|
Farimang Mamadi Singateh
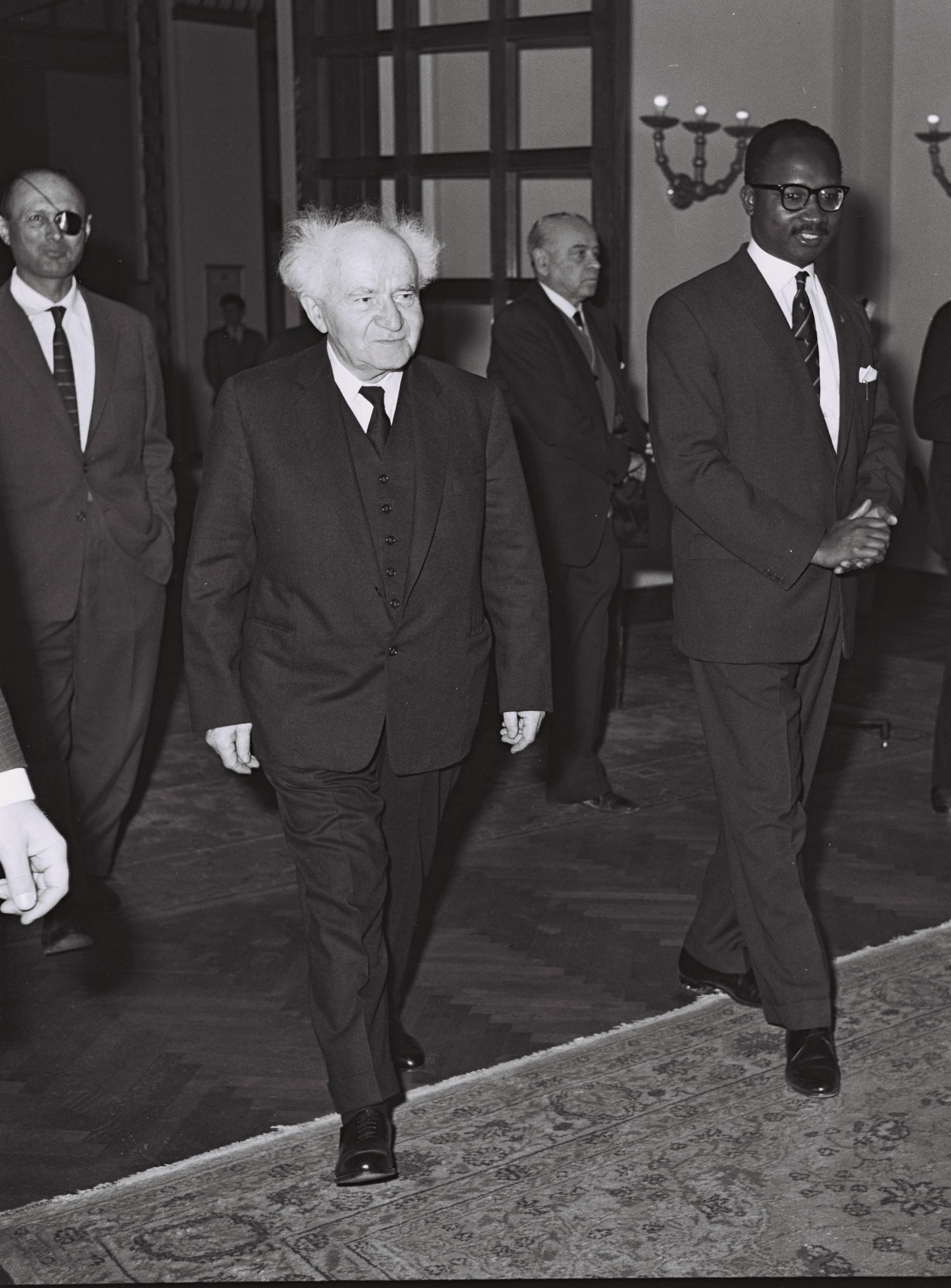
Sir Farimang Mamadi Singhateh, GCMG (10 November 1912 – 19 May 1977) was the second and last Governor-General of the Gambia, representing Queen Elizabeth II as head of state. Succeeding Sir John Warburton Paul, who had previously been the last Governor of The Gambia before independence, Sir Farimang was the only Gambian citizen to hold that post, beginning in 1966. His wife Fanta Singhateh was the first Gambian woman to be First Lady. When the country became a republic in 1970, the office was abolished, and the Prime Minister, Dauda (later Sir Dawda) Kairaba Jawara became an executive President. Sir Farimang Singhateh was working as a dispenser/pharmacist in the Royal Victoria Hospital. He then moved on to have his own clinics in Soma and Farafeni. Before going into the private sector he spent time in Basse and Mansakonko serving those communities. He was appointed as the first black Governor-General by the Queen of the United Kingdom while he was working in his Clinic at F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of St Michael And St George
The Most Distinguished Order of Saint Michael and Saint George is a British order of chivalry founded on 28 April 1818 by George, Prince of Wales (the future King George IV), while he was acting as prince regent for his father, King George III. It is named in honour of two military saints, Michael (archangel), Michael and Saint George, George. The Order of St Michael and St George was originally awarded to those holding commands or high position in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean territories acquired in the Napoleonic Wars, and it was subsequently extended to holders of similar office or position in other territories of the British Empire. It is at present awarded to men and women who hold high office or who render extraordinary or important non-military service to the United Kingdom in a foreign country, and it can also be conferred for important or loyal service in relation to foreign and Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth affairs. Description The three classes of ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawda Kairaba Jawara
Sir Dawda Kairaba Jawara (16 May 1924 – 27 August 2019) was a Gambian politician who served as prime minister from 1962 to 1970, and then as the first President of The Gambia from 1970 to 1994, when he was overthrown by Yahya Jammeh. Jawara was born in Barajally, MacCarthy Island Division, now the Central River Region. He was the son of Mamma Fatty and Almami Jawara. He was educated at the Methodist Boys' School in Banjul (Bathurst) and then attended Achimota College in the Gold Coast (now Ghana). He trained as a veterinary surgeon at the University of Glasgow's School of Veterinary Medicine, then completed his training at the University of Liverpool and the University of Edinburgh. He returned to The Gambia in 1953 and married Augusta Mahoney, beginning work as a veterinary officer. He entered politics and became secretary of the new People's Progressive Party (PPP) and was elected to the House of Representatives at the 1960 election. He became the leader of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambian Ahmadis
Gambian may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the country of the Gambia * Gambian people, a person from the Gambia, or of Gambian descent * Culture of the Gambia * Gambian cuisine See also * *Languages of the Gambia In The Gambia, Mandinka language, Mandinka is spoken as a first language by 38% of the population, Pulaar language, Pulaar by 21%, Wolof language, Wolof by 18%, Soninke language, Soninke by 9 percent, Jola-Fonyi language, Jola by 4.5 percent, Ser ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governors-general Of The Gambia
Governor-general (plural governors-general), or governor general (plural governors general), is the title of an official, most prominently associated with the British Empire. In the context of the governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general continue to be appointed as viceroy to represent the monarch of a personal union in any sovereign state over which the monarch does not normally reign in person (non-UK Commonwealth realm). In the British Empire, governors-general were appointed on the advice of the government of the United Kingdom and were often British aristocracy, but in the mid-twentieth century they began to be appointed on the advice of the independent government of each realm and be citizens of each independent state. Governors-general have also previously been appointed in respect of major colonial states or other territories held by either a monarchy or republic, such as Japan, Korea, Taiwan and France in Indochina. Current uses In modern usa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gambian Pharmacists
Gambian may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the country of the Gambia * Gambian people, a person from the Gambia, or of Gambian descent * Culture of the Gambia * Gambian cuisine See also * *Languages of the Gambia In The Gambia, Mandinka language, Mandinka is spoken as a first language by 38% of the population, Pulaar language, Pulaar by 21%, Wolof language, Wolof by 18%, Soninke language, Soninke by 9 percent, Jola-Fonyi language, Jola by 4.5 percent, Ser ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1977 Deaths
Events January * January 8 – Three bombs explode in Moscow within 37 minutes, killing seven. The bombings are attributed to an Armenia Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...n separatist group. * January 10 – Mount Nyiragongo erupts in eastern Zaire (now the Democratic Republic of the Congo). * January 17 – 49 marines from the and are killed as a result of a collision in Barcelona harbour, Spain. * January 18 ** Scientists identify a previously unknown Bacteria, bacterium as the cause of the mysterious Legionnaires' disease. ** Australia's worst Granville rail disaster, railway disaster at Granville, a suburb of Sydney, leaves 83 people dead. ** SFR Yugoslavia Prime minister Džemal Bijedić, his wife and 6 others are killed in a plane crash in Bosnia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1912 Births
This year is notable for Sinking of the Titanic, the sinking of the ''Titanic'', which occurred on April 15. In Albania, this leap year runs with only 353 days as the country achieved switching from the Julian to Gregorian Calendar by skipping 13 days. Friday, 30 November ''(Julian Calendar)'' immediately turned Saturday, 14 December 1912 ''(in the Gregorian Calendar)''. Events January * January 1 – The Republic of China (1912–49), Republic of China is established. * January 5 – The Prague Conference (6th All-Russian Conference of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party) opens. * January 6 ** German Geophysics, geophysicist Alfred Wegener first presents his theory of continental drift. ** New Mexico becomes the 47th U.S. state. * January 8 – The African National Congress is founded as the South African Native National Congress, at the Waaihoek Wesleyan Church in Bloemfontein, to promote improved rights for Black people, black South Africans, with Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of The Gambia
The president of the Republic of the Gambia is the head of state and head of government of the Gambia. The president leads the Executive (government), executive branch of the Politics of the Gambia, government of the Gambia and is the commander-in-chief of the Gambia Armed Forces. The post was created in 1970, when the Gambia became a republic and has been held by three people: Dawda Jawara, who ruled from 1970 until 1994, Yahya Jammeh, who seized power in a 1994 Gambian coup d'état, bloodless coup that year and Adama Barrow, who defeated Jammeh in 2016 Gambian presidential election, elections held in December 2016.Wiseman, John A. (2004Africa South of the Sahara 2004 (33rd edition): The Gambia: Recent History Europa Publications Ltd. p. 456. As of 2021, there are no term limits for the president in the Constitution of the Gambia. See also *List of colonial governors of the Gambia *List of heads of government of the Gambia *Lists of office-holders References *''Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Governors-General Of The Gambia
This is a list of the heads of state of The Gambia, from the independence of The Gambia in 1965 to the present day. From 1965 to 1970 the head of state under the Constitution of 1965 was the queen of the Gambia, Elizabeth II, who was also the monarch of other Commonwealth realms. The monarch was represented in the Gambia by a governor-general. The Gambia became a republic within the Commonwealth under the Constitution of 1970 and the monarch and governor-general were replaced by an executive president. Monarch (1965–1970) The succession to the throne was the same as the succession to the British throne. Governor-general The governor-general was the representative of the monarch in the Gambia and exercised most of the powers of the monarch. The governor-general was appointed for an indefinite term, serving at the pleasure of the monarch. Since the Gambia was granted independence by the Gambia Independence Act 1964, rather than being first established as a semi-autonomous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
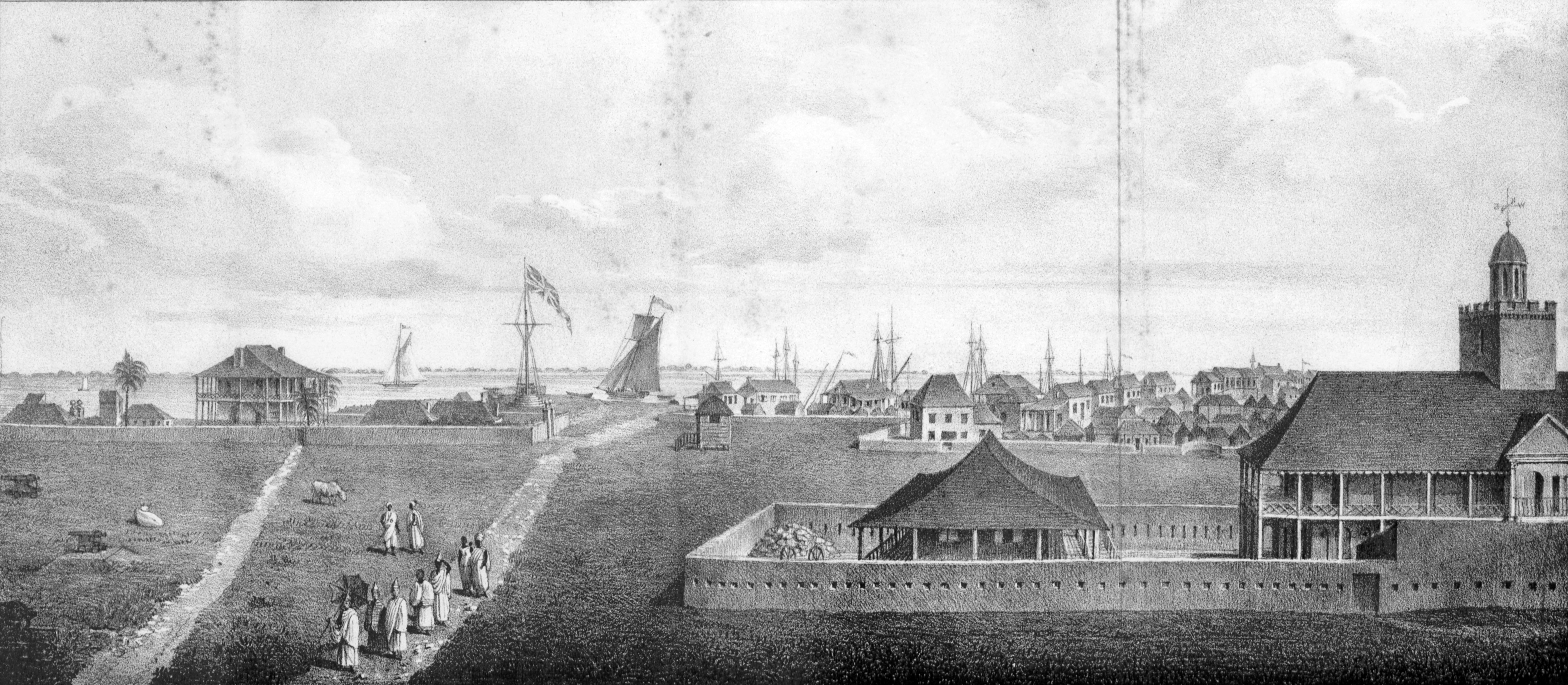
Banjul
Banjul (, (US) and ), officially the City of Banjul, is the capital city of The Gambia. It is the centre of the eponymous administrative division which is home to an estimated 400,000 residents, making it The Gambia's largest and most densely populated metropolitan area. The city Banjul is located on St Mary's Island (Banjul Island), where the Gambia River enters the Atlantic Ocean. The population of the city proper is 31,301, with the Greater Banjul Area, which includes the City of Banjul and the Kanifing Municipal Council, at a population of 413,397 (2013 census). The island is connected to the mainland to the west and the rest of Greater Banjul Area via bridges. There are also ferries linking Banjul to the mainland at the other side of the river. From the 19th century until 24 April 1973, the city was known as Bathurst. Etymology There are several etymologies for 'Banjul.' One traditional history recounts that Bandjougou, son of Barafin, came to the island after fleeing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmadiyya
Ahmadiyya, officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ), is an Islamic messianic movement originating in British India in the late 19th century. It was founded by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad (1835–1908), who said he had been divinely appointed as both the Promised Mahdi (Guided One) and Messiah expected by Muslims to appear towards the end times and bring about, by peaceful means, the final triumph of Islam; as well as to embody, in this capacity, the expected eschatological figure of other major religious traditions. Adherents of the Ahmadiyya—a term adopted expressly in reference to Muhammad's alternative name '' Ahmad'' — are known as Ahmadi Muslims or simply Ahmadis. Ahmadi thought emphasizes the belief that Islam is the final dispensation for humanity as revealed to Muhammad and the necessity of restoring it to its true intent and pristine form, which had been lost through the centuries. Its adherents consider Ahmad to have appeared as the Mahdi—bearing the qualities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Of The United Kingdom
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the form of government used by the United Kingdom by which a hereditary monarch reigns as the head of state, with their powers regulated by the British constitution. The term may also refer to the role of the royal family within the UK's broader political structure. The monarch since 8 September 2022 is King Charles III, who ascended the throne on the death of Queen Elizabeth II, his mother. The monarch and their immediate family undertake various official, ceremonial, diplomatic and representational duties. Although formally the monarch has authority over the governmentwhich is known as " His/Her Majesty's Government"this power may only be used according to laws enacted in Parliament and within constraints of convention and precedent. In practice the monarch's role, including that of Head of the Armed Forces, is limited to functions such as bestowing honours and appointing the prime min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |