|
Fenbendazole
Fenbendazole is a broad-spectrum benzimidazole anthelmintic used against gastrointestinal parasites including: roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, the tapeworm genus '' Taenia'' (but not effective against '' Dipylidium caninum'', a common dog tapeworm), pinworms, '' Aelurostrongylus'' spp., paragonimiasis, strongyles, and strongyloides that can be administered to sheep, cattle, horses, fish, dogs, cats, rabbits, most reptiles, freshwater shrimp tanks as planaria and hydra treatments, and seals. Mechanism of action Fenbendazole works by binding to tubulin, a protein that is part of the microtubules in the cells of parasites. This binding disrupts the microtubules' formation and function, leading to the parasites' inability to absorb nutrients, resulting in their eventual death. This mode of action makes fenbendazole effective against both adult and larval stages of many parasitic worms. Uses in veterinary medicine Dogs and cats Fenbendazole is commonly used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxfendazole
Oxfendazole is a broad-spectrum benzimidazole anthelmintic. Its main use is for protecting livestock against roundworm, strongyles, and pinworms. Oxfendazole is the sulfoxide metabolite of fenbendazole. Oxfendazole is an anthelmintic (wormer) compound used in veterinary practice. It comes under the chemical class of the benzimidazoles. This drug is rarely used in horses, goats, sheep, and cattle. It is very scarcely applied on dogs and cats. The drug for livestock is majorly available in the form of pills, tablets, drenches, bolus, etc. They are meant for oral consumption. Several drenches are allowed for intraruminal injection in some of the countries. Few countries also prefer injectables and pour-ons. For pet dogs, the drug is available in the form of drenches. Efficacy Both oxfendazole and fenbendazole are efficacious against gastrointestinal lungworms and roundworms of livestock, adults, and L4-larvae of the significant species for example, of the genera '' Bunostomum' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzimidazole
Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound may be viewed as fused rings of the aromatic compounds benzene and imidazole. It is a white solid that appears in form of tabular crystals. Preparation Benzimidazole was discovered during research on vitamin B12. The benzimidazole nucleus was found to be a stable platform on which drugs could be developed. Benzimidazole is produced by Condensation reaction, condensation of o-phenylenediamine with formic acid, or the equivalent trimethyl orthoformate: :C6H4(NH2)2 + HC(OCH3)3 → C6H4N(NH)CH + 3 CH3OH 2-Substituted derivatives are obtained when the condensation is conducted with aldehydes in place of formic acid, followed by oxidation. Reactions Benzimidazole is a Base (chemistry), base: :C6H4N(NH)CH + H+ → [C6H4(NH)2CH]+ It can also be deprotonated with stronger bases: :C6H4N(NH)CH + LiH → Li [C6H4N2CH] + H2 The imine can be alkylated and also serves as a ligand in coordinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbits
Rabbits are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also includes the hares), which is in the order Lagomorpha (which also includes pikas). They are familiar throughout the world as a small herbivore, a prey animal, a domesticated form of livestock, and a pet, having a widespread effect on ecologies and cultures. The most widespread rabbit genera are '' Oryctolagus'' and ''Sylvilagus''. The former, ''Oryctolagus'', includes the European rabbit, ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'', which is the ancestor of the hundreds of breeds of domestic rabbit and has been introduced on every continent except Antarctica. The latter, ''Sylvilagus'', includes over 13 wild rabbit species, among them the cottontails and tapetis. Wild rabbits not included in ''Oryctolagus'' and ''Sylvilagus'' include several species of limited distribution, including the pygmy rabbit, volcano rabbit, and Sumatran striped rabbit. Rabbits are a paraphyletic grouping, and do not constitute a clade, as hares (bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation. By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. However, when a medication is administered via routes other than intravenous, its bioavailability is lower due to intestinal epithelium absorption and first-pass metabolism. Thereby, mathematically, bioavailability equals the ratio of comparing the area under the plasma drug concentration curve versus time (AUC) for the extravascular formulation to the AUC for the intravascular formulation. AUC is used because AUC is proportional to the dose that has entered the systemic circulation. Bioavailability of a drug is an average value; to take population variability into account, deviation range is shown as ±. To ensure that the drug taker who has poor absorption is dosed appropriately, the bottom value of the deviation range is employed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticancer Drug
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs), or it may aim only to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called '' medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' now means the non-specific use of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or to induce DNA damage (so that DNA repair can augment chemotherapy). This meaning excludes the more-selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). Therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, which inhibit growth-promoting signals from classic endocrine hormones (primarily est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repurposing
Repurposing is the process by which an object with one use value is transformed or redeployed as an object with an alternative use value. Description Repurposing is as old as human civilization, with many contemporary scholars investigating how different societies re-appropriate the artifacts of older cultures in new and creative ways. More recently, repurposing has been celebrated by 21st century hobbyists and arts-and-crafts organizations such as Instructables and other Maker culture communities as a means of creatively responding to the ecological and economic crises of the 21st century. Recent scholarship has attempted to relate these activities to American left- and right-libertarianism. Repurposing is the use of a tool being re-channeled into being another tool, usually for a purpose unintended by the original tool-maker. Typically, repurposing is done using items usually considered to be junk, garbage, or obsolete. A good example of this would be the Earthship style of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants. The rumen and the reticulum make up the reticulorumen in ruminant animals. The diverse microbial communities in the rumen allows it to serve as the primary site for microbial fermentation of ingested feed, which is often fiber-rich roughage typically indigestible by mammalian digestive systems. The rumen is known for containing unique microbial networks within its multiple sac compartments to break down nutrients into usable energy and fatty acids. Brief anatomy The rumen is composed of five muscular sacs: cranial sac, ventral sac, dorsal sac, caudodorsal sac, and caudoventral blind sac. Each of these areas contain unique microbial communities, environments, and physical abilities that influence digestion. The outer lining of the rumen, known as the epithelium, serves as a protective layer and contributes to the metabolic processing of fermentation products. The inner lining of the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
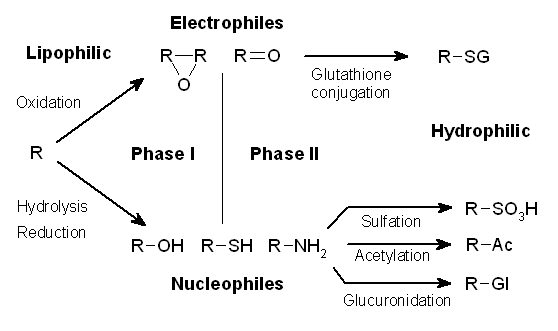
Drug Metabolism
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism (from the Greek xenos "stranger" and biotic "related to living beings") is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds (although in some cases the intermediates in xenobiotic metabolism can themselves cause toxic effects). The study of drug metabolism is the object of pharmacokinetics. Metabolism is one of the stages (see ADME) of the drug's transit through the body that involves the breakdown of the drug so that it can be excreted by the body. The metabolism of pharmaceutical drugs is an important as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niclosamide
Niclosamide, sold under the brand name Niclocide among others, is an anthelmintic medication used to treat tapeworm infestations, including diphyllobothriasis, hymenolepiasis, and taeniasis. It is not effective against other worms such as flukes or roundworms. It is taken by mouth. Side effects include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and itchiness. It may be used during pregnancy. It works by blocking glucose uptake and oxidative phosphorylation by the worm. Niclosamide was first synthesized in 1958. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Niclosamide is not available for human use in the United States. Side effects Side effects include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, and itchiness. Rarely, dizziness, skin rash, drowsiness, perianal itching, or an unpleasant taste occur. For some of these reasons, praziquantel is a preferable and equally effective treatment for tapeworm infestation. Of note, niclosamide kills the po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicylanilide
Salicylanilide is a chemical compound which is the amide of salicylic acid and aniline. It is classified as both a salicylamide and an anilide. Derivatives of salicylanilide have a variety of pharmacological uses. Chlorinated derivatives including niclosamide, oxyclozanide, and rafoxanide are used as anthelmintics, especially as flukicides. Brominated derivatives including dibromsalan, metabromsalan, and tribromsalan are used as topical antibacterials and antifungal An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as ...s. File:Bromochlorosalicylanilide.svg , Bromochlorosalicylanilide File:Niclosamide.svg , Niclosamide File:Oxyclozanide.svg , Oxyclozanide File:Rafoxanide.svg , Rafoxanide References {{Authority control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nanometer, nm and have an inner diameter between 11 and 15 nm. They are formed by the polymerization of a Protein dimer, dimer of two globular proteins, Tubulin#Eukaryotic, alpha and beta tubulin into #Structure, protofilaments that can then associate laterally to form a hollow tube, the microtubule. The most common form of a microtubule consists of 13 protofilaments in the tubular arrangement. Microtubules play an important role in a number of cellular processes. They are involved in maintaining the structure of the cell and, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, they form the cytoskeleton. They also make up the internal structure of cilia and flagella. They provide platforms for intracellular transport and are involved in a variety of cellular processes, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |