|
Fangyan (book)
The ''Fangyan'' is a Chinese dictionary compiled in the early 1st century CE by the poet and philosopher Yang Xiong (53 BCE18 CE). It was the first Chinese dictionary to include significant regional vocabulary, and is considered the "most significant lexicographic work" of its era. His dictionary's preface explains how he spent 27 years amassing and collating the dictionary. Yang collected regionalisms from many sources, particularly the 'light carriage' ( ) surveys made during the Zhou and Qin dynasties, where imperial emissaries were sent into the countryside annually to record folk songs and idioms from across China, reaching as far north as Korea. Contents The ''Fangyan'' originally contained some 9,000 characters in 15 chapters, but two chapters have since been lost. Definitions typically list regional synonyms. For example, the entry for ''hu'' ( 'tiger') is as follows: Tiger: in the regions of Chen- Wei Song- Chu entral China some call it ''lifu''; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Dictionary
There are two types of dictionaries regularly used in the Chinese language: list individual Chinese characters, and list words and phrases. Because tens of thousands of characters have been used in written Chinese, Chinese lexicographers have developed a number of methods to order and sort characters to facilitate more convenient reference. Chinese dictionaries have been published for over two millennia, beginning in the Han dynasty. This is the longest lexicographical history of any language. In addition to works for Mandarin Chinese, beginning with the 1st-century CE '' Fangyan'' dictionaries also been created for the many varieties of Chinese. One of the most influential Chinese dictionaries ever published was the '' Kangxi Dictionary'', finished in 1716 during the Qing dynasty, with the list of 214 Kangxi radicals it popularized are still widely used. Terminology The general term ''cishu'' ( zh, links=no, t=辭書, p=císhū, l=lexicographic books) semantically encompasse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Chinese
Old Chinese, also called Archaic Chinese in older works, is the oldest attested stage of Chinese language, Chinese, and the ancestor of all modern varieties of Chinese. The earliest examples of Chinese are divinatory inscriptions on oracle bones from around 1250 BC, in the Late Shang period. Chinese bronze inscriptions, Bronze inscriptions became plentiful during the following Zhou dynasty. The latter part of the Zhou period saw a flowering of literature, including Four Books and Five Classics, classical works such as the ''Analects'', the ''Mencius (book), Mencius'', and the ''Zuo Zhuan''. These works served as models for Literary Chinese (or Classical Chinese), which remained the written standard until the early twentieth century, thus preserving the vocabulary and grammar of late Old Chinese. Old Chinese was written with several early forms of Chinese characters, including Oracle bone script, oracle bone, Chinese bronze inscriptions, bronze, and seal scripts. Throughout t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Text Project
The Chinese Text Project (CTP; ) is a digital library project that assembles collections of early Chinese texts. The name of the project in Chinese literally means "The Chinese Philosophical Book Digitization Project", showing its focus on books related to Chinese philosophy. It aims at providing accessible and accurate versions of a wide range of texts, particularly those relating to Chinese philosophy, and the site is credited with providing one of the most comprehensive and accurate collections of classical Chinese texts on the Internet. Site contents Texts are divided into pre-Qin and Han texts, and post-Han texts, with the former categorized by school of thought and the latter by dynasty. The ancient (pre-Qin and Han) section of the database contains over 5 million Chinese characters, the post-Han database over 20 million characters, and the publicly editable wiki section over 5 billion characters. Many texts also have English and Chinese translations, which are paired with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Dictionary Of Modern Chinese Dialects
The ''Great Dictionary of Modern Chinese Dialects'' () is a compendium of dictionaries for 42 local varieties of Chinese following a common format. The individual dictionaries cover dialects spread across the dialect groups identified in the ''Language Atlas of China'': * Mandarin ** Northeastern Mandarin: Harbin dialect ** Ji–Lu Mandarin: Jinan dialect ** Jiao–Liao Mandarin: Muping dialect ** Central Plains Mandarin: Luoyang dialect, Wanrong dialect, Xi'an dialect, Xining dialect, Xuzhou dialect ** Lanyin Mandarin: Urumqi dialect, Yinchuan dialect ** Southwestern Mandarin: Chengdu dialect, Guiyang dialect, Liuzhou dialect, Wuhan dialect ** Lower Yangtze Mandarin: Nanjing dialect, Yangzhou dialect * Jin: Taiyuan dialect, Xinzhou dialect * Wu: Chongming dialect, Danyang dialect, Hangzhou dialect, Jinhua dialect, Ningbo dialect, Shanghai dialect, Suzhou dialect, Wenzhou dialect * Hui: Jixi dialect * Gan: Lichuan dialect, Nanchang dialect, Pingxiang dialect * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chinese Dictionaries
Notable Chinese dictionaries, past and present, include: See also * List of English dictionaries * List of French dictionaries * List of Japanese dictionaries * List of etymological dictionaries External linksLIST OF CHINESE DICTIONARIES IN ALL LANGUAGES 1967 United States Department of State The United States Department of State (DOS), or simply the State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy of the United State ... Office of External Research {{Dictionaries of Chinese * Lists of reference books ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuowen Jiezi
The ''Shuowen Jiezi'' is a Chinese dictionary compiled by Xu Shen , during the Eastern Han dynasty (25–220 CE). While prefigured by earlier reference works for Chinese characters like the ''Erya'' (), the ''Shuowen Jiezi'' contains the first comprehensive analysis of characters in terms of their structure, where Xu attempted to provide rationales for their construction. It was also the first to organize its entries into sections according to shared components called Chinese character radicals, radicals. Background Xu Shen was a scholar of the Five Classics during the Han dynasty. He finished compiling the ''Shuowen Jiezi'' in 100 CE. However, due to an unfavorable imperial attitude towards scholarship, he waited until 121 before his son Xu Chong presented it to Emperor An of Han, along with a memorial. In analyzing the structure of characters and defining the words represented by them, Xu strove to clarify the meaning of the pre-Han classics, so as to ensure order and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinitic
The Sinitic languages (), often synonymous with the Chinese languages, are a group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute a major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is a primary split between the Sinitic languages and the rest of the family (the Tibeto-Burman languages). This view is rejected by some researchers but has found phylogenetic support among others. The Macro-Bai languages, whose classification is difficult, may be an offshoot of Old Chinese and thus Sinitic; otherwise, Sinitic is defined only by the many varieties of Chinese unified by a shared historical background, and usage of the term "Sinitic" may reflect the linguistic view that Chinese constitutes a family of distinct languages, rather than variants of a single language. Population Over 91% of the Chinese population speaks a Sinitic language, of whom about three-quarters speak a Mandarin variety. Estimates of the number of global speakers of Sinitic b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
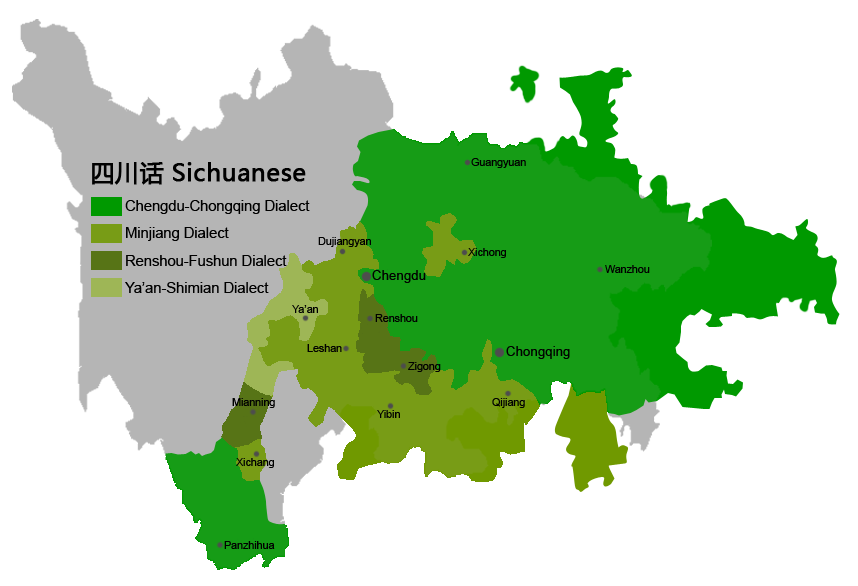
Southwestern Mandarin
Southwestern Mandarin (), also known as Upper Yangtze Mandarin (), is a Mandarin Chinese dialect spoken in much of Southwestern China, including in Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing, Guizhou, most parts of Hubei, the northwestern part of Hunan, the northern part of Guangxi and some southern parts of Shaanxi and Gansu. Southwestern Mandarin is spoken by roughly 260 million people. If considered a language distinct from central Mandarin, it would be the eighth-most spoken language by native speakers in the world, behind Mandarin itself, Spanish, English, Hindi, Portuguese, Arabic and Bengali. Overview Modern Southwestern Mandarin was formed by the waves of immigrants brought to the regions during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. Because of the comparatively recent move, such dialects show more similarity to modern Standard Mandarin than to other varieties of Chinese like Cantonese or Hokkien. For example, like most Southern Chinese dialects, Southwestern Mandarin does not possess the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Intelligibility
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between different but related language varieties in which speakers of the different varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. Mutual intelligibility is sometimes used to distinguish languages from dialects, although sociolinguistic factors are often also used. Intelligibility between varieties can be asymmetric; that is, speakers of one variety may be able to better understand another than vice versa. An example of this is the case between Afrikaans and Dutch. It is generally easier for Dutch speakers to understand Afrikaans than for Afrikaans speakers to understand Dutch. In a dialect continuum, neighbouring varieties are mutually intelligible, but differences mount with distance, so that more widely separated varieties may not be mutually intelligible. Intelligibility can be partial, as is the case with Azerbaijani and Turkish, or significant, as is the case with Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romani Language
Romani ( ; also Romanes , Romany, Roma; ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan macrolanguage of the Romani people. The largest of these are Vlax Romani language, Vlax Romani (about 500,000 speakers), Balkan Romani (600,000), and Sinte Romani (300,000). Some Romani communities speak mixed languages based on the surrounding language with retained Romani-derived vocabulary – these are known by linguists as Para-Romani varieties, rather than dialects of the Romani language itself. The differences between the various varieties can be as large as, for example, the differences between the Slavic languages. Name Speakers of the Romani language usually refer to the language as ' "the Romani language" or '' (adverb)'' "in a Rom way". This derives from the Romani word ', meaning either "a member of the (Romani) group" or "husband". This is also the origin of the term "Roma" in English, although some Roma groups refer to themselves using other demonyms (e.g. 'Kaale', 'Sinti'). C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as ( "the eloquent Arabic") or simply ' (). Arabic is the List of languages by the number of countries in which they are recognized as an official language, third most widespread official language after English and French, one of six official languages of the United Nations, and the Sacred language, liturgical language of Islam. Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |