|
Fairview Point
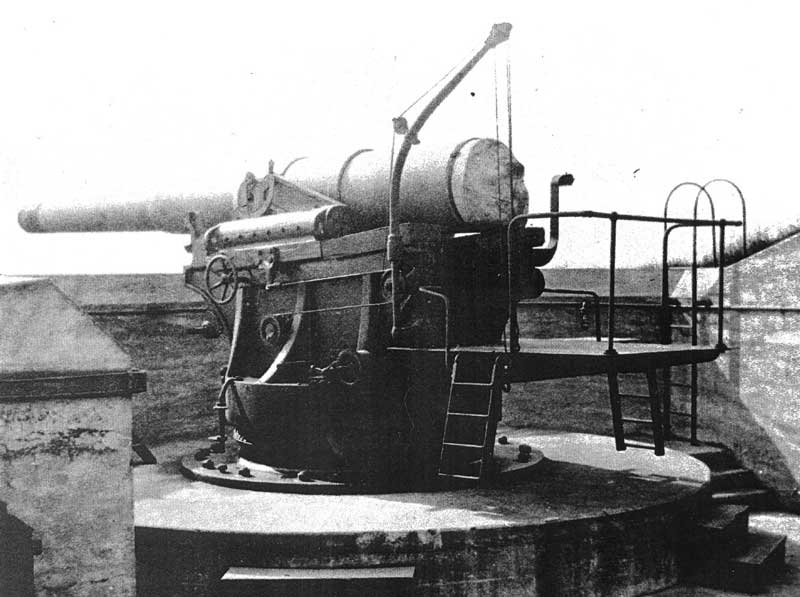
Fairview Point is a point or headland on the west side of Kaien Island on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada. History During World War II, Fairview Point played an important role in the defence of the Port of Prince Rupert and its associated CNR railhead. "A late and important addition to Prince Rupert's coast defences was the joint Canadian-US enterprise at Fairview Point, a mile south of the city limits. The establishment of an American Sub-Port of Embarkation with extensive docking facilities at Price Rupert, and a large staging camp at Port Edward, on the mainland ten miles by road and rail from the city, intensified Washington's concern about the security of the area, particularly having in mind the limited range of the "interim" counter-bombardment 6-inch battery at Fort Barrett. Early in 1942 the United States made available, to supplement the Barrett battery, two more 8-inch railway guns, similar to those already installed at Christopher Point. On arrival at Prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaien Island
Kaien Island is a Canadian island on the coast of British Columbia, just north of the mouth of the Skeena River and to the south of the Alaska Panhandle. The island has an area of about , is roughly oval, and about long along its long axis. The island consists of a central mountain ridge, surrounded by coastal lowlands, the dominant central peak is Mount Hays reaching , with a secondary peak, Mount Olfield reaching to the northeast. Located within the Hecate Depression of the Coastal Trough, Kaien Island is a subdivision of the Coast Mountains geomorphic region. The island's bedrock consists of metasedimentary amphibolite, which dips towards the east at about 35 degrees. The island is contained within the Skeena-Queen Charlotte Regional District and are part of the North Coast region. Tidal waters surrounding the island have a wide range which results in extensive exposure of mud flats and rock shoals that are prime habitat for invertebrates and intertidal fish. Kaien I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia Coast
, settlement_type = Region of British Columbia , image_skyline = , nickname = "The Coast" , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Canada , subdivision_type1 = Province , subdivision_name1 = British Columbia , parts_type = Principal cities , p1 = Vancouver , p2 = Surrey , p3 = Burnaby , p4 = Richmond , p5 = Abbotsford , p6 = Coquitlam , p7 = Delta , p8 = Nanaimo , p9 = Victoria , p10 = Chilliwack , p11 = Maple Ridge , p12 = New Westminster , p13 = Port Coquitlam , p14 = North Vancouver , area_blank1_title = 15 Districts , area_blank1_km2 = 244,778 , area_footnotes = , elevation_max_m = 4019 , elevation_min_m = 0 , elevation_max_footnotes = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Of Prince Rupert
The Port of Prince Rupert is a seaport managed by the Prince Rupert Port Authority that occupies of land and water along of waterfront. The port is located in Prince Rupert Harbour in the North Coast Regional District of British Columbia. The Port of Prince Rupert is the third busiest seaport in Canada by container volume and cargo tonnage after the Vancouver Fraser Port Authority, Port of Vancouver and Port of Montreal. History Early 20th century The Port of Prince Rupert was built upon the completion of the Grand Trunk Pacific Railway in 1914 and its development had been promoted by Grand Trunk Railway president Charles Melville Hays as an alternative to the Port of Vancouver, which was serviced by the Canadian Pacific Railway, Canadian Pacific and Canadian Northern Railway, Canadian Northern railways. In 1919, the Grand Trunk Pacific fell into bankruptcy and was Nationalization, nationalized by the federal government and merged into the Canadian National Railways (CNR). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian National Railway
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I railroad, Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern United States, Midwestern and Southern United States. CN is Canada's largest railway, in terms of both revenue and the physical size of its rail network, spanning Canada from the Atlantic coast in Nova Scotia to the Pacific coast in British Columbia across approximately of track. In the late 20th century, CN gained extensive capacity in the United States by taking over such railroads as the Illinois Central. CN is a public company with 22,600 employees, and it has a market cap of approximately CA$90 billion. CN was government-owned, having been a Crown corporations of Canada, Canadian Crown corporation from its founding in 1919 until being privatized in 1995. , Bill Gates is the largest single shareholder of CN stock, owning a 14.2% interest throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8-inch M1888
The 8-inch gun M1888 (203 mm) was a U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps gun, initially deployed 1898–1908 in about 75 fixed emplacements, usually on a disappearing carriage. During World War I, 37 or 47 of these weapons (references vary) were removed from fixed emplacements or from storage to create a railway gun version, the 8-inch Gun M1888MIA1 Barbette carriage M1918 on railway car M1918MI, converted from the fixed coast defense mountings and used during World War I and World War II. History The M1888 gun was a coastal artillery gun initially deployed as part of the Endicott system of fortifications. The first nine were deployed on the M1892 barbette carriage in 1898, but the improved M1894 and M1896 disappearing carriages soon became available, and approximately 64 additional weapons were deployed on these carriages by 1908. An "emergency" converted Rodman carriage was also used during the Spanish–American War in 1898 to quickly arm 21 emplacements with the mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plotting Board
A plotting board was a mechanical device used by the U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps as part of their fire control system to track the observed course of a target (typically a moving ship), project its future position, and derive the uncorrected data on azimuth (or direction) and range needed to direct the fire of the guns of a battery to hit that target. Plotting boards of this sort were first employed by the Coast Artillery around 1905, and were the primary means of calculating firing data until WW2. Towards the end of WW2 these boards were largely replaced by radar and electro-mechanical gun data computers, and were relegated to a back-up role. Although several different types of plotting boards were used by the Coast Artillery over the years, the example described here is the Whistler- Hearn Plotting Board, Model of 1904 which was widely employed by the Coast Artillery between about 1905 and 1925. This description is primarily derived from two manuals of the period, each of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of World War II-era Fortifications On The British Columbia Coast
This is a list of World War II-era fortifications on the British Columbia Coast. North Coast * Barrett Point *Frederick Point, Digby Island, twin QF 12 pounder naval guns * Casey Point, 2x25 pounders * Fairview Point, 2x 8" railway guns * Dundas Point * Seal Cove *Watson Island, ammunition depot, hospital, ocean dock (stores warehouse), and command post Central Coast * Bella Bella - Two 75mm guns and an anti-aircraft to protect the seaplane base * Yorke Island coastal defence fort South Coast *Fort Rodd Hill, originally built in the 19th century to defend Victoria and CFB Esquimalt * Albert Head, 9.2 inch guns, counter bombardment battery during WWII * Mary Hill *Christopher Point Battery - 1941-44 -2 x 8 inch M1888 american railway guns * Duntze Head *Ogden Point Battery - 1939-1943 with better guns replaced Breakwater Battery in 1944 *Black Rock battery - 1893-1956 * Macaulay Point, 3 gun battery dating back to 1878 *Golf Hill (WW II 1940-44 position), 2 x 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headlands Of British Columbia
A headland, also known as a head, is a coastal landform, a point of land usually high and often with a sheer drop, that extends into a body of water. It is a type of promontory. A headland of considerable size often is called a cape.Whittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 80, 246. . Headlands are characterised by high, breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion, and steep sea cliff. Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is flanked by land on three sides, whereas a headland is flanked by water on three sides. Headlands and bays form on discordant coastlines, where bands of rock of alternating resistance run perpendicular to the coast. Bays form when weak (less resistant) rocks (such as sands and clays) are eroded, leaving bands of stronger (more resistant) rocks (such as chalk, limestone, and granite) forming a headland, or peninsula. Through the deposition of sediment within the bay and the erosion of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Coast Of British Columbia
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Greek '' boreas'' "north wind, north", which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of ''Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word ''Arctic''. Other languages have other derivations. For example, in Lezgian, ''kefer'' can mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |