|
Felix Vaughan
Felix Vaughan (7 March 1766 – 22 April 1799) was an English barrister, known for his role as defence counsel in the treason trials of the 1790s. Early life The son of Samuel Vaughan of Middlesex, a tradesman, he was baptised at Westminster St James on 20 March 1766, and educated at Harrow School and Stanmore, where he was briefly a pupil of Samuel Parr, who became a lifelong friend, as did Basil William Douglas, Lord Daer, a schoolfellow, son of Dunbar Douglas, 4th Earl of Selkirk. He was admitted to the Inner Temple in 1785. He entered Jesus College, Cambridge as a fellow-commoner in 1786, graduating B.A. in 1790 and M.A. in 1794. Vaughan was in France and Geneva in 1790–1. He corresponded from the continent with John Richter and William Frend. Opponent of the Pitt clampdown Back in England, Vaughan was part of the London radical milieu including James Losh; also one of the group dining with John Horne Tooke. He was called to the bar in 1792. In spring of that year he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrister
A barrister is a type of lawyer in common law jurisdiction (area), jurisdictions. Barristers mostly specialise in courtroom advocacy and litigation. Their tasks include arguing cases in courts and tribunals, drafting legal pleadings, jurisprudence, researching the law and giving legal opinions. Barristers are distinguished from solicitors and other types of lawyers (e.g. chartered legal executives) who have more direct access to clients, and may do transactional legal work. In some legal systems, including those of Anglo-Dutch law, South Africa, Stockholm Institute for Scandinavian Law#Scandinavian Law, Scandinavia, Law of Pakistan, Pakistan, Law of India, India, Law of Bangladesh, Bangladesh and the Crown Dependencies of Law of Jersey, Jersey, Guernsey#Politics, Guernsey and the Manx Law, Isle of Man, ''barrister'' is also regarded as an honorific. In a few jurisdictions barristers are usually forbidden from "conducting" litigation, and can only act on the instructions of ano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knutsford
Knutsford () is a market town and civil parish in the Cheshire East district, in Cheshire, England; it is located south-west of Manchester, north-west of Macclesfield and south-east of Warrington. The population of the parish at the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census was 13,259. Knutsford's main town centre streets, Princess Street (also known locally as Top Street) and King Street lower down (also known as Bottom Street), form the hub of the town. At one end of the narrow King Street is an entrance to Tatton Park. The Tatton estate was home to the Egerton family and has given its name to Tatton (UK Parliament constituency), Tatton parliamentary constituency, which includes the neighbouring communities of Alderley Edge and Wilmslow. Knutsford is near Cheshire's Golden Triangle (Cheshire), ''Golden Triangle'' and is on the Cheshire Plain, between the Peak District to the east and the Welsh mountains to the west. History Knutsford was recorded in the Domesday Book of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
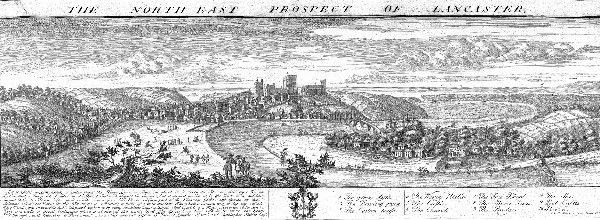
Lancaster, Lancashire
Lancaster (, ) is a city in Lancashire, England, and the main cultural hub, economic and commercial centre of City of Lancaster district. The city is on the River Lune, directly inland from Morecambe Bay. Lancaster is the county town, although Lancashire County Council has been based at County Hall, Preston, County Hall in Preston, Lancashire, Preston since its formation in 1889. The city's long history is marked by Lancaster Roman Fort, Lancaster Castle, Lancaster Priory, Lancaster Priory Church, Lancaster Cathedral and the Ashton Memorial. It is the seat of Lancaster University and has a campus of the University of Cumbria. It had a population of 52,234 in the 2011 census, compared to the district, which had a population of 138,375. The House of Lancaster was a branch of the List of English monarchs, English royal family. The Duchy of Lancaster still holds large estates on behalf of Charles III, who is the Duke of Lancaster. The Port of Lancaster and the 18th-century Lancas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Walker (merchant)
Thomas Walker (1749–1817) was an English cotton merchant and political radical. Life He was the son of Thomas Walker, a merchant in Bristol who moved to Manchester. An early influence was the teaching of James Burgh. He became a Manchester cotton merchant himself. He had a town house and warehouse on South Parade, adjacent to St Mary's Church, Manchester, and a country place at Barlow Hall, rented from William Egerton. Business campaigns In 1784 Walker led the successful local opposition to William Pitt's fustian tax. With Thomas Richardson, he testified to the Board of Trade committee in London in January 1785. After some confusion during the spring, the House of Commons voted to repeal the tax in April, and the Manchester men returned north as heroes. The same year he founded the General Chamber of Manufactures, set up to lobby against Pitt's measures on trade with Ireland. In 1787 Walker opposed the Eden Treaty, a divisive position. In 1788, at a meeting of fustian man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedom Of The Press
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the fundamental principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic Media (communication), media, especially publication, published materials, should be considered a right to be exercised freely. Such freedom implies the absence of interference from an overreaching State (polity), state; its preservation may be sought through a constitution or other legal protection and security. It is in opposition to paid press, where communities, police organizations, and governments are paid for their copyrights. Without respect to governmental information, any government may distinguish which materials are public or protected from disclosure to the public. State materials are protected due to either one of two reasons: the classified information, classification of information as sensitive, classified, or secret, or the relevance of the information to protecting the national interest. Many governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Thelwall
John Thelwall (27 July 1764 – 17 February 1834) was a radical British orator, writer, political reformer, journalist, poet, elocutionist and speech therapist.Thelwall, John (1764-1834) english-heritage.org.uk. Retrieved 30 May 2019. Life  Thelwall was born in , London, but was descended from a Welsh family which had its seat at Plas y Ward,
Thelwall was born in , London, but was descended from a Welsh family which had its seat at Plas y Ward,
|
Daniel Isaac Eaton
Daniel Isaac Eaton (1753–1814) was an English radical author, publisher and activist. He was tried eight times for selling radical literature and convicted in 1812 for selling '' The Age of Reason''. Eaton was the publisher of the popular periodical '' Politics for the People'' and was arrested on 7 December 1793 for publishing a statement by John Thelwall, a radical lecturer and debater: Thelwall had made a speech that included an anecdote about a tyrannical gamecock named "King Chanticleer". Eaton was imprisoned for three months before his trial in an effort to bankrupt him and his family. In February 1794, he was finally brought to trial and defended by John Gurney: he was acquitted. Percy Bysshe Shelley Percy Bysshe Shelley ( ; 4 August 1792 – 8 July 1822) was an English writer who is considered one of the major English Romantic poets. A radical in his poetry as well as in his political and social views, Shelley did not achieve fame durin ... wrote the essay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American 501(c)(3) organization, non-profit organization founded in 1996 by Brewster Kahle that runs a digital library website, archive.org. It provides free access to collections of digitized media including websites, Application software, software applications, music, audiovisual, and print materials. The Archive also advocates a Information wants to be free, free and open Internet. Its mission is committing to provide "universal access to all knowledge". The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archiving, web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hundreds of billions of web captures. The Archive also oversees numerous Internet Archive#Book collections, book digitization projects, collectively one of the world's largest book digitization efforts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Priestley
Joseph Priestley (; 24 March 1733 – 6 February 1804) was an English chemist, Unitarian, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher, English Separatist, separatist theologian, Linguist, grammarian, multi-subject educator and Classical liberalism, classical liberal Political philosophy, political theorist. He published over 150 works, and conducted experiments in several areas of science. Priestley is credited with his independent discovery of oxygen by the thermal decomposition of mercuric oxide, having isolated it in 1774. During his lifetime, Priestley's considerable scientific reputation rested on his invention of carbonated water, his writings on electricity, and his discovery of several "airs" (gases), the most famous being what Priestley dubbed "dephlogisticated air" (oxygen). Priestley's determination to defend phlogiston theory and to reject what would become the chemical revolution eventually left him isolated within the scientific community. Priestley's science was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison Hulk
A prison ship, is a current or former seagoing vessel that has been modified to become a place of substantive detention for convicts, prisoner of war, prisoners of war or civilian internees. Some prison ships were hulk (ship type), hulked. While many nations have deployed prison ships over time, the practice was most widespread in 18th- and 19th-century Britain, as the government sought to address the issues of overcrowded civilian jails on land and an influx of enemy detainees from the War of Jenkins' Ear, the Seven Years' War and the French Revolutionary War, French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. History The terminology "hulk" comes from the Royal Navy meaning a ship incapable of full service either through damage or from initial non-completion. In England in 1776, during the reign of King George III, due to a shortage of prison space in London, the concept of "prison hulks" moored in the Thames, was introduced to meet the need for prison space. The first such ship cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Muir Of Huntershill
Thomas Muir (24 August 1765 – 25 January 1799), also known as Thomas Muir the Younger of Huntershill, was a Scottish political reformer and lawyer. Muir graduated from Edinburgh University and was admitted to the Faculty of Advocates in 1787, aged 22. Muir was a leader of the Society of the Friends of the People. He is included in the Political Martyrs' Monument in Edinburgh. In 1793 Muir was sentenced to transportation to Botany Bay Australia for sedition. Two years later in 1796, Muir escaped from Botany Bay on the American ship ''Otter''. The ''Otter'' reached Nootka Sound, Vancouver Island in June 1796. From there Muir travelled to Mexico City, where he asked to be allowed to travel to California. On April 1797 Muir was imprisoned in Havana, Cuba and taken by Spanish ship ''Ninfa'' to Spain. On arrival at Cádiz, the Spanish ship became engaged in a battle with two British Royal Navy Men O War that were blocking the harbour. Muir received a glancing blow to his face from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association For Preserving Liberty And Property Against Republicans And Levellers
The Association for Preserving Liberty and Property against Republicans and Levellers, also known as the Crown and Anchor Society or Crown and Anchor Association, was an English loyalist, anti-Jacobin, anti-Radical society active between late 1792 and June 1793. The Association was founded on 20 November 1792 by John Reeves at the Crown and Anchor tavern in the Strand, London. It proved to be "staggeringly successful, outstripping even the Constitutional societies", with more than 2,000 local branches established before long. They disrupted Radicals' meetings, attacked printers of Thomas Paine's works, initiated prosecutions for sedition and published loyalist pamphlets. A letter to Reeves of 1792 proposed the use of ballads for propaganda:It occurred to me, that anything written in voice verse& especially to an Old English tune … made a more fixed Impression on the minds of the Younger and Lower Class of People, than any written prose, which was often forgotten as soon as Read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |