|
Fall Time
In electronics, fall time (pulse decay time) t_f is the time taken for the amplitude of a pulse to decrease (fall) from a specified value (usually 90% of the peak value exclusive of overshoot or undershoot) to another specified value (usually 10% of the maximum value exclusive of overshoot or undershoot). Limits on undershoot and oscillation (also known as ringing and hunting) are sometimes additionally stated when specifying fall time limits. See also *Rise time *Transition time Transition or transitional may refer to: Mathematics, science, and technology Biology * Transition (genetics), a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine (A ↔ G) or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine (C ↔ ... References *{{FS1037C MS188 Transient response characteristics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield of physics and electrical engineering which uses Passivity (engineering), active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog signal, analog signals to digital signal, digital signals. Electronic devices have significantly influenced the development of many aspects of modern society, such as telecommunications, entertainment, education, health care, industry, and security. The main driving force behind the advancement of electronics is the semiconductor industry, which continually produces ever-more sophisticated electronic devices and circuits in respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to compare the duration of events (or the intervals between them), and to quantify rates of change of quantities in material reality or in the qualia, conscious experience. Time is often referred to as a fourth dimension, along with Three-dimensional space, three spatial dimensions. Time is one of the seven fundamental physical quantities in both the International System of Units (SI) and International System of Quantities. The SI base unit of time is the second, which is defined by measuring the electronic transition frequency of caesium atoms. General relativity is the primary framework for understanding how spacetime works. Through advances in both theoretical and experimental investigations of spacetime, it has been shown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse (signal Processing)
A pulse in signal processing is a rapid, transient change in the amplitude of a signal from a baseline value to a higher or lower value, followed by a rapid return to the baseline value. Pulse shapes Pulse shapes can arise out of a process called pulse shaping. Optimum pulse shape depends on the application. Rectangular pulse These can be found in pulse waves, square waves, boxcar functions, and rectangular functions. In digital signals the up and down transitions between high and low levels are called the rising edge and the falling edge. In digital systems the detection of these sides or action taken in response is termed edge-triggered, rising or falling depending on which side of rectangular pulse. A digital timing diagram is an example of a well-ordered collection of rectangular pulses. Nyquist pulse A Nyquist pulse is one which meets the Nyquist ISI criterion In communications, the Nyquist ISI criterion describes the conditions which, when satisfied by a comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
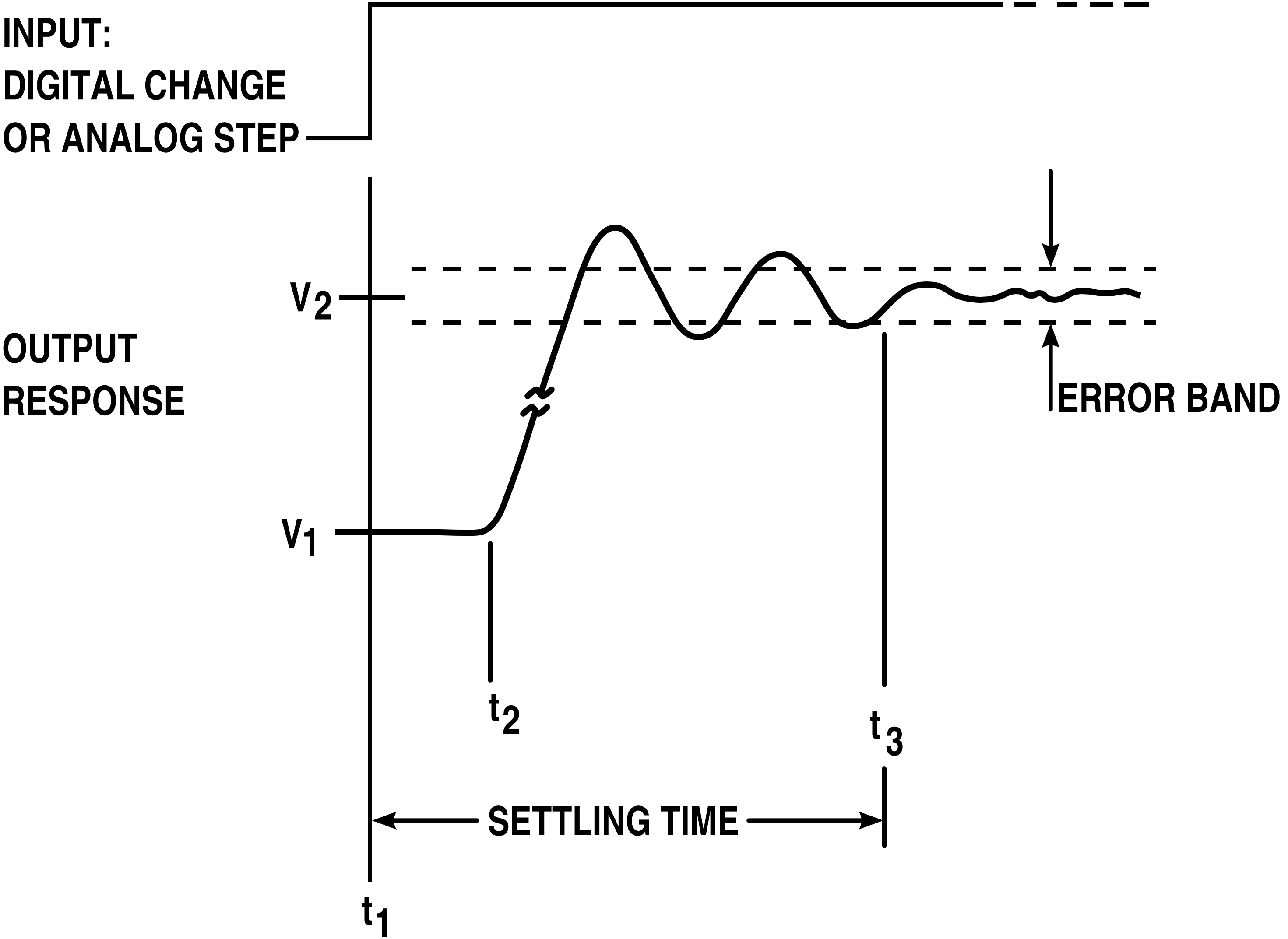
Overshoot (signal)
In signal processing, control theory, electronics, and mathematics, overshoot is the occurrence of a signal or function exceeding its target. Undershoot is the same phenomenon in the opposite direction. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filters. It is often followed by ringing (signal), ringing, and at times conflated with the latter. Definition Maximum overshoot is defined in Katsuhiko Ogata's ''Discrete-time control systems'' as "the maximum peak value of the response curve measured from the desired response of the system." Control theory In control theory, overshoot refers to an output exceeding its final, steady-state value. For a step response, step input, the ''percentage overshoot'' (PO) is the maximum value minus the step value divided by the step value. In the case of the unit step, the ''overshoot'' is just the maximum value of the step response minus one. Also see the definition of ''overshoot'' in an #Electronics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ringing (signal)
In electronics, signal processing, and video, ringing is oscillation of a signal, particularly in the step response (the response to a sudden change in input). Often ringing is undesirable, but not always, as in the case of resonant inductive coupling. It is also known as hunting. It is also known as ripple, particularly in electricity or in frequency domain response. Electrical circuits In electrical circuits, ringing is an oscillation of a voltage or current. Ringing can be undesirable because it causes extra current to flow, thereby wasting energy and causing extra heating of the components; it can cause unwanted electromagnetic radiation to be emitted; it can increase settling time for the desired final state; and it may cause unwanted triggering of bistable elements in digital circuits. Ringy communications circuits may suffer falsing. Two electrical sources of this ringing are: # A resonant transient response due to undesired parasitic capacitances and inductanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
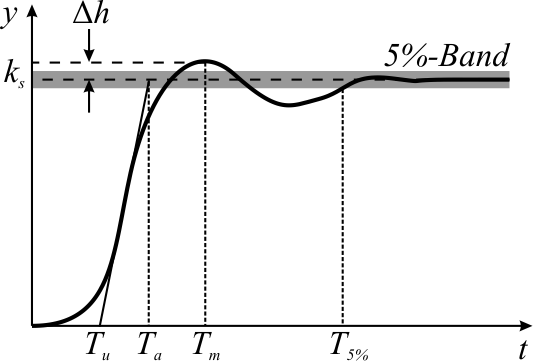
Rise Time
In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time is the time taken by a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value. These values may be expressed as ratiosSee for example , and . or, equivalently, as percentages with respect to a given reference value. In analog electronics and digital electronics, these percentages are commonly the 10% and 90% (or equivalently and ) of the output step height: however, other values are commonly used. For applications in control theory, according to , rise time is defined as "''the time required for the response to rise from to of its final value''", with 0% to 100% rise time common for underdamped second order systems, 5% to 95% for critically damped and 10% to 90% for overdamped ones.Precisely, states: "''The rise time is the time required for the response to rise from x% to y% of its final value. For overdamped second order systems, the 0% to 100% rise time is normally used, and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Time
Transition or transitional may refer to: Mathematics, science, and technology Biology * Transition (genetics), a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine (A ↔ G) or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine (C ↔ T) * Transitional fossil, any fossilized remains of a lifeform that exhibits the characteristics of two distinct taxonomic groups * A phase during childbirth contractions during which the cervix completes its dilation Gender and sex * Gender transition, the process of changing one's gender presentation to accord with one's internal sense of one's gender – the idea of what it means to be a man or woman ** Gender-affirming care, the physical aspect of a gender transition ** Gender-affirming surgery, surgical intervention a part of medical gender affirmation Physics * Phase transition, a transformation of the state of matter; for example, the change between a solid and a liquid, between liquid and gas or between gas and plasma * Quantum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |