|
Families
Family (from ) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community. Historically, most human societies use family as the primary purpose of attachment, nurturance, and socialization. Anthropologists classify most family organizations as matrifocal (a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children), conjugal (a married couple with children, also called the nuclear family), avuncular (a man, his sister, and her children), or extended (in addition to parents, spouse and children, may include grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins). The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages through history. The family is also an important economic unit studied in family economics. The word "families" can be used metaphorically to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Family
A nuclear family (also known as an elementary family, atomic family, or conjugal family) is a term for a family group consisting of parents and their children (one or more), typically living in one home residence. It is in contrast to a single-parent family, a larger extended family, or a family with more than two parents. Nuclear families typically center on a Marriage, married couple that may have any number of children. There are differences in definition among observers. Some definitions allow only biological children who are full-blood siblings, some consider adopted or half- and step-siblings a part of the immediate family, but others allow for a step-parent and any mix of dependent children, including stepchildren and adopted children. Some sociologists and anthropologists consider the extended family structure to be the most common family structure in most cultures and at most times for humans, rather than the nuclear family. The term ''nuclear family'' was popularize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Family
An extended family is a family that extends beyond the nuclear family of parents and their children to include aunts, uncles, grandparents, cousins or other relatives, all living nearby or in the same household. Particular forms include the stem and joint families. Description In some circumstances, the extended family comes to live either with or in place of a member of the immediate family. These families include, in one household or close proximity, relatives in addition to an immediate family. An example would be an elderly parent who moves in with his or her children due to old age. In modern Western cultures dominated by immediate family constructs, the term has come to be used generically to refer to grandparents, uncles, aunts, and cousins, whether they live together within the same household or not. However, it may also refer to a family unit in which several generations live together within a single household. In some cultures, the term is used synonymously with consa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genealogy
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kinship and pedigrees of its members. The results are often displayed in charts or written as narratives. The field of family history is broader than genealogy, and covers not just lineage but also family and community history and biography. The record of genealogical work may be presented as a "genealogy", a "family history", or a " family tree". In the narrow sense, a "genealogy" or a " family tree" traces the descendants of one person, whereas a "family history" traces the ancestors of one person, but the terms are often used interchangeably. A family history may include additional biographical information, family traditions, and the like. The pursuit of family history and origins tends to be shaped by several motives, including the des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
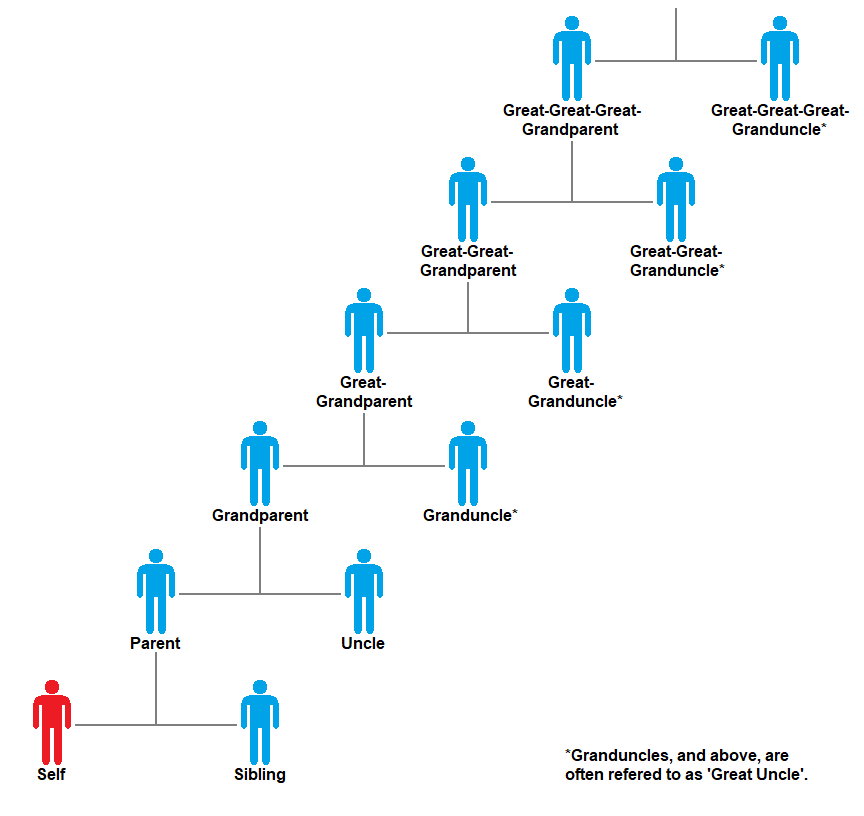
Grandparent
Grandparents, individually known as grandmother and grandfather, or Grandma and Grandpa, are the parents of a person's father or mother – paternal or maternal. Every sexually reproducing living organism who is not a genetic chimera has a maximum of four genetics, genetic grandparents, eight genetic great-grandparents, sixteen genetic great-great-grandparents, thirty-two genetic great-great-great-grandparents, sixty-four genetic great-great-great-great-grandparents, etc. In the history of modern humanity, around 30,000 years ago, the number of modern humans who lived to be a grandparent increased. It is not known for certain what spurred this increase in longevity, but it is generally believed that a key consequence of three generations being alive together was the preservation of information which could otherwise have been lost; an example of this important information might have been where to find water in times of drought. In cases where parents are unwilling or unable to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrifocal Family
A matrifocal family structure is one where mothers head families, and fathers play a less important role in the home and in bringing up children. Definition In 1956, the concept of the matrifocal family was introduced to the study of Caribbean societies by Raymond T. Smith. He linked the emergence of matrifocal families with how households are formed in the region: "The household group tends to be matri-focal in the sense that a woman in the status of 'mother' is usually the '' de facto'' leader of the group, and conversely the husband-father, although ''de jure'' head of the household group (if present), is usually marginal to the complex of internal relationships of the group. By 'marginal' we mean that he associates relatively infrequently with the other members of the group, and is on the fringe of the effective ties which bind the group together". Smith emphasises that a matrifocal family is not simply woman-centred, but rather mother-centred. Women in their role as mothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attachment Theory
Attachment theory is a psychological and evolutionary framework, concerning the relationships between humans, particularly the importance of early bonds between infants and their primary caregivers. Developed by psychiatrist and psychoanalyst John Bowlby (1907–90), the theory posits that infants need to form a close relationship with at least one primary caregiver to ensure their survival, and to develop healthy social and emotional functioning. Pivotal aspects of attachment theory include the observation that infants seek proximity to attachment figures, especially during stressful situations. Secure attachments are formed when caregivers are sensitive and responsive in social interactions, and consistently present, particularly between the ages of six months and two years. As children grow, they use these attachment figures as a secure base from which to explore the world and return to for comfort. The interactions with caregivers form patterns of attachment, which in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Economics
Family economics applies economic concepts such as production, division of labor, distribution of wealth, distribution, and decision making to the family. It is used to explain outcomes unique to family—such as marriage, the decision to have children, fertility, time devoted to domestic production, and dowry payments using economic analysis. The family, although recognized as fundamental from Adam Smith onward, received little systematic treatment in economics before the 1960s. Important exceptions are Thomas Robert Malthus#Population growth, Thomas Robert Malthus' model of population growthThomas Robert Malthus, 1798. ''An Essay on the Principle of Population''. s:An Essay on the Principle of Population, Full text on WikiSource. and Friedrich Engels'Friedrich Engels, 1981, The Origin of the Family, Private Property and State, International Publishers, pp 94-146 pioneering work on the structure of family, the latter being often mentioned in Marxian economics, Marxist and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking countries, the legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor (law), minor, in this case as a person younger than the local age of majority (there are exceptions such as, for example, the consume and purchase of alcoholic beverage even after said age of majority), regardless of their physical, mental and sexual development as biological adults. Children generally have fewer Children's rights, rights and responsibilities than adults. They are generally classed as unable to make serious decisions. ''Child'' may also describe a relationship with a parent (such as sons and daughters of any age) or, Metaphor, metaphorically, an authority figure, or signify group membership in a clan, tribe, or religion; it can also signify being str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parents
A parent is either the progenitor of a child or, in humans, it can refer to a caregiver or legal guardian, generally called an adoptive parent or step-parent. Parents who are progenitors are first-degree relatives and have 50% genetic meet. A female can also become a parent through surrogacy. Some parents may be adoptive parents, who nurture and raise an offspring, but are not related to the child. Orphans without adoptive parents can be raised by their grandparents or other family members. A parent can also be elaborated as an ancestor removed one generation. With recent medical advances, it is possible to have more than two biological parents. Examples of third biological parents include instances involving surrogacy or a third person who has provided DNA samples during an assisted reproductive procedure that has altered the recipients' genetic material. The most common types of parents are mothers, fathers, step-parents, and grandparents. A mother is "a woman in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncle
An uncle is usually defined as a male relative who is a sibling of a parent or married to a sibling of a parent, as well as the parent of the cousins. Uncles who are related by birth are second-degree relatives. The female counterpart of an uncle is an aunt, and the reciprocal relationship is that of a nephew or niece. The word comes from , the diminutive of ''avus'' (grandfather), and is a family relationship within an extended or immediate family. A popular colloquial term in English is Unc. In some cultures and families, children may refer to the cousins of their parents as uncle (or aunt). It is also used as a title of respect for older relatives, neighbours, acquaintances, family friends, and even total strangers in some cultures, for example Aboriginal Australian elders. Using the term in this way is a form of fictive kinship. Any social institution where a special relationship exists between a man and his sisters' children is known as an avunculate (or avunculism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aunt
An aunt is a woman who is a sibling of a parent or married to a sibling of a parent. Aunts who are related by birth are second-degree relatives. Alternate terms include auntie or aunty. Aunt, auntie, and aunty also may be titles bestowed by parents and children to close friends of one or both parents who assume a sustained caring or nurturing role for the children. Children in some cultures and families may refer to the cousins of their parents as aunt or uncle due to the age and generation gap. The word comes from via Old French ''ante'' and is a family">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''ante'' and is a family relationship within an extended or immediate family. The male counterpart of an aunt is an uncle, and the reciprocal relationship is that of a niece and nephew, nephew or niece. The gender-neutral term pibling, a shortened form of ''parent's sibling'', may refer to eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spouse
A spouse is a significant other in a marriage. A female spouse is called a wife while a male spouse is called a husband. Married The legal status of a spouse, and the specific rights and obligations associated with that status, vary significantly among the jurisdictions of the world. These regulations are usually described in family law statutes. However, in many parts of the world, where civil marriage is not that prevalent, there is instead customary marriage, which is usually regulated informally by the community. In many parts of the world, spousal rights and obligations are related to the payment of bride price, dowry or dower. Historically, many societies have given sets of rights and obligations to male marital partners that have been very different from the sets of rights and obligations given to female marital partners. In particular, the control of marital property, inheritance rights, and the right to dictate the activities of children of the marriage, have typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |