arkil (Arkyll) was the first mormaer. He fled Northumberland for Scotland about 1070 and was made Mormaer of Levenax by Malcolm. That title was in the 12th century changed to earl of Lennox.] The earldom may in fact have been created in the late twelfth century by William I of Scotland, King William the Lion for his brother David, Earl of Huntingdon, David, and after David gained the higher title Earl of Huntingdon, he resigned the Earldom of Lennox and it passed to Ailin. Earl Ailin's parentage and background is unknown. His line continue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter De Moray
Sir Walter de Moray (died c.1278), Lord of Petty, Bracholy, Boharm, Arteldol and Bothwell, Justiciar of Lothian was a 13th-century Scottish noble. Life Moray was a son of William de Moravia of Petty and a daughter of David de Olifard. He had succeeded his father by 1226 and accompanied King Alexander II of Scotland into England to meet with King Henry III of England in 1236. Walter inherited the lands of Bothwell and Drumsargard in Lanarkshire and Smailholm in Berwickshire in 1242. He served as Justiciar of Lothian in 1255. His eldest son succeeded in 1278, and was known as "Dominius de Bothwell" (Lord of Bothwell). He also held lands in Agenway, Botruphin, Kainermonth, Croy, Ardtrillen, Lunyn and Duldavy. Marriage and issue Walter married a daughter of Máel Coluim II, Earl of Fife and are known to have had the following issue: * William de Moray of Bothwell (died c. 1300), without issue. *Andrew de Moray (died 1298), married firstly a daughter of John I Comyn, Lord of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the recipient admits a limited (or inferior) status within the relationship, and it is within that sense that charters were historically granted, and it is that sense which is retained in modern usage of the term. In early medieval Britain, charters transferred land from donors to recipients. The word entered the English language from the Old French ', via -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ', via Latin ', and ultimately from Ancient Greek">Greek (', meaning "layer of papyrus"). It has come to be synonymous with a document that sets out a grant of rights or privileges. Other usages The term is used for a special case (or as an exception) of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uilleam I, Earl Of Ross
William I, Earl of Ross (Gaelic: ''Uilleam''; died 1274) was ruler of the province of Ross in northern Scotland. Biography William appears as early as 1232, witnessing a charter as the son of Ferquhard, Earl of Ross. He succeeded his father as Earl around 1251. He played a pioneering role in the Scottish reconquest of the Hebrides, which had been under Norwegian control. Indeed, in many ways, he may be regarded as the instigator of Scottish aggression. ''Hákonar saga Hákonarsonar'' tells us that in Norway: "''In the previous summer'' .e. that of 1262', letters came east from the Hebrides ... and they brought forward much about the dispeace that the Earl of Ross ... and other Scots, had made in the Hebrides, when they went out to Skye, and burned towns and churches, and slew very many men and women ... They said that the Scottish king intended to lay under himself all the Hebrides''." 1 Uilleam's attacks on Norwegian possessions earned him the ire of King Haakon, who planne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |