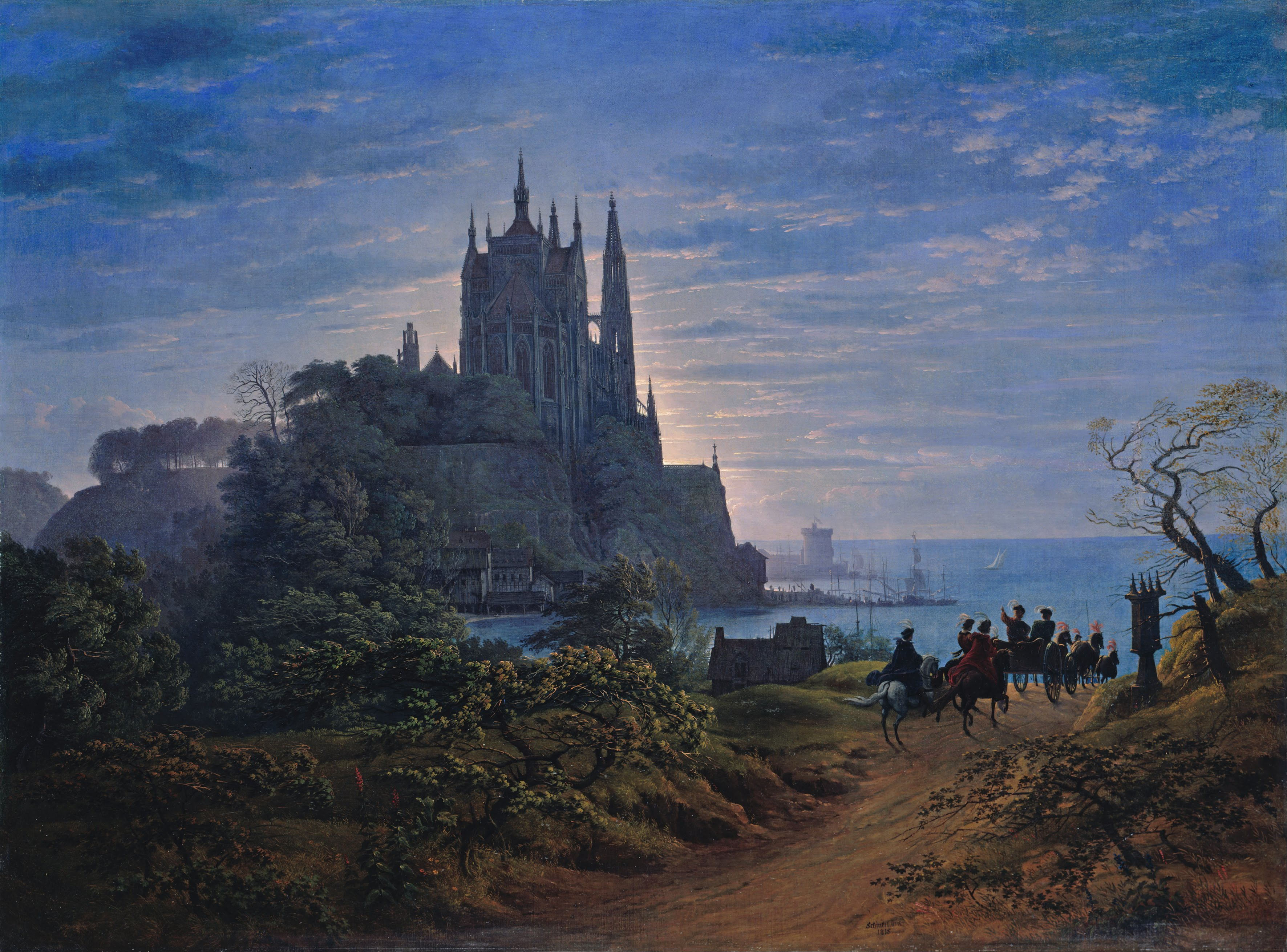|
Fences In Saint Petersburg
The fences in Saint Petersburg, Russia are highly varied, with many notable examples remaining in use today from different periods in Russian architectural history. The works on the fences' creation began in the second half of 18th century (1770–1784) following the project of Yury Felten. The fencing consists of 36 granite columns, 32 links of shod fencings and the big gate in the centre and small ones on both sides. The gate are opposite the Summer garden avenues. Length of fencing is 232 metres. In 1866 there was an assassination against the Emperor Alexander II. In the memory of his rescue the chapel was constructed in place of the central gate. In 1930 a chapel was demolished, but the authentic image was lost. Church of the Savior on Blood The fencing at the Church of the Savior on Blood was created following the project of Alfred Alexandrovich Parland and executed in 1903-1907. This fencing has beautiful patterns formed by shod links with a large vegetative ornaments. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russland - St
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Friedrich Schinkel
Karl Friedrich Schinkel (13 March 1781 – 9 October 1841) was a Prussian architect, city planner An urban planner (also known as town planner) is a professional who practices in the field of town planning, urban planning or city planning. An urban planner may focus on a specific area of practice and have a title such as city planner, town ... and painter who also designed furniture and stage sets. Schinkel was one of the most prominent architects of Germany and designed both neoclassical and neogothic buildings. His most famous buildings are found in and around Berlin. Biography Schinkel was born in Neuruppin, Margraviate of Brandenburg. When he was six, his father died in the disastrous Neuruppin fire of 1787. He became a student of architect Friedrich Gilly (1772–1800) (the two became close friends) and his father, David Gilly, in Berlin. At that time, the architectural taste in Prussia was shaped in neoclassical style, mainly by Carl Gotthard Langhans, the archit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considering the limitations imposed by practicality, regulation, safety and cost. "Science is knowledge based on our observed facts and tested truths arranged in an orderly system that can be validated and communicated to other people. Engineering is the creative application of scientific principles used to plan, build, direct, guide, manage, or work on systems to maintain and improve our daily lives." The word ''engineer'' (Latin ) is derived from the Latin words ("to contrive, devise") and ("cleverness"). The foundational qualifications of an engineer typically include a four-year Bachelor of Engineering, bachelor's degree in an engineering discipline, or in some jurisdictions, a Master of Engineering, master's degree in an engineering discipline plus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge Of Four Lions
Bridge of Four Lions (russian: Львиный мост, Мост о четырех львах) is a 28-metre-long pedestrian bridge over the Griboedov Canal in St Petersburg, connecting L'vinyi Drive to Malaya Podyacheskaya Street. The Lion Bridge is in the Admiralteysky District of St. Petersburg, connecting the Kazansky and Spassky Islands. Its abutments are crowned with four cast iron sculptures of lions, which give the bridge its name. The structure, suspended by cables Cable may refer to: Mechanical * Nautical cable, an assembly of three or more ropes woven against the weave of the ropes, rendering it virtually waterproof * Wire rope, a type of rope that consists of several strands of metal wire laid into a hel ... emerging from the mouths of lions, was constructed in 1825 according to the design of two well-established bridge builders, Tratter and Kristianovich. It is an outstanding monument of bridge-building architecture of the first quarter of the 19th century It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architect
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that have human occupancy or use as their principal purpose. Etymologically, the term architect derives from the Latin ''architectus'', which derives from the Greek (''arkhi-'', chief + ''tekton'', builder), i.e., chief builder. The professional requirements for architects vary from place to place. An architect's decisions affect public safety, and thus the architect must undergo specialized training consisting of advanced education and a ''practicum'' (or internship) for practical experience to earn a license to practice architecture. Practical, technical, and academic requirements for becoming an architect vary by jurisdiction, though the formal study of architecture in academic institutions has played a pivotal role in the development of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liteyny Bridge
The Liteyny Bridge () is the second permanent bridge across the Neva river in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It connects Liteyny Prospekt with Vyborgsky district. The bridge's length is 396 meters, the width is 34 meters. At the vicinity of the Liteyny Bridge, the Neva river reaches the maximum depth of 24 meters. Location Upstream there is the Bolsheokhtinsky bridge, below the Troitsky bridge and Sampsonievsky bridge (across Bolshaya Nevka). The nearest metro stations are Chernyshevskaya and Lenin Square. Name The bridge is named ''Liteyney'' which literally means ''Foundry'' after the Liteyny Prospekt and Liteyny district which in turn were named after the large foundry that was established on the left bank in 1711. In 1879 the bridge was renamed ''Aleksandrovsky'' in name of tzar Alexander II. But this name was never adopted by the public and after the October Revolution in 1917 the original name ''Liteyny Bridge'' was restored. History The ancient maps reveal that even before t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornament (architecture)
An ornament is something used for decoration. Ornament may also refer to: Decoration *Ornament (art), any purely decorative element in architecture and the decorative arts * Biological ornament, a characteristic of animals that appear to serve only a decorative purpose * Bronze and brass ornamental work, decorative work that dates back to antiquity * Christmas ornament, a decoration used to festoon a Christmas tree * Dingbat, decorations in typography * Garden ornament, a decoration in a garden, landscape, or park * Hood ornament, a decoration on the hood of an automobile * Lawn ornament, a decoration in a grassy area * Ornamental plant, a decorative plant * Peak ornament, a decoration under the peak of the eaves of a gabled building Music * Ornament (music), a flourish that serves to decorate music *Ornament, a Russian band, forerunner to the band Kukuruza Other uses * Ornament (football), the football team from Hong Kong * Ornaments Rubric, a prayer of the Church of England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blagoveshchensky Bridge
The Annunciation Bridge ( - ''Blagoveshchensky most''; from 1855 to 1918 Nikolaevsky Bridge, ; from 1918 to 2007 called Lieutenant Schmidt Bridge, ) is the first permanent bridge built across the Neva River in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It connects Vasilievsky Island and the central part of the city ( Admiralteysky raion). The bridge's length is 331 meters and the width was 24 meters. The original name of the bridge was Nevsky Bridge. It was later renamed Blagoveshchensky Bridge. After the death of Tsar Nicholas I, it was named Nikolaevsky Bridge in his honor, and in 1918 it was renamed for Lieutenant Schmidt. In 1727 a temporary bridge was built at the location of the modern bridge. The place was chosen by Menshikov whose palace is located at the opposite bank. This bridge, named Issakievsky, existed until the current bridge was built, at which time it was moved to the location of where Palace Bridge is located today. The bridge was built in 1843-1850. It was designed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mermaid
In folklore, a mermaid is an aquatic creature with the head and upper body of a female human and the tail of a fish. Mermaids appear in the folklore of many cultures worldwide, including Europe, Asia, and Africa. Mermaids are sometimes associated with perilous events such as floods, storms, shipwrecks, and drownings. In other folk traditions (or sometimes within the same traditions), they can be benevolent or beneficent, bestowing boons or falling in love with humans. The male equivalent of the mermaid is the merman, also a familiar figure in folklore and heraldry. Although traditions about and sightings of mermen are less common than those of mermaids, they are generally assumed to co-exist with their female counterparts. The male and the female collectively are sometimes referred to as merfolk or merpeople. The Western concept of mermaids as beautiful, seductive singers may have been influenced by the Sirens of Greek mythology, which were originally half-birdlike, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neptune (mythology)
Neptune ( la, Neptūnus ) is the god of freshwater and the sea in Roman religion. He is the counterpart of the Greek god Poseidon.''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. In the Greek tradition, he is a brother of Jupiter and Pluto; the brothers preside over the realms of heaven, the earthly world (including the underworld), and the seas. Salacia is his wife. Depictions of Neptune in Roman mosaics, especially those in North Africa, were influenced by Hellenistic conventions. He was likely associated with freshwater springs before the sea. Like Poseidon, he was also worshipped by the Romans as a god of horses, as ''Neptunus equestris'' (a patron of horse-racing). Worship The theology of Neptune is limited by his close identification with the Greek god Poseidon, one of many members of the Greek pantheon whose theology was later tied to a Roman deity. The '' lectisternium'' of 399 BC indicated that the Greek figures of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trident
A trident is a three- pronged spear. It is used for spear fishing and historically as a polearm. The trident is the weapon of Poseidon, or Neptune, the God of the Sea in classical mythology. The trident may occasionally be held by other marine divinities such as Tritons in classical art. Tridents are also depicted in medieval heraldry, sometimes held by a merman-Triton. In Hinduism, it is the weapon of Shiva, known as ''trishula'' (Sanskrit for "triple-spear"). Etymology The word "trident" comes from the French word ''trident'', which in turn comes from the Latin word ' or ': ''tri'' meaning "three" and ''dentes'' meaning "teeth", referring specifically to the three prongs, or "teeth", of the weapo The Greek language, Greek equivalent is (''tríaina''), from Proto-Greek ''trianja'', meaning "threefold". The Greek term does not imply three of anything specific, and is vague about the shape, thus the assumption it was originally of "trident" form has been challenged. Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pig-iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate product of the iron industry in the production of steel which is obtained by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with silica and other constituents of dross, which makes it brittle and not useful directly as a material except for limited applications. The traditional shape of the molds used for pig iron ingots is a branching structure formed in sand, with many individual ingots at right angles to a central channel or "runner", resembling a litter of piglets being nursed by a sow. When the metal had cooled and hardened, the smaller ingots (the "pigs") were simply broken from the runner (the "sow"), hence the name "pig iron". As pig iron is intended for remelting, the uneven size of the ingots and the inclusion of small amounts of sand cause only insignificant problems considering the ease of casting and handling them. History Smelting and producing wroug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |