|
Fakanau
A fakanau (meaning "spells") is a traditional Tuvaluan male dance, accompanied by singing and rhythmic clapping. ''Fakanau'' singing and dancing are typical of Niutao and Nukufetau islands of Tuvalu, formerly known as the Ellice Islands, a group of nine low-lying coral islands in the central Pacific that are inhabited by Polynesian people. ''Fakanau'' is described as having "a tune that is between speech and singing hichwas performed while dancers are standing on their feet." Examples include ''Te onge ne tupu ia Kiollli'', ''Neutuakina te vao i napanapa'', and ''Ko na fakanau nei e kamata ifo mai gauta oi fakaholo atu ai ki gatai kafai te vaka e hoho ifo ki gatai.'' Other dances within the genre include the ''mako'', the ''fakaseasea'', the ''fatele'', the ''lue'', the ''sea'', and the ''oga''. Form Male dancers performed around a circle, in a sitting position with arms, hands and upper body gestures, and all of them singing. An old dance master, at the center of the circle, kept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuvaluan Music
The traditional music of Tuvalu consists of dances, including ''fatele'', ''fakanau'' and ''fakaseasea''. The influence of the Samoan missionaries sent to Tuvalu by the London Missionary Society from the 1860s resulted in the suppression of songs about the traditional religions or magic and many songs were lost. As the influence of the missionaries diminished in the 20th century the traditional dances were revived and the siva dance tradition from Samoa also became popular. The ''fatele'', in its modern form, is performed at community events and to celebrate leaders and other prominent individuals. ''Te titi tao'' is a traditional skirt placed upon another skirt - a ''titi kaulama'' - and tops (''teuga saka''), headbands, armbands, and wristbands continue to be used in performances of the ''fatele''. Te Vaka, an Oceanic music group, contains Tuvaluans and musicians with Tuvaluan ancestry; Te Vaka performs original contemporary Pacific music or "South Pacific Fusion". History Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Tuvalu
The traditional music of Tuvalu consists of dances, including '' fatele'', '' fakanau'' and '' fakaseasea''. The influence of the Samoan missionaries sent to Tuvalu by the London Missionary Society from the 1860s resulted in the suppression of songs about the traditional religions or magic and many songs were lost. As the influence of the missionaries diminished in the 20th century the traditional dances were revived and the siva dance tradition from Samoa also became popular. The ''fatele'', in its modern form, is performed at community events and to celebrate leaders and other prominent individuals. ''Te titi tao'' is a traditional skirt placed upon another skirt - a ''titi kaulama'' - and tops (''teuga saka''), headbands, armbands, and wristbands continue to be used in performances of the ''fatele''. Te Vaka, an Oceanic music group, contains Tuvaluans and musicians with Tuvaluan ancestry; Te Vaka performs original contemporary Pacific music or "South Pacific Fusion". History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fakaseasea
The fakaseasea is a tradition dance song of Tuvalu. Dancing songs are the most common type of the traditional Tuvaluan songs, with other tradition dance styles including ''fakanau'' and ''fatele''. Tuvaluan dance music Dancing songs are the most common type of traditional Tuvaluan songs. Older style dancing songs were known to be performed while sitting, kneeling or standing. The two primary traditional dances of Tuvalu are the ''fakanau'' (for men) and ''oga'' (for women) and the ''fakaseasea''. The modern ''fatele'' involves the women on their feet, dancing in lines; with the men facing the dancers, sitting on the floor beating the time with their hands on the mats or on wooden boxes, such as tea chests. Performance of the fakaseasea The ''fakaseasea'' was mainly performed by women, who were on their feet, dancing and moving their arms, hand and upper body; while men and women would sing and beat the time. It is a slower song with very loose rules on how to dance to it, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerd Koch
Gerd Koch (11 July 1922 – 19 April 2005) was a German cultural anthropologist best known for his studies on the material culture of Kiribati, Tuvalu and the Santa Cruz Islands in the Pacific. He was associated with the Ethnological Museum of Berlin (german: link=no, Ethnologisches Museum; until 1999 ''Museum für Völkerkunde''). His field work was directed to researching and recording the use of artefacts in their indigenous context, to begin to understand these societies. His work in cultural and social anthropology extended to researching and recording the music and dance of the Pacific Islands. He collaborated with Dieter Christensen, a music-ethnologist, on ''The Music of the Ellice Islands'' (German: ''Die Musik der Ellice-Inseln'') (1964) and Koch also published the ''Songs of Tuvalu'' (translated by Guy Slatter) (2000). In Tuvalu he was also known as 'Keti'. Biography As a child Gerd Koch was fascinated by accounts of explorers including the Pacific voyages of J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatele
The fatele is a traditional dance song of Tuvalu. Dancing songs are the most common type of traditional Tuvaluan song, with other tradition dance styles including ''fakanau'' and ''fakaseasea''. The ''fatele'', in its modern form, is performed at community events and to celebrate leaders and other prominent individuals, such as the visit of the Duke and Duchess of Cambridge in September 2012. ''Te titi tao'' is a traditional skirt placed upon another skirt - a ''titi kaulama'' - and tops (''teuga saka''), headbands, armbands, and wristbands continue to be used in performances of the ''fatele''. The modern Tuvaluan style has absorbed many influences and can be described "as a musical microcosm of Polynesia, where contemporary and older styles co-exist". The traditional fatele The traditional ''fatele'' was performed in the sitting or kneeling position by five or six young unmarried women, who while singing, moved their arms, hand and upper body; the men and women act as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuvalu
Tuvalu ( or ; formerly known as the Ellice Islands) is an island country and microstate in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. Its islands are situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. They lie east-northeast of the Santa Cruz Islands (which belong to the Solomon Islands), northeast of Vanuatu, southeast of Nauru, south of Kiribati, west of Tokelau, northwest of Samoa and Wallis and Futuna, and north of Fiji. Tuvalu is composed of three reef islands and six atolls. They are spread out between the latitude of 5° and 10° south and between the longitude of 176° and 180°. They lie west of the International Date Line. Tuvalu has a population of 10,507 (2017 census). The total land area of the islands of Tuvalu is . The first inhabitants of Tuvalu were Polynesians, according to well-established theories regarding a migration of Polynesians into the Pacific that began about three thousand years ago. Long before European contact with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
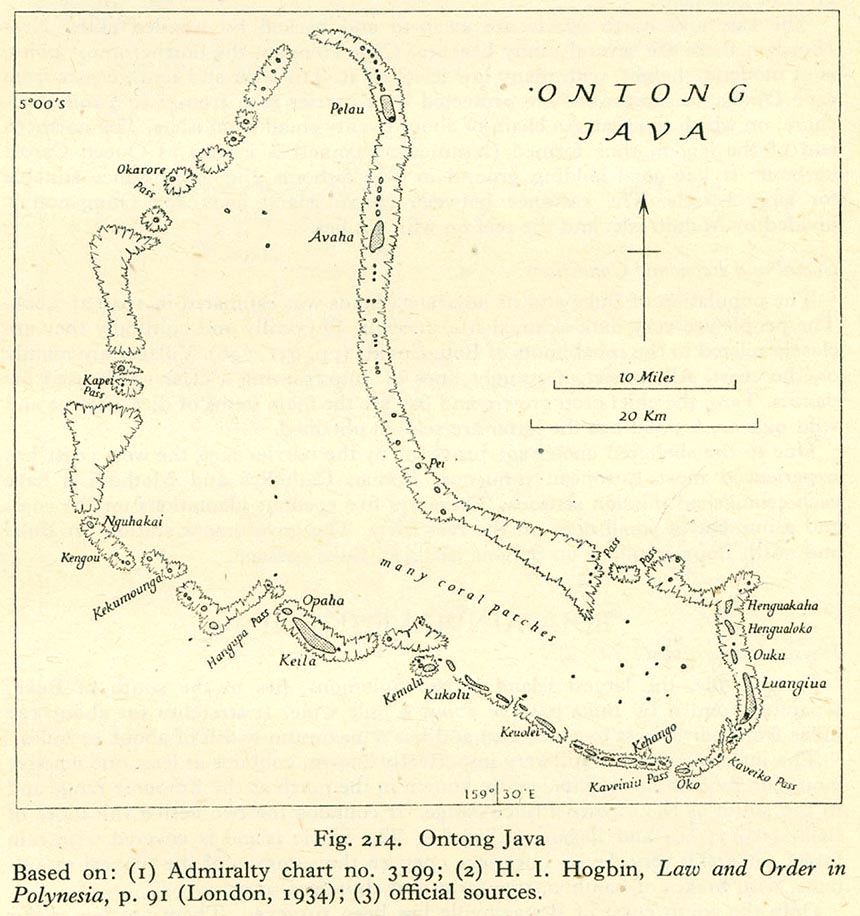
Ontong Java Atoll
Ontong Java Atoll or Luangiua, (formerly ''Lord Howe Atoll'', not to be confused with Lord Howe Island) is one of the largest atolls on earth. Geographically it belongs to a scattered group of three atolls which includes nearby Nukumanu Atoll and the wholly submerged Roncador Reef located to the south. Description Administratively Ontong Java belongs to Solomon Islands Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its ca .... As an outlying part of Malaita Province, it forms the northernmost tract of land of this state, over north of Santa Isabel Island. The closest land, however, is Nukumanu Atoll, which lies only due north of Ontong Java's northern tip and, though historically closely related to Ontong Java, is now under the administration of Papua New Guinea. Ontong Java is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropologist
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and values of societies. Linguistic anthropology studies how language affects social life, while economic anthropology studies human economic behavior. Biological (physical), forensic and medical anthropology study the biological development of humans, the application of biological anthropology in a legal setting and the study of diseases and their impacts on humans over time, respectively. Education Anthropologists usually cover a breadth of topics within anthropology in their undergraduate education and then proceed to specialize in topics of their own choice at the graduate level. In some universities, a qualifying exam serves to test both the breadth and depth of a student's understanding of anthropology; the students who pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niutao
Niutao is a reef island in the northern part of Tuvalu. It is one of the nine districts (islands) of Tuvalu. It is also one of the three districts that consist of only one island - not counting the three islets inside the closed lagoon. Niutao has a population of 582 (2017 census). Geography There are two lakes (ponds or lagoons), which are brackish to saline. The larger has three islands and a dam. There are three wells from which fresher water sits in a "lens" above the salt water that leaches in through the coral. Older maps show the only village as Tuapa (with the neighbourhood of Angafoulua). The main village is Kulia; another village is Teava. There is a maneapa (community hall), Uepele Primary School, a church named ''Tineifale'' of the Church of Tuvalu, a post office, and three wells. A gravel road rings the island to connect the graveyard, half mile (800 m) counter clockwise from the village, and clockwise a quarter of a mile (400 m) to the hospital. The island is somew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono and Apolima); and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands (Nu'utele, Nu'ulua, Fanuatapu and Namua). Samoa is located west of American Samoa, northeast of Tonga (closest foreign country), northeast of Fiji, east of Wallis and Futuna, southeast of Tuvalu, south of Tokelau, southwest of Hawaii, and northwest of Niue. The capital city is Apia. The Lapita culture, Lapita people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language and Samoan culture, Samoan cultural identity. Samoa is a Unitary state, unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy with 11 Administrative divisions of Samoa, administrative divisions. It is a sovereign state and a member of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists of an archipelago of more than 330 islands—of which about 110 are permanently inhabited—and more than 500 islets, amounting to a total land area of about . The most outlying island group is Ono-i-Lau. About 87% of the total population of live on the two major islands, Viti Levu and Vanua Levu. About three-quarters of Fijians live on Viti Levu's coasts: either in the capital city of Suva; or in smaller urban centres such as Nadi—where tourism is the major local industry; or in Lautoka, where the sugar-cane industry is dominant. The interior of Viti Levu is sparsely inhabited because of its terrain. The majority of Fiji's islands were formed by volcanic activity starting around 150 million years ago. Some geothermal activity st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |