|
Facial Artery
The facial artery, formerly called the external maxillary artery, is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies blood to superficial structures of the medial regions of the face. Structure The facial artery arises in the carotid triangle from the external carotid artery, a little above the lingual artery, and sheltered by the ramus of the mandible. It passes obliquely up beneath the digastric and stylohyoid muscles, over which it arches to enter a groove on the posterior surface of the submandibular gland. It then curves upward over the body of the mandible at the antero-inferior angle of the masseter ( the antegonial notch); passes forward and upward across the cheek to the angle of the mouth, then ascends along the side of the nose, and ends at the medial commissure of the eye, under the name of the angular artery. The facial artery is remarkably tortuous. This is to accommodate itself to neck movements such as those of the pharynx in swallowing; and facia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Carotid Artery
The external carotid artery is the major artery of the head and upper neck. It arises from the common carotid artery. It terminates by splitting into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland. Structure Origin The external carotid artery arises from the common carotid artery just inferior to the upper border of the thyroid cartilage. At its origin, this artery is closer to the skin and more medial than the internal carotid, and is situated within the carotid triangle. Course and fate It curves to pass anterosuperiorly before inclining posterior-ward to reach the space posterior the neck of the mandible, where it divides into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland. It rapidly diminishes in size as it travels up the neck, owing to the number and large size of its branches. Relations At the origin, external carotid artery is more medial than internal carotid artery. When external carotid artery ascends the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submandibular Gland
The paired submandibular glands (historically known as submaxillary glands) are major salivary glands located beneath the floor of the mouth. In adult humans, they each weigh about 15 grams and contribute some 60–67% of unstimulated saliva secretion; on stimulation their contribution decreases in proportion as parotid gland secretion rises to 50%. The average length of the normal adult human submandibular salivary gland is approximately 27 mm, while the average width is approximately 14.3 mm. Structure Each submandibular gland is divided into a superficial lobe and a deep lobe, the two being separated by the mylohyoid muscle: * The superficial lobe comprises most of the gland, with the mylohyoid muscle runs under it * The deep lobe is the smaller part Submandibular duct Secretions are delivered into the submandibular duct on the deep portion after which they hook around the posterior edge of the mylohyoid muscle and proceed on the superior surface laterally. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomaticus Major
The zygomaticus major muscle is a muscle of the face. It arises from either zygomatic arch (cheekbone); it inserts at the corner of the mouth. It is innervated by branches of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII). It is a muscle of facial expression, which draws the angle of the mouth superiorly and posteriorly to allow one to smile. Bifid zygomaticus major muscle is a notable variant, and may cause cheek dimples. Structure Origin The zygomaticus major muscle originates from the superior margin of the lateral surface of the temporal process of zygomatic bone, just anterior to the zygomaticotemporal suture. Insertion It inserts at the corner of the mouth by blending with the levator anguli oris muscle, the orbicularis oris muscle, and the deeper muscular structures. Nerve supply The muscle receives motor innervation from the buccal branch and zygomatic branch of the facial nerve (CN VII). Vasculature The muscle receives arterial supply from the superior labial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risorius
The risorius muscle is a highly variable muscle of facial expression. It has numerous and very variable origins, and inserts into the angle of the mouth. It receives motor innervation from branches of facial nerve (CN VII). It may be absent or asymmetrical in some people. It pulls the angle of the mouth sidewise, such as during smiling. Structure The risorius muscle is highly variable. Attachments Its peripheral attachments may include (some or all of): the parotid fascia, masseteric fascia, the fascia enveloping the pars modiolaris of the platysma muscle, fascia overlying the mastoid part of temporal bone, and/or the zygomatic arch. Its apical and subapical (i.e. convergent) attachment is at the modiolus. Innervation The risorius receives motor innervation from the buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN VII). Vasculature The risorius receives arterial supply mostly from the superior labial artery. Variation The risorius muscle is highly variable. It ranges in for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Pharyngeal Constrictor
The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a quadrilateral muscle of the pharynx. It is the uppermost and thinnest of the three pharyngeal constrictors. The muscle is divided into four parts according to its four distincts origins: a pterygopharyngeal, buccopharyngeal, mylopharyngeal, and a glossopharyngeal part. The muscle inserts onto the pharyngeal raphe, and pharyngeal spine. It is innervated by pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve via the pharyngeal plexus. It acts to convey a bolus down towards the esophagus, facilitating swallowing. Anatomy The superior constrictor muscle is a quadrilateral, sheet-like muscle. It is thinner than the middle and inferior constrictor muscles. Origin The sites of origin of the muscles collectively are the pterygoid hamulus (and occasionally the adjoining posterior margin of the medial pterygoid plate) anteriorly, (the posterior margin of) the pterygomandibular raphe, the posterior extremity of the mylohyoid line of mandible, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Pharyngeal Constrictor
The middle pharyngeal constrictor is a fan-shaped muscle located in the neck. It is one of three pharyngeal constrictor muscles. It is smaller than the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. The middle pharyngeal constrictor originates from the greater cornu and lesser cornu of the hyoid bone, and the stylohyoid ligament. It inserts onto the pharyngeal raphe. It is innervated by a branch of the vagus nerve through the pharyngeal plexus. It acts to propel a bolus downwards along the pharynx towards the esophagus, facilitating swallowing. Structure The middle pharyngeal constrictor is a sheet-like, fan-shaped muscle. The muscle's fibers diverge from their origin: the more inferior fibres descend deep to the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle; the middle portion of fibres pass transversely; the more superior fibers ascend and overlap the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle. Origin Two parts of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle are distinguished according t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
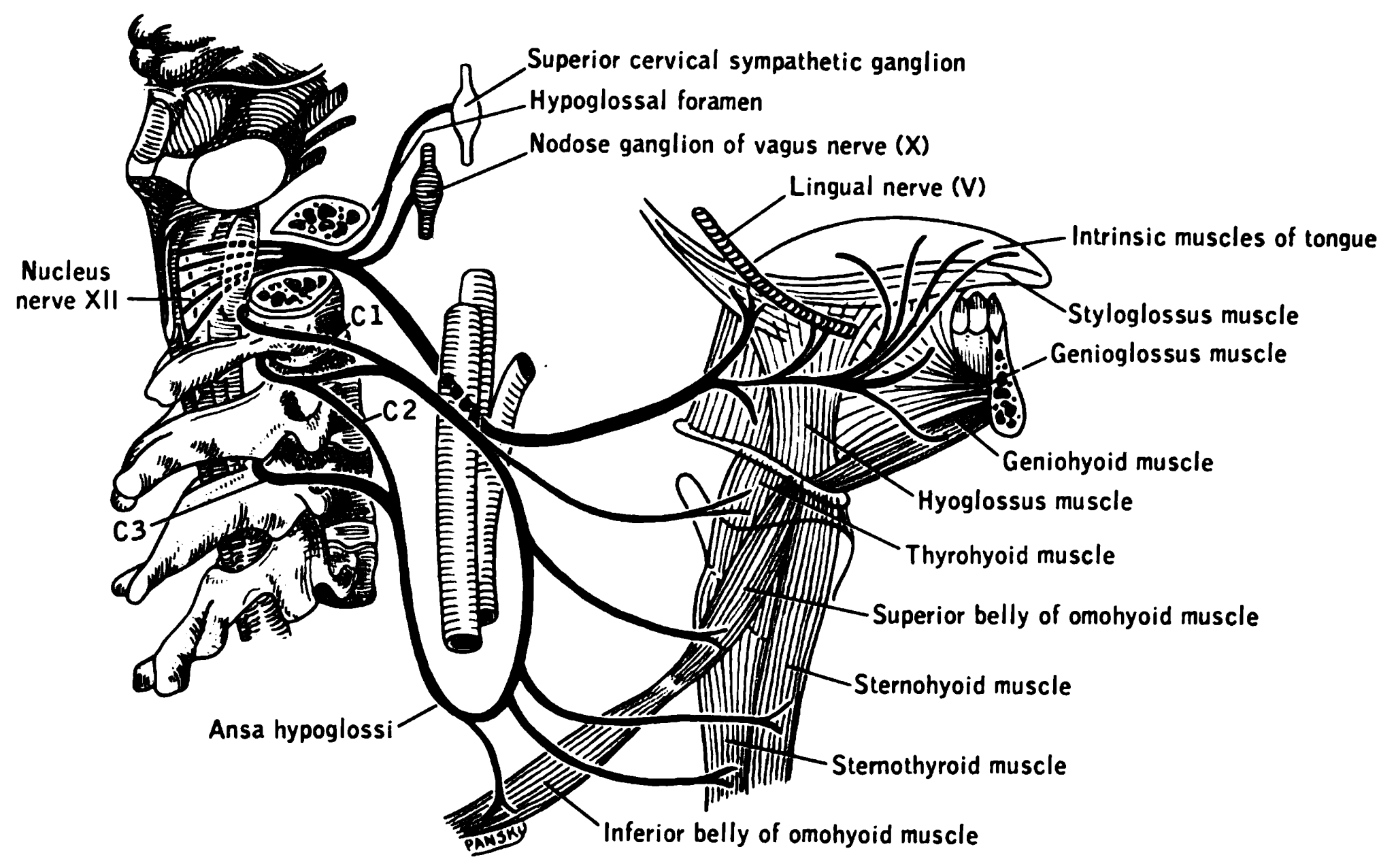
Hypoglossal Nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve. CN XII is a nerve with a sole motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, pass through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue. The nerve is involved in controlling tongue movements required for speech and swallowing, including sticking out the tongue and moving it from side to side. Damage to the nerve or the neural pathways which control it can affect the ability of the tongue to move and its appearance, with the most common sources of damage being injury from trauma or surgery, and motor neuron disease. The first recorded description of the nerve was by Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platysma
The platysma muscle or platysma is a :wikt:superficial, superficial muscle of the human neck that overlaps the sternocleidomastoid. It covers the anterior surface of the neck superficially. When it contracts, it produces a slight wrinkling of the neck, and a "bowstring" effect on either side of the neck. Etymology First recorded in the period 1685–1695, the word comes via Neo-Latin from Greek language, Greek ''plátysma'', a plate, literally, something wide and flat, equivalent to ''platý(nein)'', to widen, + -''sma'', a variant of the Resultative#Adjectival resultatives, resultative suffix ''-ma''. The botanist William T. Stearn argues that ''platýs'', "in Greek compound words, usually signifies ''broad'', rarely ''flat''," which describes the platysma's broad sheet of muscle. Structure The platysma muscle is a broad sheet of muscle arising from the fascia covering the upper parts of the pectoralis major, pectoralis major muscle and deltoid muscle. Its fibers cross the clavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Artery
The facial artery, formerly called the external maxillary artery, is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies blood to superficial structures of the medial regions of the face. Structure The facial artery arises in the carotid triangle from the external carotid artery, a little above the lingual artery, and sheltered by the ramus of the mandible. It passes obliquely up beneath the digastric and stylohyoid muscles, over which it arches to enter a groove on the posterior surface of the submandibular gland. It then curves upward over the body of the mandible at the antero-inferior angle of the masseter ( the antegonial notch); passes forward and upward across the cheek to the angle of the mouth, then ascends along the side of the nose, and ends at the medial commissure of the eye, under the name of the angular artery. The facial artery is remarkably tortuous. This is to accommodate itself to neck movements such as those of the pharynx in swallowing; and facia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheeks
The cheeks () constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. ''Buccal'' means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside of the cheek and the teeth and gums is called the vestibule of the mouth, vestibule or ''buccal'' pouch or ''buccal'' cavity and forms part of the Human mouth, mouth. In other animals, the cheeks may also be referred to as "wikt:jowl, jowls". Structure Cheeks are fleshy in humans, the skin being suspended by the chin and the jaws, and forming the lateral wall of the human mouth, visibly touching the cheekbone below the eye. The inside of the cheek is lined with a mucous membrane (''buccal'' mucosa, part of the oral mucosa). During mastication (chewing), the cheeks and tongue between them serve to keep the food between the teeth. Clinical significance The cheek is the most common location from which a DNA sample can be taken. (Some saliva is collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla). The jawbone is the skull's only movable, posable bone, sharing joints with the cranium's temporal bones. The mandible hosts the lower teeth (their depth delineated by the alveolar process). Many muscles attach to the bone, which also hosts nerves (some connecting to the teeth) and blood vessels. Amongst other functions, the jawbone is essential for chewing food. Owing to the Neolithic advent of agriculture (), human jaws evolved to be smaller. Although it is the strongest bone of the facial skeleton, the mandible tends to deform in old age; it is also subject to fracturing. Surgery allows for the removal of jawbone fragments (or its entirety) as well as regenerative methods. Additionally, the bone is of great forensic significance. Struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swallowing
Swallowing, also called deglutition or inglutition in scientific and medical contexts, is a physical process of an animal's digestive tract (e.g. that of a human body) that allows for an ingested substance (typically food) to pass from the mouth to the pharynx and then into the esophagus. In colloquial English, the term "swallowing" is also used to describe the action of ''gulping'', i.e. taking in a large mouthful of food without any biting. Swallowing is performed by an initial push from back part of the tongue (with the tongue tip contacting the hard palate for mechanical anchorage) and subsequent coordinated muscle contraction, contractions of the pharyngeal muscles. The portion of food, drink and/or other material (e.g. mucus, secretions and medications) that moves into the gullet in one swallow is called a bolus, which is then propelled through to the stomach for further digestion by autonomic peristalsis of the esophagus. Swallowing is an important part of eating and dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |