|
Facial Expressions
Facial expression is the motion and positioning of the muscles beneath the skin of the face. These movements convey the emotional state of an individual to observers and are a form of nonverbal communication. They are a primary means of conveying social information between humans, but they also occur in most other mammals and some other animal species. Humans can adopt a facial expression voluntarily or involuntarily, and the neural mechanisms responsible for controlling the expression differ in each case. Voluntary facial expressions are often socially conditioned and follow a cortical route in the brain. Conversely, involuntary facial expressions are believed to be innate and follow a subcortical route in the brain. Facial recognition can be an emotional experience for the brain and the amygdala is highly involved in the recognition process. Beyond the accessory nature of facial expressions in spoken communication between people, they play a significant role in communication wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
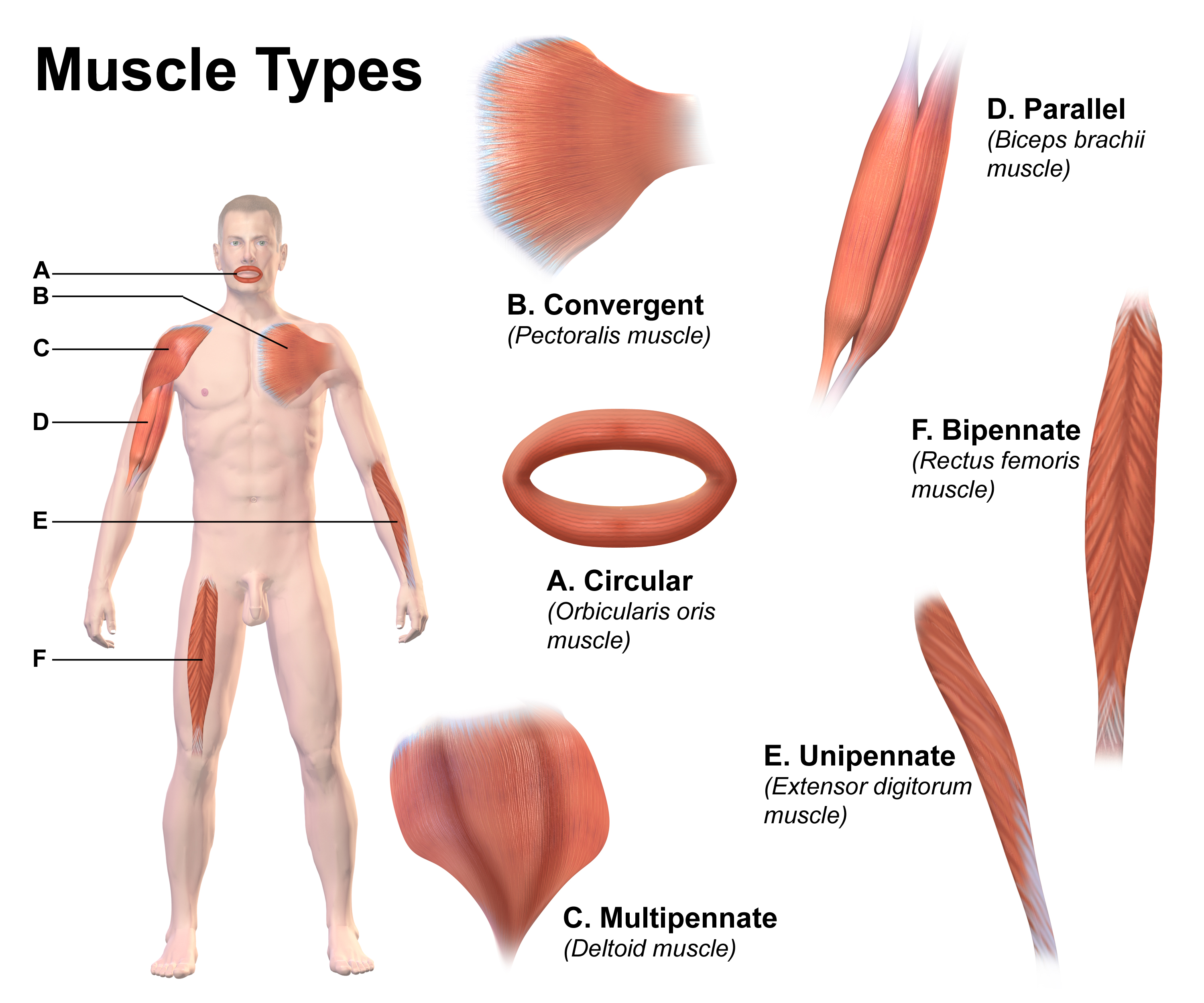
Skeletal Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramidal Tract
The pyramidal tracts include both the corticobulbar tract and the corticospinal tract. These are aggregations of efferent nerve fibers from the upper motor neurons that travel from the cerebral cortex and terminate either in the brainstem (''corticobulbar'') or spinal cord (''corticospinal'') and are involved in the control of motor functions of the body. The corticobulbar tract conducts impulses from the brain to the cranial nerves. These nerves control the muscles of the face and neck and are involved in facial expression, mastication, swallowing, and other motor functions. The corticospinal tract conducts impulses from the brain to the spinal cord. It is made up of a lateral and anterior tract. The corticospinal tract is involved in voluntary movement. The majority of fibres of the corticospinal tract cross over in the medulla oblongata, resulting in muscles being controlled by the opposite side of the brain. The corticospinal tract contains the axons of the pyramidal ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
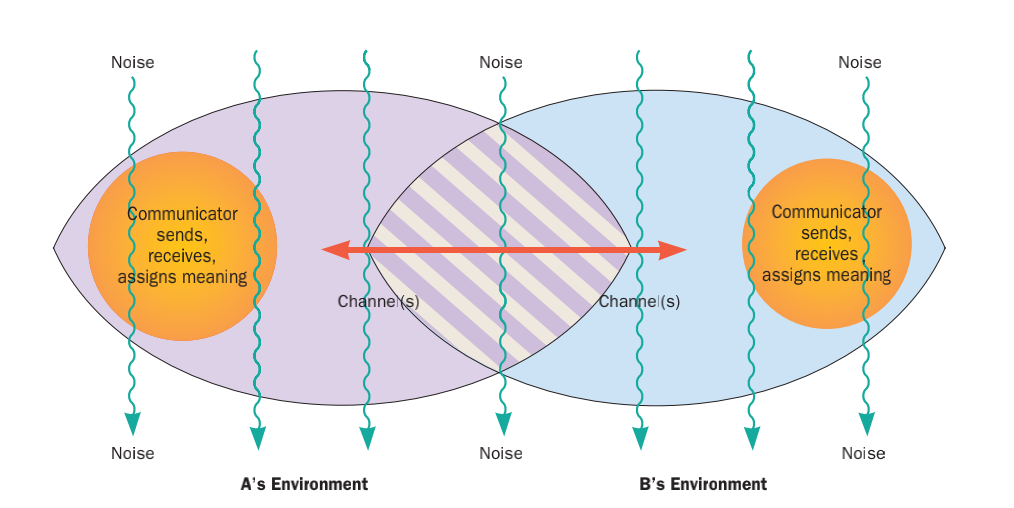
Non-verbal Communication
Nonverbal communication is the transmission of messages or signals through a nonverbal platform such as eye contact (oculesics), body language (kinesics), social distance (proxemics), touch (Haptic communication, haptics), voice (prosody (linguistics), prosody and paralanguage), physical environments/appearance, and use of objects. When communicating, nonverbal channels are utilized as means to convey different messages or signals, whereas others interpret these messages. The study of nonverbal communication started in 1872 with the publication of ''The Expression of the Emotions in Man and Animals'' by Charles Darwin. Darwin began to study nonverbal communication as he noticed the interactions between animals such as lions, tigers, dogs etc. and realized they also communicated by gestures and expressions. For the first time, nonverbal communication was studied and its relevance noted. Today, scholars argue that nonverbal communication can convey more meaning than verbal communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston College
Boston College (BC) is a private university, private Catholic Jesuits, Jesuit research university in Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1863 by the Society of Jesus, a Catholic Religious order (Catholic), religious order, the university has more than 15,000 total students. Boston College was originally located in the South End, Boston, South End of Boston, Massachusetts, Boston before moving most of its campus to Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts, Chestnut Hill in 1907. Its Boston College Main Campus Historic District, main campus is a historic district and features some of the earliest examples of collegiate gothic architecture in North America. The campus is 6 miles west of downtown Boston. It offers bachelor's degrees, master's degrees, and doctoral degrees through its nine colleges and schools. Boston College is classified as a "Research 1: Very High Research Spending and Doctorate Production" university by the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of High ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish several personal and relational goals. Communication includes utilizing communication skills within one's surroundings, including physical and psychological spaces. It is essential to see the visual/nonverbal and verbal cues regarding the physical spaces. In the psychological spaces, self-awareness and awareness of the emotions, cultures, and things that are not seen are also significant when communicating. Interpersonal communication research addresses at least six categories of inquiry: 1) how humans adjust and adapt their verbal communication and nonverbal communication during Face-to-face interaction, face-to-face communication; 2) how messages are produced; 3) how uncertainty influences behavior and information-management strategies; 4) Interpersonal deception theory, deceptive com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nottingham Trent University
Nottingham Trent University (NTU) is a public research university located in Nottingham, England. Its origins date back to 1843 with the establishment of the Nottingham School of Design, Nottingham Government School of Design, which still operates within the university. Nottingham Trent University is composed of nine academic schools: School of Animal, Rural & Environmental Sciences, School of Architecture, Design & the Built Environment, Nottingham Trent University, School of Art and Design, School of Art & Design, School of Arts & Humanities, Nottingham Business School, Nottingham Law School, School of Science & Technology, School of Social Sciences, and Confetti Institute of Creative Technologies, Confetti. The university is the list of universities in the United Kingdom by enrolment, seventh-largest university in the UK with over 38,000 students across six different campuses mainly concentrated in Nottingham (including the city centre, Southwell, and Clifton). The univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portraits
A portrait is a painting, photograph, sculpture, or other artistic representation of a person, in which the face is always predominant. In arts, a portrait may be represented as half body and even full body. If the subject in full body better represents personality and mood, this type of presentation may be chosen. The intent is to display the likeness, personality, and even the mood of the person. For this reason, in photography a portrait is generally not a snapshot, but a composed image of a person in a still position. A portrait often shows a person looking directly at the painter or photographer, to most successfully engage the subject with the viewer, but portrait may be represented as a profile (from aside) and 3/4. History Prehistorical portraiture Plastered human skulls were reconstructed human skulls that were made in the ancient Levant between 9000 and 6000 BC in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B period. They represent some of the oldest forms of art in the Middle E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymmetries
Asymmetry is the absence of, or a violation of, symmetry (the property of an object being invariant to a transformation, such as reflection). Symmetry is an important property of both physical and abstract systems and it may be displayed in precise terms or in more aesthetic terms. The absence of or violation of symmetry that are either expected or desired can have important consequences for a system. In organisms Due to how cells divide in organisms, asymmetry in organisms is fairly usual in at least one dimension, with biological symmetry also being common in at least one dimension. Louis Pasteur proposed that biological molecules are asymmetric because the cosmic .e. physicalforces that preside over their formation are themselves asymmetric. While at his time, and even now, the symmetry of physical processes are highlighted, it is known that there are fundamental physical asymmetries, starting with time. Asymmetry in biology Asymmetry is an important and widespread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Affectivity
In psychology, negative affectivity (NA), or negative affect, is a personality variable that involves the experience of negative emotions and poor self-concept. Negative affectivity subsumes a variety of negative emotions, including anger, contempt, disgust, guilt (emotion), guilt, fear, and Anxiety, nervousness. Low negative affectivity is characterized by frequent states of calmness and serenity, along with states of confidence, activeness, and great enthusiasm. Individuals differ in negative emotional reactivity.Tellegen, A. (1985). Structures of mood and personality and their relevance to assessing anxiety, with an emphasis on self-report. In A. H. Tuma & J. D. Maser (Eds.), Anxiety and the Anxiety disorders, (pp. 681-706), Hilssdale, NJ: Erlbaum. Trait negative affectivity roughly corresponds to the dominant personality factor of anxiety/neuroticism that is found within the Big Five personality traits as emotional stability. The Big Five are characterized as openness, conscie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emotional Expression
An emotional expression is a behavior that communicates an emotional state or attitude. It can be verbal or nonverbal, and can occur with or without self-awareness. Emotional expressions include facial movements like smiling or scowling, simple behaviors like crying, laughing, or saying " thank you," and more complex behaviors like writing a letter or giving a gift. Individuals have some conscious control of their emotional expressions;Dorset Research & Development Support Unit, 2003"Emotional Expression." Retrieved on: July 23, 2007. however, they need not have conscious awareness of their emotional or affective state in order to express emotion. Researchers in psychology have proposed many different and often competing theoretical models to explain emotions and emotional expression, going as far back as Charles Darwin's discussion of emotion as an evolved capacity. Though there is no universally accepted theory of emotion, theorists in emotion agree that experience of emot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Hemisphere
The lateralization of brain function (or hemispheric dominance/ lateralization) is the tendency for some neural functions or cognitive processes to be specialized to one side of the brain or the other. The median longitudinal fissure separates the human brain into two distinct cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. Both hemispheres exhibit brain asymmetries in both structure and neuronal network composition associated with specialized function. Lateralization of brain structures has been studied using both healthy and split-brain patients. However, there are numerous counterexamples to each generalization and each human's brain develops differently, leading to unique lateralization in individuals. This is different from specialization, as lateralization refers only to the function of one structure divided between two hemispheres. Specialization is much easier to observe as a trend, since it has a stronger anthropological history. The best example of an establ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
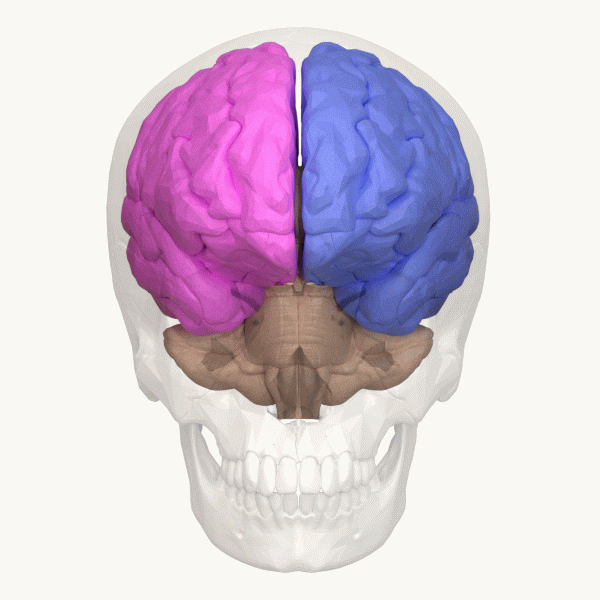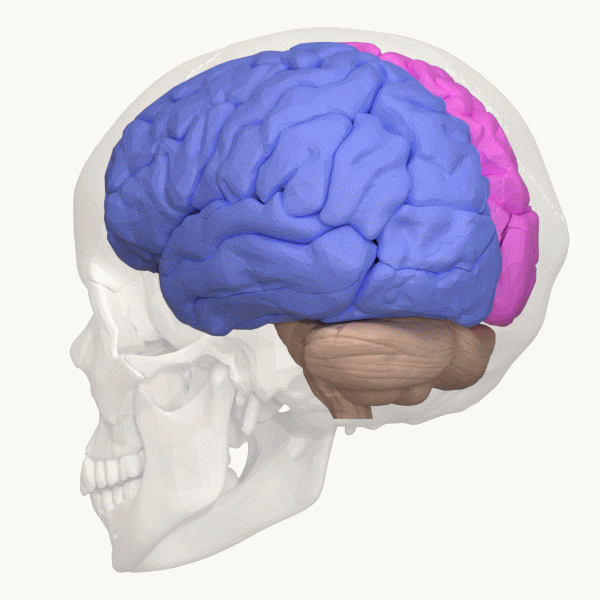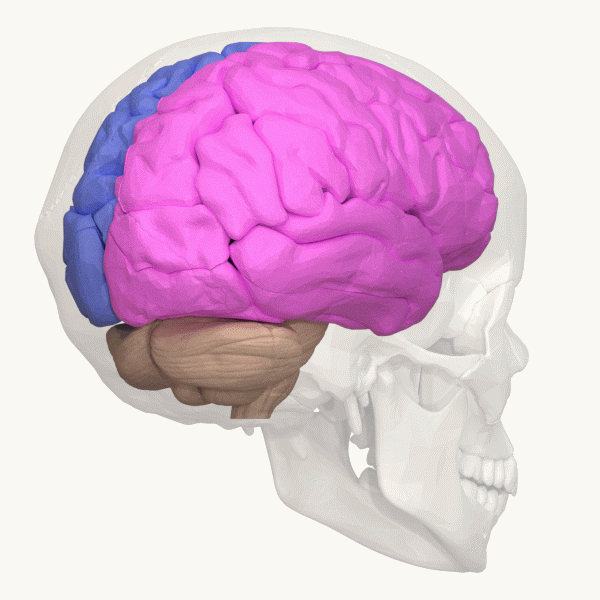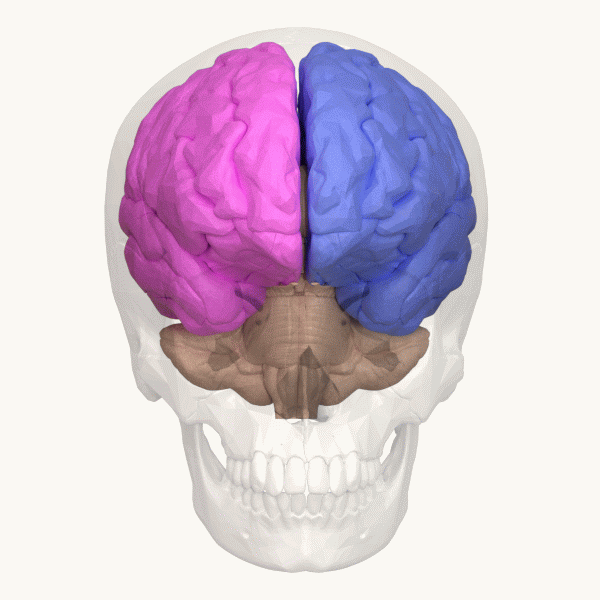
Cerebral Hemisphere
The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter, the cerebral cortex, that is supported by an inner layer of white matter. In eutherian (placental) mammals, the hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum, a very large bundle of axon, nerve fibers. Smaller commissures, including the anterior commissure, the posterior commissure and the fornix (neuroanatomy), fornix, also join the hemispheres and these are also present in other vertebrates. These commissures transfer information between the two hemispheres to coordinate localized functions. There are three known poles of the cerebral hemispheres: the ''occipital lobe, occipital pole'', the ''frontal lobe, frontal pole'', and the ''temporal lobe, temporal pole''. The central sulcus is a prominent fissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |