|
Febrile Neutropenia
Febrile neutropenia is the development of fever, often with other signs of infection, in a patient with neutropenia, an abnormally low number of neutrophil granulocytes (a type of white blood cell) in the blood. It is an oncologic emergency, and is the most common serious complication in patients with hematopoietic cancers or receiving chemotherapy for cancer. The term neutropenic sepsis is also applied, although it tends to be reserved for patients who are less well. In 50% of cases, an infection is detectable; bacteremia (bacteria in the bloodstream) is present in approximately 20% of all patients with this condition. Definition Febrile neutropenia or neutropenic fever is a defined as a single oral temperature value of ≥ 38.3 C (101 F) or a temperature ≥ 38 C (100.4 F) for ≥ 1 hour, with an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) < 1500 cell/microliter. In case of severe neutropenia, the ANC is < 500 cell/microliter. In profoundly severe neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point in the hypothalamus. There is no single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature: sources use values ranging between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle tone, muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes Flushing (physiology), flushed, and may begin to Perspiration, sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral infection, viral, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina, or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage — bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage — a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage — bleeding in the brain caused by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piperacillin/tazobactam
Piperacillin/tazobactam, sold under the brand name Tazocin among others, is a combination medication containing the antibiotic piperacillin and the β-lactamase inhibitor tazobactam. The combination has activity against many Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria including ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa''. It is used to treat pelvic inflammatory disease, intra-abdominal infection, pneumonia, cellulitis, and sepsis. It is given by injection into a vein. Common adverse effects include headache, trouble sleeping, rash, nausea, constipation, and diarrhea. Serious adverse effects include ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. Those who are allergic to other β-lactam are more likely to be allergic to piperacillin/tazobactam. Use in pregnancy or breastfeeding appears to generally be safe. It usually results in bacterial death through blocking their ability to make a cell wall. Piperacillin/tazobactam was approved for medical use in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomembranous Colitis
Colitis is swelling or inflammation of the large intestine ( colon). Colitis may be acute and self-limited or long-term. It broadly fits into the category of digestive diseases. In a medical context, the label ''colitis'' (without qualification) is used if: * The cause of the inflammation in the colon is undetermined; for example, ''colitis'' may be applied to ''Crohn's disease'' at a time when the diagnosis is unknown, or * The context is clear; for example, an individual with ulcerative colitis is talking about their disease with a physician who knows the diagnosis. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of colitis are quite variable and dependent on the cause of the colitis and factors that modify its course and severity. Common symptoms of colitis may include: mild to severe abdominal pains and tenderness (depending on the stage of the disease), persistent hemorrhagic diarrhea with pus either present or absent in the stools, fecal incontinence, flatulence, fatigue, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, this statistical approach involves extracting effect sizes and variance measures from various studies. By combining these effect sizes the statistical power is improved and can resolve uncertainties or discrepancies found in individual studies. Meta-analyses are integral in supporting research grant proposals, shaping treatment guidelines, and influencing health policies. They are also pivotal in summarizing existing research to guide future studies, thereby cementing their role as a fundamental methodology in metascience. Meta-analyses are often, but not always, important components of a systematic review. History The term "meta-analysis" was coined in 1976 by the statistician Gene V. Glass, Gene Glass, who stated ''"Meta-analysis refers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meropenem
Meropenem, sold under the brand name Merrem among others, is an intravenous carbapenem antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Some of these include meningitis, intra-abdominal infection, pneumonia, sepsis, and anthrax. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, constipation, headache, rash, and pain at the site of injection. Serious side effects include ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection, seizures, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. Those who are allergic to other β-lactam antibiotics are more likely to be allergic to meropenem as well. Use in pregnancy appears to be safe. It is in the carbapenem family of medications. Meropenem usually results in bacterial death through blocking their ability to make a cell wall. It is resistant to breakdown by many kinds of β-lactamase enzymes, produced by bacteria to protect themselves from antibiotics. Meropenem was patented in 1983. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imipenem
Imipenem (trade name Primaxin among others) is a synthetic beta-lactam, β-lactam antibiotic belonging to the carbapenems chemical class. developed by Merck scientists Burton Christensen, William Leanza, and Kenneth Wildonger in the mid-1970s. Carbapenems are highly resistant to the β-lactamase enzymes produced by many multiple drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, thus playing a key role in the treatment of infections not readily treated with other antibiotics. It is usually administered through intravenous injection. Imipenem was patented in 1975 and approved for medical use in 1985. It was developed via a lengthy trial-and-error search for a more stable version of the natural product thienamycin, which is produced by the bacterium ''Streptomyces cattleya''. Thienamycin has antibacterial activity, but is unstable in aqueous solution, thus it is practically of no medicinal use. Imipenem has a broad spectrum of activity against Aerobic organism, aerobic and Anaerobic organism, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbapenem
Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Similar to penicillins and cephalosporins The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''. Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotic ..., carbapenems are members of the beta-lactam antibiotics drug class, which kill bacteria by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, thus inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. However, these agents individually exhibit a broader spectrum of activity compared to most cephalosporins and penicillins. Furthermore, carbapenems are typically unaffected by emerging antibiotic resistance, even to other beta-lactams. Carbapenem antibiotics were originall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cefepime
Cefepime is a fourth-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Cefepime has an extended spectrum of activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, with greater activity against both types of organism than third-generation agents. A 2007 meta-analysis suggested when data of trials were combined, mortality was increased in people treated with cefepime compared with other β-lactam antibiotics. In response, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) performed their own meta-analysis which found no mortality difference. Cefepime was patented in 1982 by Bristol-Myers Squibb and approved for medical use in 1994. It is available as a generic drug and sold under a variety of trade names worldwide. It was removed from the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines in 2019. Medical use Cefepime is usually reserved to treat moderate to severe nosocomial pneumonia, infections caused by multiple drug-resistant microorganisms (e.g. ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'') and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
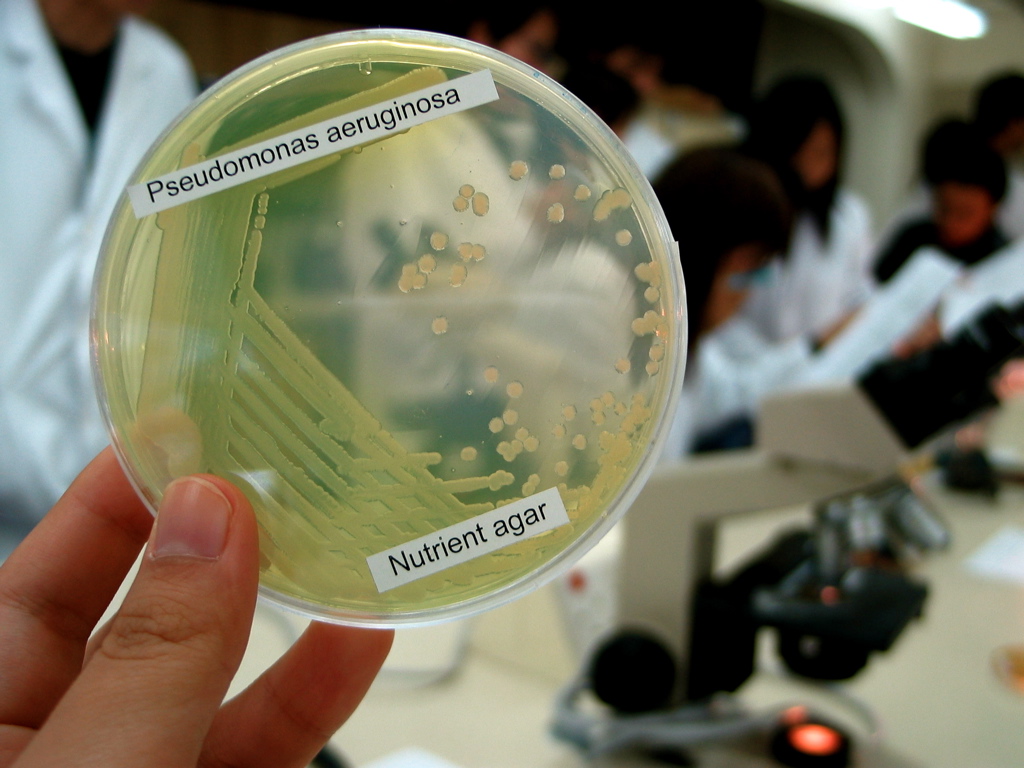
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aeruginosa'' is a multiple drug resistance, multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes. ''P. aeruginosa'' is able to selectively inhibit various antibiotics from penetrating its outer membrane'' ''– and has high resistance to several antibiotics. According to the World Health Organization ''P. aeruginosa'' poses one of the greatest threats to humans in terms of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalosporin
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus '' Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''. Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems. Cephalosporins were discovered in 1945, and first sold in 1964. Discovery The aerobic mold which yielded cephalosporin C was found in the sea near a sewage outfall in Su Siccu, by Cagliari harbour in Sardinia, by the Italian pharmacologist Giuseppe Brotzu in July 1945. Structure Cephalosporin contains a 6-membered dihydrothiazine ring. Substitutions at position 3 generally affect pharmacology; substitutions at position 7 affect antibacterial activity, but these cases are not always true. Medical uses Cephalosporins can be indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of infections caused by bacteria susceptible to this particular form of antibiotic. First-generation cephalosporins are active predominant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin infections, typhoid fever, and urinary tract infections, among others. For some infections it is used in addition to other antibiotics. It can be taken by mouth, as eye drops, as ear drops, or intravenously. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Severe side effects include tendon rupture, hallucinations, and nerve damage. In people with myasthenia gravis, there is worsening muscle weakness. Rates of side effects appear to be higher than some groups of antibiotics such as cephalosporins but lower than others such as clindamycin. Studies in other animals raise concerns regarding use in pregnancy. No problems were identified, however, in the children of a small number of women who took the medication. It appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |