|
Faustus Flavianus
Marcus Cocceius Anicius Faustus Flavianus (fl. 3rd century AD) was a Roman senator who was appointed suffect consul sometime around AD 250/252. Probably either the son or nephew of Anicius Faustus Paulinus, suffect consul before AD 230, Faustus Flavianus was a member of the Patrician 3rd century ''gens Anicia''. Faustus Flavianus was appointed ''Curator rei publicae Cirtae'' (or curator of the city of Cirta) in AD 251. It is believed that sometime around this time, c. AD 250/252, he was appointed suffect consul.Mennen, pg. 87 It is speculated that Faustus Flavianus was the brother of Sextus Cocceius Anicius Faustus Paulinus Sextus Cocceius Anicius Faustus Paulinus (fl. 3rd century AD) was a Roman senator who was appointed suffect consul sometime before AD 260/268. Biography Probably either the son or nephew of Anicius Faustus Paulinus, suffect consul before AD 230, ..., suffect consul prior to AD 268. Sources * Mennen, Inge, ''Power and Status in the Roman Empire, AD 193-284 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate Of The Roman Empire
The Senate of the Roman Empire was a political institution in the ancient Roman Empire. After the fall of the Roman Republic, the constitutional balance of power shifted from the Roman Senate to the Roman Emperor. Beginning with the first emperor, Augustus, the Emperor and the Senate were technically two co-equal branches of government. In practice, however, the actual authority of the imperial Senate was negligible, as the Emperor held the true power of the state. As such, membership in the senate became sought after by individuals seeking prestige and social standing, rather than actual authority. During the reigns of the first Emperors, legislative, judicial, and electoral powers were all transferred from the " Roman assemblies" to the Senate. However, since the control that the Emperor held over the senate was absolute, the Senate acted as a vehicle through which the Emperor exercised his autocratic powers. Procedure The first emperor, Augustus, inherited a Senate whose membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Consul
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the '' cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspired) after that of the censor. Each year, the Centuriate Assembly elected two consuls to serve jointly for a one-year term. The consuls alternated in holding '' fasces'' – taking turns leading – each month when both were in Rome and a consul's '' imperium'' extended over Rome and all its provinces. There were two consuls in order to create a check on the power of any individual citizen in accordance with the republican belief that the powers of the former kings of Rome should be spread out into multiple offices. To that end, each consul could veto the actions of the other consul. After the establishment of the Empire (27 BC), the consuls became mere symbolic representatives of Rome's republican heritage and held very l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anicius Faustus Paulinus (suffect Consul)
Quintus Anicius Faustus Paulinus (or possibly Sextus Anicius Faustus Paulinus) (fl. 3rd century AD) was a Roman military officer and senator who was appointed suffect consul sometime before AD 230. Biography Probably the son of Quintus Anicius Faustus, suffect consul in AD 198, and a member of the third century ''gens Anicia'', Faustus Paulinus was appointed ''Legatus Augusti pro praetore'' (or imperial governor) of the province of Moesia Inferior in around AD 229/230. As this posting was consular in rank, it is therefore assumed that sometime prior to AD 230, he had been appointed suffect consul. It is speculated that Faustus Paulinus either married a daughter of Sextus Cocceius Vibianus, ''consul suffectus'' sometime during the late 2nd or early 3rd century AD, or that he was the brother-in-law to a son of Sextus Cocceius Vibianus. He may therefore have been the father (or perhaps uncle) of Marcus Cocceius Anicius Faustus Flavianus, suffect consul c. AD 250/252, and Sextus Coccei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrician (ancient Rome)
The patricians (from la, patricius, Greek: πατρίκιος) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–50 .... The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom, and the early Roman Republic, Republic, but its relevance waned after the Conflict of the Orders (494 BC to 287 BC). By the time of the late Republic and Roman Empire, Empire, membership in the patriciate was of only nominal significance. The social structure of Ancient Rome revolved around the distinction between the patricians and the plebeians. The status of patricians gave them more political power than the plebeians. The relationship between the patricians and the plebeians eventually caused the Conflict of the Orders. This time period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anicia (gens)
The gens Anicia (or the Anicii) was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, mentioned first towards the end of the fourth century BC. The first of the Anicii to achieve prominence under the Republic was Lucius Anicius Gallus, who conducted the war against the Illyrii during the Third Macedonian War, in 168 BC. A noble family bore this name in the imperial era, and may have been descended from the Anicii of the Republic.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', William Smith, Editor. Origin The Anicii may have been from the Latin town of Praeneste. The earliest of the family to hold any curule magistracy at Rome bore the surname ''Praenestinus''. Praenomina The Anicii are known to have used the praenomina ''Lucius, Quintus, Marcus, Gnaeus, Titus,'' and ''Gaius''. Branches and cognomina The only major branch of the family during the Republic used the cognomen ''Gallus'', which may refer to a cock, or to a Gaul. The surname ''Praenestinus'', found in earlier ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
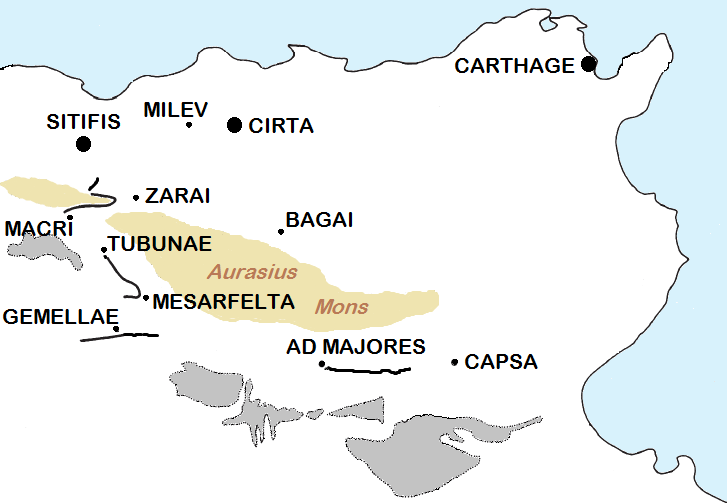
Cirta
Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria. Cirta was the capital city of the Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city was Russicada. Although Numidia was a key ally of the ancient Roman Republic during the Punic Wars (264–146BC), Cirta was subject to Roman invasions during the 2nd and 1st centuriesBC. Eventually it fell under Roman dominion during the time of Julius Caesar. Cirta was then repopulated with Roman colonists by Caesar and Augustus and was surrounded by the autonomous territory of a " Confederation of four free Roman cities" (with Chullu, Russicada, and Milevum), ruled initially by Publius Sittius. The city was destroyed in the beginning of the 4thcentury and was rebuilt by the Roman emperor Constantine the Great, who gave his name to the newly constructed city, Constantine. The Vandals damaged Cirta, but emperor reconquered and imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffect Consul
A consul held the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC), and ancient Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum'' (an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspired) after that of the censor. Each year, the Centuriate Assembly elected two consuls to serve jointly for a one-year term. The consuls alternated in holding '' fasces'' – taking turns leading – each month when both were in Rome and a consul's ''imperium'' extended over Rome and all its provinces. There were two consuls in order to create a check on the power of any individual citizen in accordance with the republican belief that the powers of the former kings of Rome should be spread out into multiple offices. To that end, each consul could veto the actions of the other consul. After the establishment of the Empire (27 BC), the consuls became mere symbolic representatives of Rome's republican heritage and held very little ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sextus Cocceius Anicius Faustus
Sextus Cocceius Anicius Faustus Paulinus (fl. 3rd century AD) was a Roman senator who was appointed suffect consul sometime before AD 260/268. Biography Probably either the son or nephew of Anicius Faustus Paulinus, suffect consul before AD 230, Faustus Paulinus was a member of the Patrician 3rd century ''gens Anicia''. He was appointed suffect consul sometime before AD 260/268, and was the proconsular governor of Africa, most likely around AD 265/268, but it has been acknowledged that he may have filled the office sometime later, possibly between AD 276 and 285. It has been speculated that he was possibly the father of Anicius Faustus Paulinus, the consul Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states th ... of AD 298.Martindale & Jones, pg. 681 Sources * Martindale, J. R.; Jones, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Undated Roman Consuls
This is a list of Roman consuls, individuals who were either elected or nominated to the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic, or a high office of the Empire, but for whom an exact date of when they served in office is absent. Most are reckoned to be suffect consuls, but occasionally it encompasses an ordinary consul. 3rd century BC 1st century AD 2nd century 3rd century 4th century Footnotes References {{Reflist, 30em Sources * Alföldy, Géza ''Konsulat und Senatorenstand unter der Antoninen'' Bonn: Rudolf Habelt Verlag (1977) * Jones, A. H. M.; Martindale, J. R.; Morris, J. ''The Prosopography of the later Roman Empire, Vol. I, AD 260-395'' (1971) * Leunissen, Paul M. M. ''Konsuln und Konsulare in der Zeit von Commodus bis Severus Alexander'' (1989) Roman consuls Consuls A consul is an official representative of the government of one state in the territory of another, normally acting to assist and protect the citizens of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century Romans
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 ( CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassanids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Roman Consuls
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism. Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to: Places United States * Imperial, California * Imperial, Missouri * Imperial, Nebraska * Imperial, Pennsylvania * Imperial, Texas * Imperial, West Virginia * Imperial, Virginia * Imperial County, California * Imperial Valley, California * Imperial Beach, California Elsewhere * Imperial (Madrid), an administrative neighborhood in Spain * Imperial, Saskatchewan, a town in Canada Buildings * Imperial Apartments, a building in Brooklyn, New York * Imperial City, Huế, a palace in Huế, Vietnam * Imperial Palace (other) * Imperial Towers, a group of lighthouses on Lake Huron, Canada * The Imperial (Mumbai), a skyscraper apartment complex in India Animals and plants * '' Cheritra'' or imperial, a genus of butterfly Architecture, design, and fashion * Imperial, a luggage case for the top of a coach * Imperial, the top, roof or second-storey compartm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |