|
Falling Cat Problem
The falling cat problem is a problem that consists of explaining the underlying physics behind the observation of the cat righting reflex. Although amusing and trivial to pose, the solution of the problem is not as straightforward as its statement would suggest. The apparent contradiction with the law of conservation of angular momentum is resolved because the cat is not a rigid body, but instead is permitted to change its shape during the fall owing to the cat's flexible vertebral column, backbone and non-functional collar-bone. The behavior of the cat is thus typical of the mechanics of deformable bodies. Several explanations have been proposed for this phenomenon since the late 19th century: * Cats rely on conservation of angular momentum. * The rotation angle of the front body is larger than that of the rear body. * The dynamics of the falling cat have been explained using the Udwadia–Kalaba equation. History The falling cat problem has elicited interest from scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat Fall 150x300 6fps
The cat (''Felis catus''), also referred to as the domestic cat or house cat, is a small Domestication, domesticated carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species of the family Felidae. Advances in archaeology and genetics have shown that the domestication of the cat occurred in the Near East around 7500 BC. It is commonly kept as a pet and working cat, but also ranges freely as a feral cat avoiding human contact. It is valued by humans for companionship and its ability to kill vermin. Its retractable claws are adapted to killing small prey species such as mice and rats. It has a strong, flexible body, quick reflexes, and sharp teeth, and its night vision and sense of smell are well developed. It is a social species, but a solitary hunter and a crepuscular predator. Cat intelligence is evident in their ability to adapt, learn through observation, and solve problems. Research has shown they possess strong memories, exhibit neuroplasticity, and display cognitive skil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comptes Rendus De L'Académie Des Sciences
(, ''Proceedings of the Academy of Sciences''), or simply ''Comptes rendus'', is a French scientific journal published since 1835. It is the proceedings of the French Academy of Sciences. It is currently split into seven sections, published on behalf of the Academy until 2020 by Elsevier: ''Mathématique, Mécanique, Physique, Géoscience, Palévol, Chimie, ''and'' Biologies.'' As of 2020, the ''Comptes Rendus'' journals are published by the Academy with a diamond open access model. Naming history The journal has had several name changes and splits over the years. 1835–1965 ''Comptes rendus'' was initially established in 1835 as ''Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des séances de l'Académie des Sciences''. It began as an alternative publication pathway for more prompt publication than the ''Mémoires de l'Académie des Sciences,'' which had been published since 1666. The ''Mémoires,'' which continued to be published alongside the ''Comptes rendus'' throughout the ninetee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Journal Of Physiology
The ''American Journal of Physiology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal on physiology published by the American Physiological Society. Vols. for 1898–1941 and 1948-56 include the Society's proceedings, including abstracts of papers presented at the 10th-53rd annual meetings, and the 1948-56 fall meetings. Subjournals The ''American Journal of Physiology'' has seven subjournals; according to the 2019 Journal Citation Reports their impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ...s vary from 2.992 to 4.406: * ''AJP-Cell Physiology'' * ''AJP-Endocrinology and Metabolism'' * ''AJP-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology'' * ''AJP-Heart and Circulatory Physiology'' * ''AJP-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology'' * ''AJP-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Nature
''La Nature'' (English: ''Nature'') was a French language magazine aimed at the popularization of science established in 1873 by French scientist and adventurer Gaston Tissandier. The magazine also received an enormous amount of time, effort, and contributions from his brother, Albert Tissandier. Evolution The beginning From 1873 to 1914, each year's volume started at the beginning of December. The second six-month period began with the first issue in June. Starting in 1915, ''La Natures publishing year was brought in sync with the calendar year. A weekly magazine until the 1920s, it became first fortnightly and then monthly in 1948. Second World War During the Second World War, ''La Nature'' was published only erratically. The first interruption in publishing lasted from September 15 to December 15, 1939, with only an additional six issues published during all of 1940. 1941 saw 12 issues published, on the 15th of each month. There were other suspensions in publication, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Archive
The Internet Archive is an American 501(c)(3) organization, non-profit organization founded in 1996 by Brewster Kahle that runs a digital library website, archive.org. It provides free access to collections of digitized media including websites, Application software, software applications, music, audiovisual, and print materials. The Archive also advocates a Information wants to be free, free and open Internet. Its mission is committing to provide "universal access to all knowledge". The Internet Archive allows the public to upload and download digital material to its data cluster, but the bulk of its data is collected automatically by its web crawlers, which work to preserve as much of the public web as possible. Its web archiving, web archive, the Wayback Machine, contains hundreds of billions of web captures. The Archive also oversees numerous Internet Archive#Book collections, book digitization projects, collectively one of the world's largest book digitization efforts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Parking Problem
The parallel parking problem is a motion planning problem in control theory and mechanics to determine the path a car must take to parallel park into a parking space. The front wheels of a car are permitted to turn, but the rear wheels must stay aligned. When a car is initially adjacent to a parking space, to move into the space it would need to move in a direction perpendicular to the allowed path of motion of the rear wheels. The admissible motions of the car in its configuration space are an example of a nonholonomic system. See also * Automatic parking * Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics * Falling cat problem The falling cat problem is a problem that consists of explaining the underlying physics behind the observation of the cat righting reflex. Although amusing and trivial to pose, the solution of the problem is not as straightforward as its state ... * Moving sofa problem References * . * . Control theory {{applied-math-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
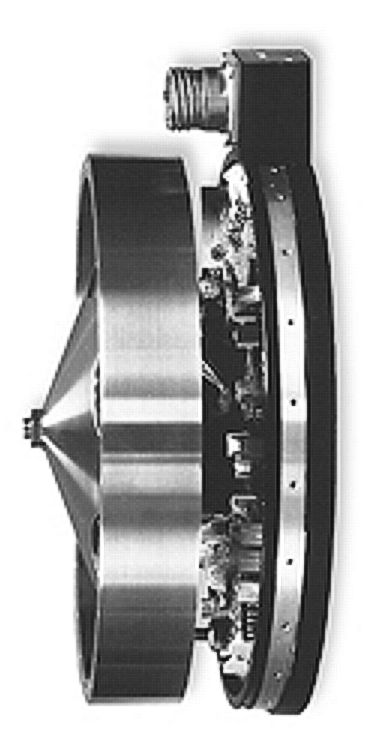
Momentum Wheel
A reaction wheel (RW) is an electric motor attached to a flywheel, which, when its rotation speed is changed, causes a counter-rotation proportionately through Angular momentum#Conservation of angular momentum, conservation of angular momentum. A reaction wheel can rotate only around its center of mass; it is not capable of moving from one place to another (translation (physics), translational force). Reaction wheels are used primarily by spacecraft for three-axis Spacecraft attitude control, attitude control, and do not require Rocket engine, rockets or external applicators of torque, which reduces the payload fraction, mass fraction needed for fuel. They provide a high pointing accuracy, and are particularly useful when the spacecraft must be rotated by very small amounts, such as keeping a telescope pointed at a star. A reaction wheel is sometimes operated at a constant (or near-constant) rotation speed, to provide a satellite with a large amount of stored angular momentum. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buttered Cat Paradox
The buttered cat paradox is a common joke based on the combination of two adages: * Cats always land on their feet. * Buttered toast always lands buttered side down. The paradox arises when one considers what would happen if one attached a piece of buttered toast (butter side up) to the back of a cat, then dropped the cat from a large height. The buttered cat paradox, submitted by artist John Frazee of Kingston, New York, won a 1993 '' Omni'' magazine competition about paradoxes. The basic premise, stating the conditions of the cat and bread and posed as a question, was presented in a routine by comic and juggler Michael Davis, appearing on '' The Tonight Show with Johnny Carson'', July 22, 1988. Thought experiments The buttered cat paradox has been highlighted as a paradigmatic example of a thought experiment. Some people jokingly maintain that the experiment produces an anti-gravity effect. They propose that as the cat falls toward the ground, it slows down and starts to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge Field
In physics, a gauge theory is a type of field theory in which the Lagrangian, and hence the dynamics of the system itself, does not change under local transformations according to certain smooth families of operations (Lie groups). Formally, the Lagrangian is invariant under these transformations. The term "gauge" refers to any specific mathematical formalism to regulate redundant degrees of freedom in the Lagrangian of a physical system. The transformations between possible gauges, called gauge transformations, form a Lie group—referred to as the ''symmetry group'' or the gauge group of the theory. Associated with any Lie group is the Lie algebra of group generators. For each group generator there necessarily arises a corresponding field (usually a vector field) called the gauge field. Gauge fields are included in the Lagrangian to ensure its invariance under the local group transformations (called gauge invariance). When such a theory is quantized, the quanta of the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Planning
Motion planning, also path planning (also known as the navigation problem or the piano mover's problem) is a computational problem to find a sequence of valid configurations that moves the object from the source to destination. The term is used in computational geometry, computer animation, robotics and computer games. For example, consider navigating a mobile robot inside a building to a distant waypoint. It should execute this task while avoiding walls and not falling down stairs. A motion planning algorithm would take a description of these tasks as input, and produce the speed and turning commands sent to the robot's wheels. Motion planning algorithms might address robots with a larger number of joints (e.g., industrial manipulators), more complex tasks (e.g. manipulation of objects), different constraints (e.g., a car that can only drive forward), and uncertainty (e.g. imperfect models of the environment or robot). Motion planning has several robotics applications, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Theory
Control theory is a field of control engineering and applied mathematics that deals with the control system, control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive the system to a desired state, while minimizing any ''delay'', ''overshoot'', or ''steady-state error'' and ensuring a level of control Stability theory, stability; often with the aim to achieve a degree of Optimal control, optimality. To do this, a controller with the requisite corrective behavior is required. This controller monitors the controlled process variable (PV), and compares it with the reference or Setpoint (control system), set point (SP). The difference between actual and desired value of the process variable, called the ''error'' signal, or SP-PV error, is applied as feedback to generate a control action to bring the controlled process variable to the same value as the set point. Other aspects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |